We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +357 26030221 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Navigating the world of GCSEs can feel like a maze, with each choice potentially shaping your future. Among the many terms you’ll encounter, “GCSE Grade Boundaries” often stands out. But what exactly are these boundaries, and why are they so crucial? This blog will guide you through everything you need to know about GCSE Grade Boundaries, helping you make informed subject choices and prepare effectively for success.
Table of Contents
1) What are the GCSE Grade Boundaries?
2) Why does GCSE Grade Boundaries Matter?
3) How GCSE Grade Boundaries Work
4) The new GCSE grading system
5) Comparing New and Old GCSE Grades
6) Who Determines GCSE Grade Boundaries?
7) Passing GCSEs: Required Grades
8) Data Used by Examiners to Set Grade Boundaries
9) Impact of Grade Boundaries on Students
10) Tips for Navigating GCSE Grade Boundaries
11) Conclusion
What are the GCSE Grade Boundaries?
Grade boundaries in GCSE exams are the cutoff points that determine the grade you receive based on your exam performance. These boundaries are set by exam boards after the exams are marked and can vary each year depending on overall student performance.
To achieve a particular grade, you need to score at or above the boundary for that grade. For instance, a grade 7 in Maths might require 70% of the total marks one year and 72% the next. These adjustments ensure that grading remains fair and consistent across different years, so the same level of achievement is awarded the same grade, regardless of exam difficulty
Practical Example
Imagine a student who scores 65% in their GCSE English Language exam. If the Grade Boundary for a seven that year is 66%, the student will miss out on grade 7 and be awarded a grade 6 instead. Understanding this system helps students and teachers set realistic goals and work towards achieving the necessary marks for their desired grades.
Why Does GCSE Grade Boundaries Matter
GCSE Grade Boundaries are not just numbers—they can have profound implications for a student’s academic future. The grades you achieve in your GCSEs can influence the subjects you are eligible to study at A-level, affecting your university choices and career prospects.
Academic Implications
Higher education institutions often require minimum GCSE grades for specific courses. For example, universities may require at least a grade 5 or 6 in English and Maths, regardless of the student's chosen subject. Not meeting these requirements can limit options for further study and impact career paths. Additionally, certain A-level subjects may require specific GCSE grades in related subjects; for instance, to study A-level Chemistry, a student might need at least a grade 7 in GCSE Chemistry.
Long-term Impact
The impact of GCSE Grade Boundaries reaches beyond academic choices. Employers consider GCSE results when hiring, especially for entry-level positions. Strong grades make a candidate stand out, while lower grades might require alternative routes for similar career goals. Additionally, GCSEs reflect a student's diligence and ability to handle academic pressure, instilling confidence and laying a solid foundation for future success.
How GCSE Grade Boundaries Work
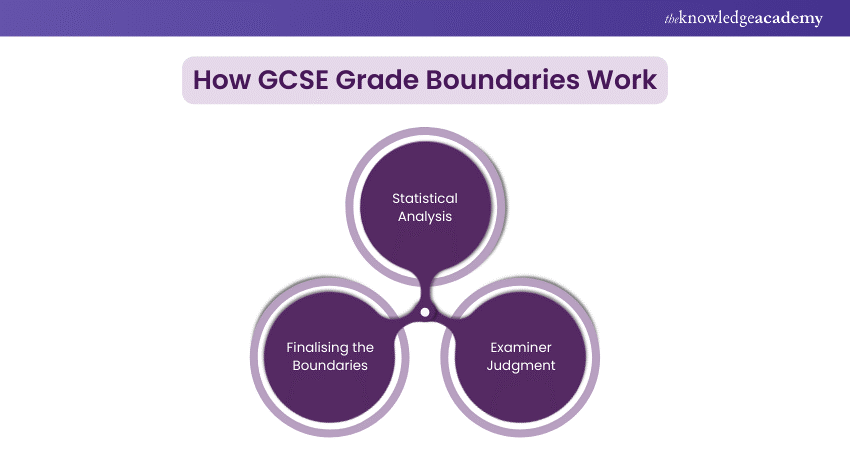
Setting GCSE Grade Boundaries is a meticulous process involving several stages to ensure fairness. Examiners review marks distribution, exam difficulty, and overall student performance.
Statistical Analysis
Exam boards use statistical analysis to compare the current year's performance with previous years to determine if an exam was more difficult. If a paper was more complicated than expected, Grade Boundaries might be lowered to ensure students aren’t unfairly penalised.
Examiner Judgment
Experienced examiners' judgment is crucial in setting Grade Boundaries. They review exam scripts to ensure accurate marking and consider the exam's content and structure when determining Boundaries. For instance, they may adjust Boundaries if a particularly challenging question stumps many students.
Finalising the Boundaries
The final grade boundaries are set based on data analysis and examiner judgments to ensure consistent grading across exam boards and years. This ensures that a grade represents the same level of achievement regardless of the year it is attained.
Empower your team with expert supervision skills—join our Supervisor Training today!
The New GCSE Grading System
In recent years, the GCSE grading system has changed quite a bit. The old A*-G grades are out, and now it's all numbers from 9 to 1, with nine being the best. This switch was made to create more apparent differences between students, especially those at the top end, and to bring GCSEs more in line with international standards.
Reasons for the Change in GCSE Grading
Issues with the former A*–G grading system made it difficult to identify top achievers. The new 9-1 grading scheme is a step above. It makes tracking pupils' development easier and gives more precise information.
For example, in the previous system, an A* may have been awarded to a student who scored 90% and another student who earned 100%. The student with a 100% score would receive a nine under the new method, whereas the 90% mark may obtain an 8. This makes it possible to recognise their accomplishments more precisely.
Timing of GCSE Grade Boundary Releases
GCSE Grade Boundaries are typically released on results day, after all exams have been marked, and the necessary analysis has been completed. This timing ensures that students receive grades that accurately reflect their performance relative to the rest of the cohort, considering any variations in exam difficulty.
Releasing Grade Boundaries on results day also ensures that students and teachers can see the marks required for each grade, providing transparency in the grading process. However, this timing can also add to the anxiety of results day, as students eagerly await to see if they have met the necessary Boundaries for their desired grades.
Land your dream job faster—Join our Job Search Course today!
Comparing New and Old GCSE Grades
The transition to the new GCSE grading system has raised concerns among students and parents regarding converting the latest number of grades to the old letter grades. Comprehending these differences is crucial as they significantly impact one's ability to interpret one's results and make informed decisions about one's future academic and professional endeavours.
Understanding the Conversion
The new GCSE grades range from 9 to 1, with nine being the highest and one the lowest. In comparison, the old grades ranged from A* to G. The new system is designed to be more rigorous, with a grade 7 broadly equivalent to an A under the old system and a grade 4 equivalent to a C.
Implications for Higher Education
Higher education institutions have adapted to the new grading system, with many settings specific grade 5 or 6 requirements for entry into certain courses. Students need to understand how universities and employers will perceive their grades under the new system and to plan accordingly.
Who Determines GCSE Grade Boundaries?
The exam boards, such as AQA, Edexcel, and OCR, are responsible for setting GCSE Grade Boundaries. These boards employ experienced examiners who review exam results, analyse data, and set Boundaries to ensure fairness and consistency.
Role of Ofqual
Ofqual, the Office of Qualifications and Examinations Regulation, oversees the process to ensure that all exam boards adhere to the same standards. Ofqual monitors the setting of Grade Boundaries to ensure that the process is transparent, fair, and consistent across all subjects and exam boards.
Examiner Expertise
Examiners play a crucial role in setting Grade Boundaries. These are usually experienced teachers or subject specialists who deeply understand the curriculum and the assessment process. They review a sample of exam papers to ensure that the marks awarded accurately reflect the quality of the student's work.
Tell compelling stories and make an impact—start your journey with our Journalism Course today!
Passing GCSEs: Required Grades
Under the old grading system, a GCSE exam typically requires achieving at least a grade of 4, equivalent to a C. However, for core subjects like English and Maths, many institutions now require a grade 5, known as a "strong pass," for further education and employment purposes.
Core Subject Requirements
Achieving the required grades in core subjects is essential for students looking to continue their education at A-level or to pursue certain career paths. Many A-level courses and higher education institutions require at least a grade 5 in English and Maths, and in some cases, a grade 6 or 7 may be required for more competitive courses.
Consequences of Not Meeting Grade Requirements
If a student does not meet the required Grade Boundaries, several options are available, including resitting the exam or exploring alternative qualifications. Students should be aware of these options and seek advice from teachers and career advisors if they are concerned about their grades.
Data Used by Examiners to Set Grade Boundaries
Examiners use various data to set GCSE Grade Boundaries. This data includes the cohort's overall performance, the difficulty of the exam, and statistical analyses that ensure consistency in grading across different subjects and years.
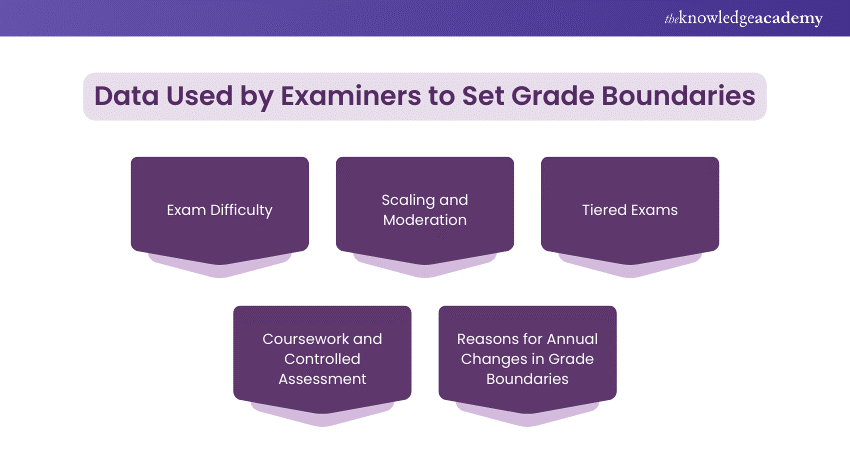
Exam Difficulty
One critical factor examiners consider when setting Grade Boundaries is the difficulty of the exam. If an exam is deemed more challenging than in previous years, the Grade Boundaries may be lowered to ensure students are not unfairly penalised.
Scaling and Moderation
Scaling and moderation are processes used to adjust marks to account for exam difficulty differences and ensure consistency across different exam boards and years. This helps maintain fairness in the grading process and ensures that a grade in one subject is comparable to the same grade in another subject.
Tiered Exams
In subjects like Math and Science, students are entered for foundation or higher-tier papers, each with its Grade Boundaries. The boundaries for these tiers differ, reflecting the difficulty levels and ensuring that students are graded fairly regardless of the tier they are entered for.
Coursework and Controlled Assessment
Coursework and controlled assessments also determine Grade Boundaries. These components often carry significant weight in the final grade, and their impact is carefully balanced to ensure that the overall grade accurately reflects the student's abilities.
Reasons for Annual Changes in Grade Boundaries
Grade Boundaries can change from year to year due to various factors, such as changes in exam difficulty, the overall performance of the cohort, and the introduction of new syllabuses. These changes ensure that grades remain consistent and fair across different exam sessions.
Enhance your focus and boost productivity—sign up for our Attention Management Training now!
Impact of Grade Boundaries on Students
GCSE Grade Boundaries directly influence students' academic progress and opportunities. Higher Boundaries can lead to better grades, enhancing chances for further education and career prospects. Conversely, lower Boundaries limit these opportunities. Additionally, the pressure to meet Grade Boundaries can affect students' mental health, making adequate preparation and support crucial for managing stress and achieving desired results.
Academic Advancement
GCSE Grade Boundaries can significantly impact students' academic advancement. Higher grades open doors to further education opportunities, while lower grades may limit options. Understanding these Boundaries helps students set realistic goals and work towards achieving the grades needed for their desired paths.
Effects on Mental Health and Well-being
The pressure to meet GCSE Grade Boundaries can damage students' mental health and well-being. High expectations, fear of failure, and the uncertainty of Grade Boundaries can lead to stress and anxiety. Students should manage these pressures effectively and seek support when needed.
Tips for Navigating GCSE Grade Boundaries
Understanding the GCSE Grade Boundaries is crucial for effective study techniques and strategic planning. By comprehending the boundaries, creating a focused study plan, and utilising all available resources, you can enhance your exam performance and achieve your target grades. Here are some useful tips to assist you in navigating the grading process and reaching your academic goals.
Preparing Effectively for Exams
Effective preparation is key to navigating GCSE Grade Boundaries. This includes creating a study plan, practising past papers, and focusing on areas for improvement. Staying organised and managing your time well can also significantly boost your confidence and exam performance.
Utilising Resources and Support Systems
Maximise the resources and support systems around you, like teachers, tutors, and online tools. Understanding the exam format and marking criteria can help you get your desired grades. And feel free to ask for help if you find any of your studies challenging.
Conclusion
Navigating GCSE Grade Boundaries is crucial for academic success and future opportunities. You can be better prepared and make informed decisions by understanding how these Boundaries are set and their impact. Remember, while grades are important, they are just one aspect of your educational journey—focus on learning, growth, and personal development to succeed truly.
Master the art of productivity—join our Time Management Training and take control of your time today!
Frequently Asked Questions

To improve your chances, start by understanding the GCSE Grade Boundaries and focusing on areas where you can gain the most marks. Use past papers, seek help from teachers, and create a revision plan that covers all topics comprehensively.

If you're unhappy with your GCSE grades, you can consider options such as requesting a remark, resitting the exams, or pursuing alternative qualifications. Discussing your options with your teachers and considering what’s best for your future goals is essential.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Personal Development Courses, including the Career Development Course, Time Management Training and Attention Management Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into How to Become a Teaching Assistant.
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to Career Development, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Career Development skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Career Development Course
Career Development Course
Fri 28th Feb 2025
Fri 4th Apr 2025
Fri 27th Jun 2025
Fri 29th Aug 2025
Fri 24th Oct 2025
Fri 5th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


