We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +420 210012971 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Are you seeking an effective Project Management approach that emphasises flexibility, collaboration, and continuous improvement? If yes, then look no further than Implementing Agile Project Management with Scrum.
Today, Scrum Framework within Agile has become one of the topmost choices of organisations to facilitate their projects successfully. According to the 16th State of Agile Survey Report, approximately 87% of organisations have adopted Scrum for Agile Project Management.
But what is Scrum in Agile, how does it work and how to implement it? Worry no more. Read this blog to learn about Agile Project Management with Scrum. Also, explore how to implement it and harness the benefits of iterative development.
Table of Contents
1) Agile Project Management with Scrum – An overview
2) What is Scrum?
3) Benefits of Agile Project Management with Scrum
4) How to implement Agile Project Management with Scrum?
5) Conclusion
Agile Project Management with Scrum – An overview
When it comes to Agile, the topic of "Agile Project Management vs Scrum" often arises, creating a platform for dialogue about different methodologies. Agile Project Management with Scrum provides a structured and iterative approach to Project Management that allows teams to respond effectively to changing requirements and deliver value incrementally. It provides a lightweight yet powerful structure for managing complex projects.
Scrum also embraces an empirical approach, where decisions are based on observations and experimentation rather than rigid upfront planning. Further, the framework offers a set of Scrum Values and Principles, defined roles, Artefacts, and Events that enable teams to work cohesively and deliver value incrementally. This Agile Project Management Framework is built upon three fundamental pillars that form the foundation of its framework. They are as follows:
a) Transparency: Ensures that all stakeholders understand the project’s progress, challenges, and objectives. Therefore, this Agile Project Management framework allows for better collaboration, trust, and informed decision-making.
b) Inspection: Through inspection, the team can promptly identify deviations from the desired outcomes and take corrective actions. This process allows teams to detect issues early and adjust to deliver successful outcomes.
c) Adaptation: The framework encourages teams to embrace change and adjust their plans based on new information and insights. Scrum acknowledges that requirements and circumstances can evolve throughout the project. As a result, it enables teams to respond proactively to changing needs, reduce risks, and maximise project success.

What is Scrum?
Scrum is a way of working together and getting work done in a collaborative and Agile manner. Scrum is based on the principles of empiricism, which means that decisions are made based on observation, experience, and experimentation. Scrum helps teams deliver value incrementally in short cycles called Sprints, which are usually one month or less. Scrum also provides opportunities for feedback and improvement throughout the process.
History of Scrum
Scrum originated from a 1986 paper by Hirotaka Takeuchi and Ikujiro Nonaka in the Harvard Business Review. The paper, titled “The New New Product Development Game”, used rugby as a metaphor for innovative Product Development and delivery by self-organising teams. Jeff Sutherland, Ken Schwaber, and Mike Beedle adapted the ideas and the metaphor from this paper to the Software Development domain.
They named their new approach Scrum, after the rugby formation where teams form a circle and compete for the ball. They implemented Scrum for the first time at Easel Corporation in 1993. Schwaber and Beedle shared their experiences and results in their book Agile Software Development with Scrum in 2002. Schwaber also wrote Agile Project Management with Scrum in 2004, which included his work with Primavera.
The Scrum Framework
The Scrum Framework is a way of organising and managing work based on the principles of empiricism. It means that decisions are made based on observation, experience, and experimentation. The Scrum Framework also provides opportunities for feedback and improvement throughout the process.
The Scrum Framework consists of a team of people who have different roles and responsibilities. The Scrum Team works together to produce a valuable and usable product increment at the end of each sprint. The Scrum Framework also consists of a set of events and artefacts that help the team structure and manage their work. Let's explore them below:
1) Events: The events are Sprint Planning, where the team plans what to do in the next Sprint.
2) Daily Scrum: This is where the team coordinates their daily activities.
3) Sprint Review: Here, the team inspects the product increment and gets feedback from stakeholders.
4) Sprint Retrospective: This is where the team review their performance and identifies areas for improvement.
5) Artefacts: The artefacts are Product Backlog, where the Product Owner maintains a list of the work to be done
6) Sprint Backlog: Here, the developers select and plan the work for the current Sprint.
7) Increment: This is where the developers produce a product increment at the end of each and every sprint.
Unlock your potential and drive your career forward with our SAFe Agile Certification!
Roles and responsibilities
Scrum is a popular framework for managing complex projects in an agile way. Scrum has three roles: the Product Owner, the Scrum Master, and the Development Team. Each role has different responsibilities and works together to deliver value to the customer. Here is a brief explanation of each role and its responsibilities:
1) Product Owner:
The Product Owner is the individual who represents the needs of the customer and the business. They are responsible for defining and prioritising the product backlog, which is a list of key features and requirements for the product. Product Owners also communicate the vision and goals of the product to the Scrum Team and stakeholders. They cooperate with the Development Team and the Scrum Master to ensure that the product fulfils the expectations and delivers value.
2) Scrum Master:
The Scrum Master is the person who facilitates the Scrum process and ensures that the Scrum Team follows the Scrum values and principles. They are responsible for coaching and mentoring the Scrum Team, removing any impediments or obstacles that might hinder the team’s progress. Besides, they organise and lead the Scrum events, such as the sprint planning, the daily Scrum, the sprint review, and the sprint retrospective. They also work with the Product Owner and the stakeholders to create a productive and collaborative environment.
3) Development Team:
The Development Team is the group of people who do the actual work of developing and delivering the product. They are responsible for planning and executing the sprints, which are short iterations of work that result in a potentially releasable product increment. The Development Team is self-organising, cross-functional, and accountable for the quality and functionality of the product. The Development Team also collaborates with the Product Owner and the Scrum Master to provide feedback and suggestions for improvement
4) The Stakeholder:
The Stakeholder is anyone who has an interest or influence in the product or the project, such as the customer, the user, the sponsor, the manager, the analyst, the tester, etc. The stakeholder is not part of the Scrum Team, but they may provide feedback, requirements, or support to the team.
The Stakeholder may also attend some Scrum events, such as the Sprint review, to inspect the product and share their opinions. They should respect the Scrum values and principles and collaborate with the Product Owner and the Scrum Master to ensure the success of the project.
5) The Agile Coach:
The Agile Coach is someone who has extensive experience and knowledge in Agile Methodologies, such as Scrum, and who can help the organisation and the teams to adopt and improve their agile practices. The Agile Coach is not part of the Scrum Team, but they may work with the team, the Scrum Master, the Product Owner, and the stakeholders to provide guidance, training, mentoring, and facilitation.
The Agile Coach may also help resolve any conflicts or challenges that the team may face and foster a culture of innovation and learning. They should have a deep understanding of Scrum's values and principles and help the team achieve their full potential.
Ready to lead? Elevate your career! Embrace the role of a Project Manager today.
Benefits of Agile Project Management with Scrum
As part of Agile Project Management, Scrum offers numerous benefits that contribute to successful project outcomes. Let’s explore the Benefits of Agile Project Management with Scrum:
a) Improved flexibility: Scrum in Agile Project Management lets teams to adapt quickly to changing requirements and business priorities. This enhances project flexibility and responsiveness.
b) Enhanced collaboration: The Framework promotes close collaboration and communication between stakeholders, customers and team members. This helps foster a shared understanding and increases project success.
c) Faster delivery: By delivering value incrementally in short iterations (sprints), Scrum enables faster delivery of tangible results, ensuring that stakeholders receive value sooner.
d) Increased customer satisfaction: Scrum in Agile Project Management ensures regular stakeholder involvement and feedback. This helps improve customer satisfaction and alignment with expectations.
e) Higher quality: Scrum’s iterative and incremental approach enables continuous inspection and adaptation, resulting in higher-quality deliverables and reduced risks of defects.
f) Transparency: Scrum in Agile Project Management emphasises transparency by making project progress, challenges, and objectives visible to all stakeholders. As a result, itfosters trust and informed decision-making.
g) Efficient resource utilisation: Scrum also enables optimal resource allocation and utilisation through self-organising teams, ensuring that project resources are effectively utilised.
h) Continuous improvement: The framework promotes a culture of continuous improvement through regular retrospectives. This allows teams to identify areas for growth and implement changes to enhance future performance.
i) Reduced project risks: Scrum’s iterative nature allows teams to identify and mitigate project risks early, reducing the likelihood of significant issues or failures.
j) Empowered teams: Agile Project Management, along with Scrum, empowers teams to take ownership and make decisions, resulting in increased engagement, motivation, and accountability.
How to implement Agile Project Management with Scrum?
Implementing Scrum in Agile Project Management involves several key steps to ensure a smooth and effective transition. Here is a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Establishing the Agile mindset
To begin with, it's crucial to establish an Agile mindset within the organisation. This involves the following:
a) Embracing change and adaptability as inherent aspects of the project
b) Encouraging self-organising teams
c) Empowering teams to make informed decisions and take ownership of their work
Step 2: Defining the product vision and backlog
Clearly defining the project's goals, objectives, and vision. This step in Agile Project Management includes performing the following activities:
a) Identifying the desired outcomes and benefits the project aims to achieve.
b) Creating a product backlog that represents all the requirements, features, and enhancements needed for the project.
c) Prioritising backlog items based on business value and stakeholder needs.
Step 3: Forming the Scrum Team
Assembling a dedicated Scrum Team that will work collaboratively throughout the project involves:
a) Defining the roles and responsibilities of each team member, including the Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team
b) Selecting team members with the required skills and expertise to deliver the project increment
c) Encouraging cross-functional collaboration.
d) Ensuring that the team has the right mix of skills to address all project requirements.
Step 4: Planning and executing Sprints
Sprints are time-boxed iterations where the Scrum Team works to release a potentially shippable product increment. The key activities are as follows:
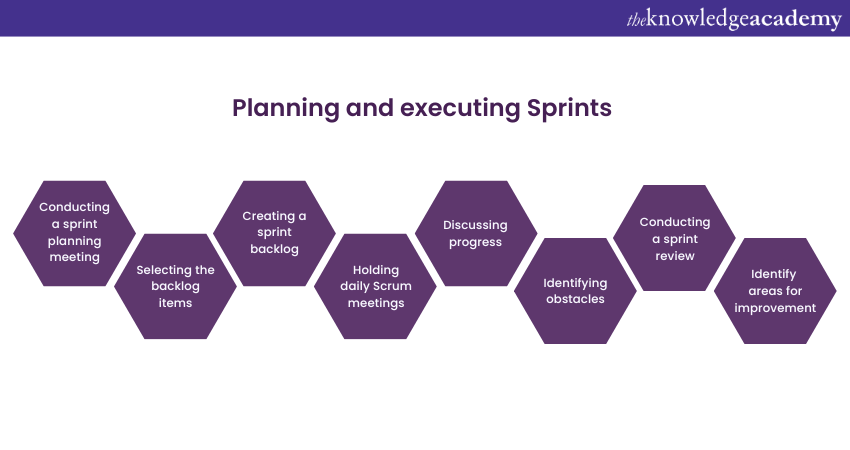
a) Conducting a sprint planning meeting to define the scope of the sprint.
b) Selecting the backlog items to be addressed.
c) Creating a sprint backlog that outlines the tasks required to complete the selected backlog items.
d) Holding daily Scrum meetings to provide updates.
e) Discussing progress, identifying and addressing any obstacles.
f) Conducting a sprint review to showcase the completed increment to stakeholders and gather feedback.
g) Facilitating a sprint retrospective to reflect on the sprint.
h) Identify areas for improvement in future sprints.
Step 5: Monitoring progress and adaptation
In this step, it is essential to monitor the team's progress and adapt accordingly. This includes:
Tracking Scrum Team’s velocity and using burndown charts to visualise the progress and identify any deviations.
Conducting regular retrospectives to evaluate the team's performance and identify opportunities for improvement.
Adapting and improving processes based on the insights gained from retrospectives to enhance productivity and delivery efficiency.
Gain an in-depth understanding of Agile practices with our Certified Professional In Agile Project Management (CPAPM) Course.
Step 6: Delivering value incrementally
The ultimate goal of Scrum in Agile Project Management is to deliver value incrementally. This involves the following:
a) Adopting an incremental approach to product development
b) Delivering and ensuring that stakeholders receive tangible value at the end of each sprint
c) Actively seeking customer feedback
d) Incorporating it into the product development procedure to ensure customer satisfaction and alignment with their expectations
Conclusion
Agile Project Management with Scrum provides endless possibilities. By embracing the Agile mindset and Scrum principles, teams in Agile can navigate complex projects, seize opportunities, and achieve project success.
Ignite your potential in the dynamic world of Agile methodologies with our Agile Project Management Foundation & Practitioner (AgilePM®) Course.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does Agile Scrum helps in better Project Management?

Scrum is a popular framework that allows teams to deliver products using Agile methodology by following an iterative and incremental approach. Scrum is often considered a way of managing projects in a flexible and effective manner.
Is Scrum good for Project Management?

Scrum is a framework for delivering a product that meets the customer’s needs and expectations in an Agile way. Scrum can be good for Project Management depending on the type, size, and complexity of the project, as well as the skills, experience, and preferences of the team and the stakeholders.
What are the other resources and offers provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What are related Agile courses and blogs provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers many Agile Courses and blogs that can help you boost your knowledge in this domain. Moreover, these courses can help boost your career prospects by enhancing your skills, knowledge, and credentials in various aspects of Project Management. If interested, you can check them out in our Agile Courses section. As for blogs, you can find them in our Resources section.
Upcoming Project Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Managing Agile Projects with Scrum
Managing Agile Projects with Scrum
Fri 4th Apr 2025
Fri 1st Aug 2025
Fri 5th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


