We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +420 210012971 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Ever wondered how organisations safeguard their vast troves of sensitive data in today’s digital landscape? The answer lies in Big Data Security. It’s all about ensuring that massive amounts of data remain safe and secure.
Big Data Security aims to keep data private, accurate, and accessible only to authorised individuals. It encompasses a set of measures and practices designed to protect data from unauthorised access, breaches, and other digital threats.Curious about how you can protect your organisation’s and users’ data in this digital age? Dive into this blog to explore Big Data Security, its management strategies, and real-world use cases.
Table of Contents
1) What is Big Data Security?
2) How Big Data Security Works?
3) Big Data Security Technologies
4) Notable Big Data Security Breaches
5) Benefits of Big Data Security
6) Big Data Security Use Cases
7) Challenges to Big Data Security
8) Big Data Security Best Practices
9) Conclusion
What is Big Data Security?
Big Data Security is the practice of protecting and securing the vast amount of data that organisations accumulate and manage in their computer systems. It involves using various security measures and technologies to prevent unauthorised access, data breaches, and other potential threats to this data.
The aim is to uphold the privacy, reliability, and accessibility of this valuable information while ensuring that it is only accessible to authorised individuals or systems.
How Big Data Security Works?
Big Data Security is all about protecting data from unauthorised access and ensuring its safety at every stage of its lifecycle. This involves using firewalls, strong user authentication, end-user training, Intrusion Protection Systems (IPS) and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS).
Unlike regular network security, Big Data Security must operate across three distinct stages. Each stage presents challenges and requires specific security measures to keep the data safe.
Stage 1: Data Sources
Big data comes from various sources, including user-generated content like Customer Relationship Management (CRM) or Enterprise Resource Management (ERM0 data, transactional data, and unstructured data such as emails or social media posts. It also includes machine-generated data from logs and sensors. To protect this data, it must be secured while in transit from its source to the big data platform.
Stage 2: Stored Data
Once the data is stored, robust security measures such as encryption at rest, strong user authentication, and intrusion protection are required. Since big data is often stored across multiple servers and nodes, security tools must work across this distributed environment. Additionally, log files and analytics tools within the platform need to be secured to prevent unauthorised access.
Stage 3: Output Data
The purpose of a big data platform is to analyse huge amounts of data and generate valuable insights. These insights are then output to applications, reports, and dashboards. Since this output is highly valuable, it must be encrypted to prevent unauthorised access. Moreover, it’s crucial to ensure that any data shared with end-users complies with regulations and does not include sensitive or restricted information.
Big Data Security Technologies
Implementing robust security in big data environments requires the use of advanced technologies designed to protect data at every stage of its lifecycle. Here are some key Big Data Security technologies:
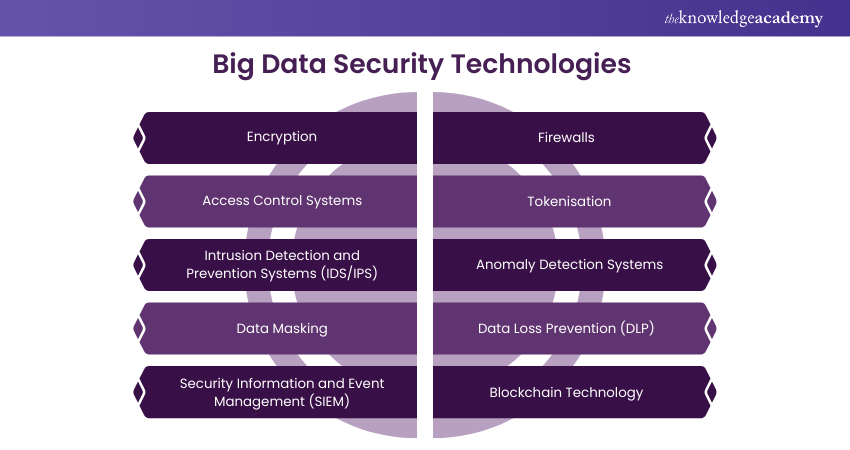
a) Encryption: Encryption technologies secure data by converting it into a coded format that can only be deciphered by authorised parties with the correct decryption key. This is crucial fors afeguarding data both in transit and at rest, ensuring that sensitive information remains inaccessible to unauthorised users.
b) Access Control Systems: These systems regulate who can access data and what actions they can perform. Role-based Access Control (RBAC) and Attribute-based Access Control (ABAC) are commonly used to enforce strict access policies, ensuring that only the right people have access to specific data sets.
c) Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): IDS and IPS technologies monitor network traffic and system activities for signs of malicious behaviour. IDS alerts administrators to potential security breaches, while IPS can actively block or prevent those threats from causing harm.
d) Data Masking: Data masking technologies hide sensitive information within data sets, allowing non-sensitive data to be used for analysis or testing without exposing the underlying sensitive details. This is particularly useful in environments where data needs to be shared but must remain confidential.
e) Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM tools analyse log data from various sources to provide real-time monitoring and analysis of security events. SIEM systems help detect and respond to potential security threats more quickly by offering a centralised view of security activities.
f) Firewalls: Firewalls are essential for controlling the flow of data between trusted and untrusted networks. They act as barriers that filter incoming and outgoing traffic based on predetermined security rules, preventing unauthorised access to sensitive data.
g) Tokenisation: Tokenisation replaces sensitive data elements with non-sensitive equivalents (tokens) that can be safely used in place of the actual data. The original data is stored securely in a token vault, while the tokens are used in applications, reducing the risk of data exposure.
h) Anomaly Detection Systems: These systems use Machine Learning and analytics to detect unusual patterns or behaviours within big data environments. By identifying anomalies that deviate from normal activity, these technologies help uncover potential security threats before they can escalate.
i) Data Loss Prevention (DLP): DLP technologies monitor the movement of sensitive data across networks, devices, and endpoints. They help prevent unauthorised data transfers and protect against data leaks, ensuring that sensitive information remains within secure boundaries.
j) Blockchain Technology: Blockchain provides a secure way to record transactions and data exchanges. In big data environments, Blockchain can be used to create a transparent record of data activities, enhancing data integrity and security.
Notable Big Data Security Breaches
Here are some examples of Big Data Security. These examples illustrate how data breaches and security incidents can have significant consequences. So, let’s explore some instances where inadequate security measures led to data breaches:
Equifax Data Breach (2017)
One of the biggest data breaches in history was the Equifax breach, which exposed the personal information of over 147 million Americans. The breach happened because Equifax didn't fix a known flaw in their web application software quickly enough. This incident showed how important it is to manage security patches proactively and the serious risks of ignoring vulnerabilities in big data systems.
Yahoo Data Breaches (2013 and 2014)
Yahoo experienced two massive data breaches that compromised the data of billions of users. The breaches, which were not disclosed until years later, included stolen user account information, including email addresses and hashed passwords. These incidents underscored the importance of timely detection and response to security breaches, as well as the need for transparency in reporting such incidents.
Facebook-Cambridge Analytica Scandal (2018)
While not a traditional data breach, this scandal exposed significant privacy and security issues related to big data. Cambridge Analytica, a political consulting firm, gained unauthorised access to the personal data of several Facebook users through a third-party app. The incident raised concerns about data misuse and the need for stronger data protection measures in the era of social media and big data analytics.
Target Data Breach (2013)
In one of the most well-known retail data breaches, cybercriminals infiltrated Target's network. They gained access to credit and debit card information of around 40 million customers. This breach occurred due to a successful malware attack on the company's point-of-sale systems. It highlighted the importance of securing not only customer data but also the systems that process it.
Marriott International Data Breach (2018)
Marriott suffered a data breach that leaked the personal information of approximately 500 million guests. The breach occurred because of a cyberattack on the Starwood guest reservation database, which Marriott had acquired. The incident underscored the need for thorough security assessments and due diligence when merging or acquiring companies with access to large amounts of customer data.
Benefits of Big Data Security
Big Data Security provides several important benefits:
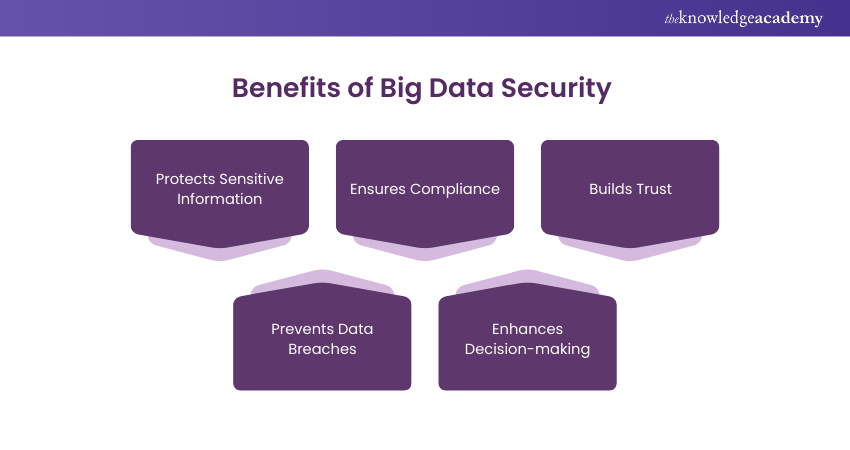
a) Protects Sensitive Information: Big Data Security keeps personal and business data safe from unauthorised access. It prevents hackers or other malicious actors from stealing valuable information. This protection is crucial for maintaining privacy and security in any organisation.
b) Ensures Compliance: It helps companies follow legal and regulatory rules for data protection. By following these rules, businesses can avoid fines and legal trouble. It also ensures that the company is operating within the law when handling sensitive data.
c) Builds Trust: When a company protects its data, it builds trust with customers and business partners. People are more likely to do business with companies that take security seriously. Trust is essential for maintaining long-term relationships and business success.
d) Prevents Data Breaches: Strong security measures help prevent data breaches, which can be very costly. Data breaches can affect a company’s reputation and lead to financial losses. Preventing them is key to protecting the company’s future.
e) Enhances Decision-making: With secure and accurate data, businesses can make better decisions. There’s no worry about the data being altered or tampered with. Reliable data leads to more informed and effective business strategies.
Big Data Security Use Cases
Big Data Security requires a range of measures to protect sensitive information across various stages of data processing. Here are some examples of Big Data Security in action:
Data Encryption in Financial Services
A major bank uses encryption to protect customer data, both when it is stored in Big Data Databases and when it is transmitted between servers. This ensures that information, such as account numbers and transaction details, is secure from unauthorised access.
Access Control in Healthcare
A healthcare provider implements RBAC to restrict access to patient records. Doctors and nurses can only view and edit the records relevant to their patients, while administrative staff have limited access, reducing the risk of data breaches.
Intrusion Detection in E-commerce
An e-commerce company uses Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) to monitor its network for suspicious activity. The system detects and alerts the security team to unusual behaviour, such as attempts to access the customer database from unknown IP addresses, allowing for swift action to prevent data theft.
Data Masking in Retail
A retail company uses data masking to protect sensitive customer information during data analysis. Customer names and credit card numbers are masked, allowing analysts to work with the data without exposing the actual details and ensuring privacy and compliance with data protection regulations.
Blockchain for Data Integrity in Supply Chain Management
A supply chain management firm employs blockchain technology to create a secure, immutable ledger of transactions. This ensures that data about shipments, deliveries, and payments cannot be tampered with, providing a reliable and transparent record for all parties involved.
Compliance Management in Telecommunications
A telecommunications company implements a compliance management system to ensure that all data handling practices meet regulatory standards such as GDPR. Regular audits and automated compliance checks help the company avoid fines and legal issues related to data protection.
Anomaly Detection in Manufacturing
A manufacturing company uses anomaly detection systems powered by machine learning to monitor production data for signs of equipment failure or security breaches. The system identifies deviations from normal operating patterns, allowing the company to address potential issues before they lead to data loss or downtime.
Backup and Recovery in Education
A university implements a robust backup and recovery system to protect its large volumes of academic and administrative data. In case of a ransomware attack or system failure, the university can quickly restore its data, minimising disruption to its operations and safeguarding student information.
Learn the various advanced analytical theories with our Big Data Analytics & Data Science Integration Course – Join today!
Challenges to Big Data Security
Keeping big data secure can be challenging as it involves tons of data in various forms. It moves quickly, and various people and risks are involved in this. Discussed below are a few of the Big Data Security challenges:
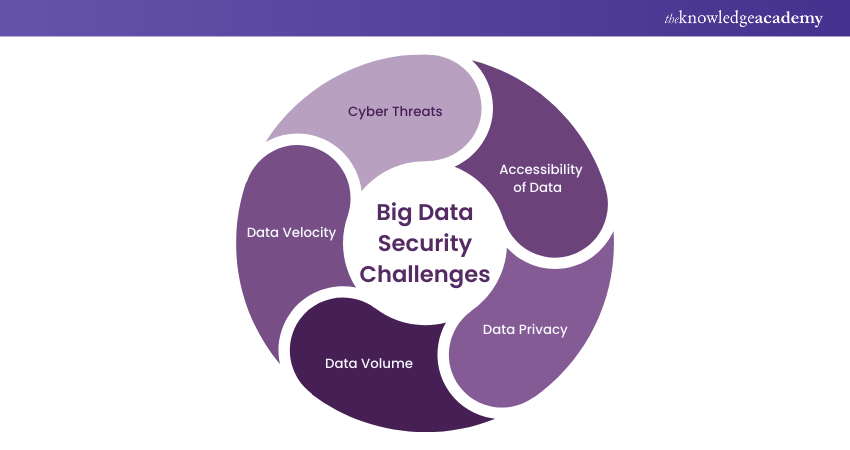
Cyber Threats
Big data is valuable for cybercriminals who attempt to breach security defences and steal or manipulate the data. Protecting against these digital threats requires robust security measures and constant vigilance of data.
Accessibility of Data
Many users and applications may need access to big data for analysis and decision-making. Controlling and managing who accesses what data and how they use it is a complex security task.
Data Privacy
Data privacy refers to the protection of individuals' private information and ensuring that it is not accessed or disclosed without their consent. Big data often involves handling sensitive and valuable information. Keeping it safe and preventing any unauthorised access to these data is a big challenge.
Data Volume
Big data volume, as the word suggests, is dealing with a huge amount of information. This huge volume of data can be challenging to manage and protect. It requires a lot of resources and specialised tools to keep it safe from any cyber threats.
Data Velocity
Data velocity refers to how quickly information in big data is created and changed. This high-speed data flow can make it difficult to stay on top of things. It is challenging to make sure that data stays safe in real-time.
Big Data Security Best Practices
Big Data Security ensures the integrity of your data environment. Here are some essential best practices to follow:
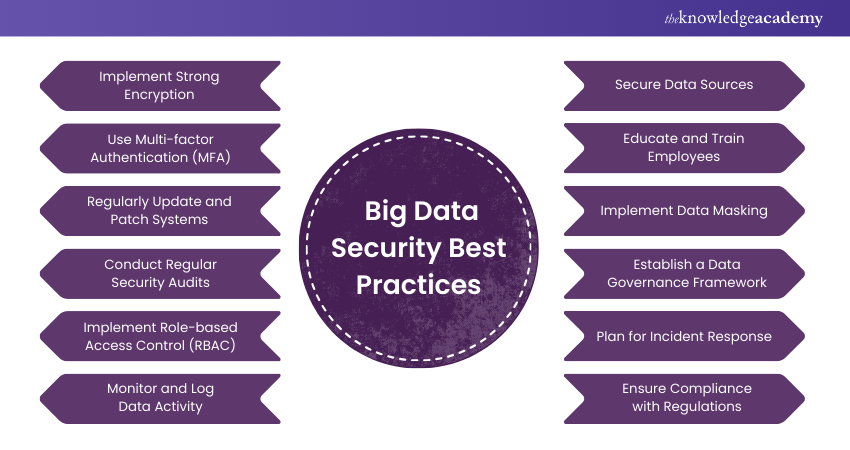
a) Implement Strong Encryption: Always encrypt sensitive data both at rest and in transit. This ensures that even if data is intercepted or accessed by unauthorised users, it remains unreadable without the proper decryption keys.
b) Use Multi-factor Authentication (MFA): Make it compulsory for MFA to access sensitive data and critical systems. MFA adds a security by requiring users to verify their identity through methods, such as a password and a fingerprint scan.
c) Regularly Update and Patch Systems: Keep all software, systems, and security tools up to date with the updates. Regular updates help protect against known vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
d) Conduct Regular Security Audits: Perform regular security audits to assess the effectiveness of your security measures. Audits should include penetration testing, vulnerability assessments, and reviews of access controls and security policies.
e) Implement Role-based Access Control (RBAC): Limit access to sensitive data based on the user’s role within the organisation. RBAC ensures that employees can only access the data they need to perform their job functions, reducing the risk of unauthorised access.
f) Monitor and Log Data Activity: Continuously monitor data access and usage across your big data environment. Implement logging mechanisms to track who accesses data, what actions they perform, and when these actions occur. Regularly review logs to find and respond to any suspicious activities.
g) Secure Data Sources: Protect data at its source by implementing security measures such as encryption and access controls. Ensure that data is protected as it moves from its source to your big data platform.
h) Educate and Train Employees: Provide regular training to employees on data security, including how to recognise phishing attempts, securely handle sensitive data, and respond to security incidents. Well-informed employees are a critical line of defence against security breaches.
i) Implement Data Masking: Use data masking techniques to hide sensitive information when it’s not necessary for analysis or testing. Masked data can be used safely in non-production environments without exposing the actual sensitive information.
j) Establish a Data Governance Framework: Develop a comprehensive data governance framework that outlines how data is managed, protected, and used within your organisation. This framework should include policies for data classification, access control, compliance, and data lifecycle management.
k) Plan for Incident Response: Have a well-defined incident response plan in place for addressing data breaches or security incidents. The plan should include procedures for investigation and remediation to minimise the impact of any security breach.
l) Ensure Compliance with Regulations: Stay informed about relevant data protection regulations and ensure that your Big Data Security practices comply with them. Frequently review and update your security policies to meet evolving legal and regulatory requirements.
Conclusion
Big Data Security is a crucial practice for keeping massive amounts of data safe from unauthorised access, breaches, and other threats. It's like a set of digital locks and keys that organisations use to protect their valuable information. Without it, sensitive data could be at risk, which can lead to significant problems. So, it's essential for ensuring the privacy and integrity of data in today's digital age.
Learn the fundamentals of big data with our Big Data Analysis Course – Join today!
Frequently Asked Questions

Responsibility for Big Data Security is shared across the organisation, including IT teams, data security specialists, and management. Everyone involved in handling and processing data must follow security protocols to protect sensitive information.

Big data helps cyber security by analysing large volumes of data to detect patterns and find potential threats. It enables quicker response to security incidents and helps in predicting and preventing future cyberattacks.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Big Data and Analytics Training, including the Big Data Analytics & Data Science Integration Course, Hadoop Big Data Certification, and Big Data Analysis Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Data Grid.
Our Data, Analytics & AI Blogs cover a range of topics related to Big Data, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Data Analysis skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Data, Analytics & AI Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Hadoop Big Data Certification
Hadoop Big Data Certification
Thu 23rd Jan 2025
Thu 20th Mar 2025
Thu 22nd May 2025
Thu 17th Jul 2025
Thu 18th Sep 2025
Thu 20th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


