We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +420 210012971 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

What would you do if an emergency struck right now? An Emergency Action Plan (EAP) is a guide to help people respond safely and quickly in unexpected situations. From fires to medical emergencies, an EAP provides clear instructions so everyone knows how to act. It assigns specific roles, outlines evacuation routes, and explains how to communicate during a crisis.
This plan keeps panic at bay and helps people stay calm when it matters most. An EAP isn’t just a document. It’s a lifeline that protects lives by ensuring everyone is ready when every second counts. What to know more about EAP? Let’s discover it in this blog.
Table of Contents
1) What is an Emergency Action Plan?
2) Why is an Emergency Action Plan so Important?
3) Emergency Action Plan Elements
4) How to Make an Emergency Action Plan?
5) Guidelines for Executing an Emergency Action Plan
6) Conclusion
What is an Emergency Action Plan?
An Emergency Action Plan (EAP) details the procedures for responding to emergencies. It outlines who will perform specific tasks and the necessary steps to ensure safety, protect property, maintain business continuity, and minimise disruptions. An EAP is essential for organisations to prepare for emergencies, establishing a coordinated and effective response.
By clearly defining roles and actions, an EAP helps safeguard people and assets, maintaining operations during critical situations. It is a proactive measure that enhances an organisation's resilience and ability to handle unexpected events efficiently.
Why is an Emergency Action Plan so Important?
EAP is essential for organisations to effectively manage emergency protocols. It aims to eliminate confusion, prevent injuries, and protect property during workplace emergencies, such as blasting incidents.
Regularly updating EAPs helps teams identify hazardous conditions that could worsen emergencies. This enables safety professionals to implement preventive measures. This practice helps avoid severe losses, including casualties and financial setbacks for the organisation.
Drive agile transformation and lead your team to success with our specialised Agile Leadership Training – Join now!
Emergency Action Plan Elements
While each emergency scenario may need unique actions, general action plan elements help keep workplaces safe and organised. An effective Emergency Action Plan includes the following OSHA standard elements:
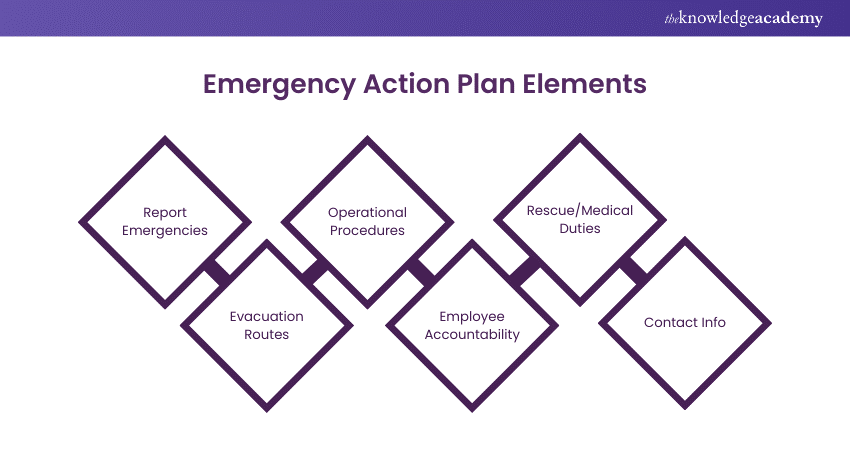
1) Report Emergencies
List your organisation's preferred methods for reporting emergencies, such as dialling 911, using an internal system, or pulling a fire alarm. Include instructions on what information to provide, like the nature and location of the emergency and the caller's contact details.
2) Evacuation Routes
Outline evacuation and escape routes for safe exits. Identify who is responsible for ordering evacuations and when they are necessary. Include steps for employees to follow, like turning off equipment and closing doors.
3) Operational Procedures
Assign employees to perform tasks like shutting down gas or electrical systems during emergencies. These duties prevent equipment damage and safety hazards. Define who is responsible and the steps to follow.
4) Employee Accountability
Include measures to ensure all employees have exited the building. Assign specific employees to check the building and take roll calls. Designate evacuation leaders to oversee the process.
5) Rescue/Medical Duties
Identify employees with first aid or CPR certifications or provide such training. List these personnel and their contact information for emergency assistance until public resources arrive.
6) Contact Info
Provide a list of internal personnel for employees to contact about the emergency plan. These individuals should have authoritative roles and can answer questions related to the plan and assigned duties. Include their names, job titles, departments, and contact details.
Transform your creativity into impactful solutions with our expert-led Design Thinking Course – Sign up now!
How to Make an Emergency Action Plan?
Emergencies are inevitable in the workplace, so health and safety managers should ensure all employees are prepared. Here are simple steps to integrate an Emergency Action Plan:
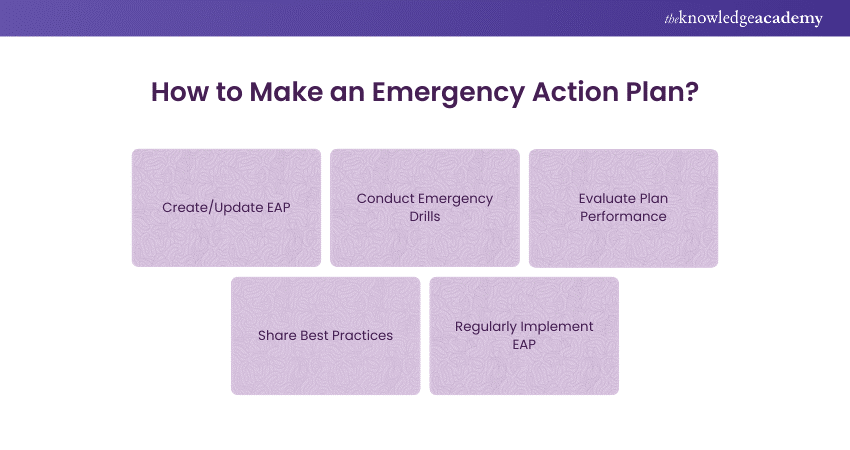
1) Create/Update EAP
Create or update the EAP with a cross-functional team, including employees with relevant knowledge and experience, and local government representatives. This ensures the plan is comprehensive and effective.
2) Conduct Emergency Drills
Perform announced or unannounced emergency drills to test the plan's effectiveness. Announced drills remind coordinators to review the plan, while unannounced drills test their immediate response.
3) Evaluate Plan Performance
After drills, gather a team to analyse the results. Identify any issues and discuss improvements. Use the OSHA EAP template to assess the plan's effectiveness.
4) Share Best Practices
Recognise and reinforce positive behaviours. Provide training for areas needing improvement. Highlight best practices and implement necessary changes.
5) Regularly Implement EAP
Conduct annual drills as advised by OSHA. Regular testing ensures the plan's effectiveness and builds a proactive safety culture in the workplace.
Lead with confidence and inspire change. Sign up with our Leadership Courses and make a lasting impact.
Guidelines for Executing an Emergency Action Plan
Here are simple tips to implement an Emergency Action Plan:
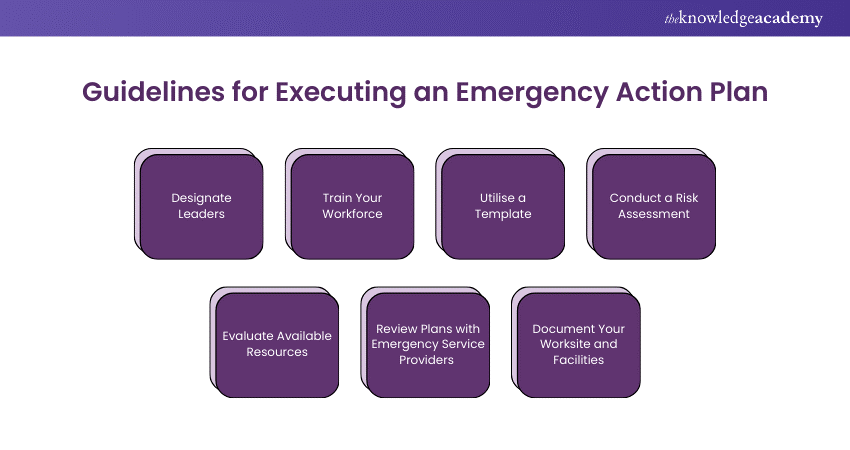
1) Designate Leaders
Research Emergency Action Plan templates from sources like OSHA or the CDC. These templates, checklists, and resources help ensure you don’t miss any important details.
2) Train Your Workforce
Your Emergency Action Plan needs leaders to manage emergency responses. These leaders can be employees or managers. Assign them tasks like turning off equipment or managing evacuations. They may have the authority to implement emergency procedures. Clearly define their roles and responsibilities. Ensure everyone knows who to turn to during an emergency.
3) Utilise a Template
Research Emergency Action Plan templates to make planning easier. Government resources like OSHA or the CDC offer templates, checklists, and guidance. These resources provide a strong starting point. They help ensure you don't miss any important details when creating emergency plans for the first time.
4) Conduct a Risk Assessment
To draft an Emergency Action Plan, start with a risk assessment. Identify potential emergencies specific to your organisation and location. For example, industrial plants may face chemical spills, while some areas may deal with natural disasters like earthquakes, hurricanes, or tornadoes.
Discuss the potential outcomes of each emergency. For example, natural disasters may cause power outages, affecting your operations and income. Include procedures to mitigate the impacts, such as backing up important data. Understanding the risks and their effects will help you create detailed and effective Emergency Action Plans.
5) Evaluate Available Resources
When creating your Emergency Action Plan, identify internal and external resources. These may include local public services like fire departments, law enforcement, or emergency medical services. Internal resources could be alarm systems, fire extinguishers, or helpful individuals. Provide accurate, up-to-date names and contact information for these resources to prevent confusion during emergencies.
6) Review Plans with Emergency Service Providers
When possible, meet with local emergency service providers and share your Emergency Action Plan. These professionals know the best practices for responding to emergencies and can offer valuable insights. They may also connect you with resources to help develop your plans and train employees. Coordinate drills with them to assess your employees and get feedback for improvement.
7) Document Your Worksite and Facilities
Create site and floor plans to help employees and emergency personnel understand your organisation's layout. Include building entrances, utility or equipment controls, emergency equipment, and security systems in the documentation. Employees need this information to follow evacuation or escape procedures and perform response activities, like pulling fire alarms.
Share these documents with local emergency responders to make their efforts more efficient. When possible, invite these professionals to tour your facilities for safety inspections or drills so they can become familiar with the layout.
Conclusion
An Emergency Action Plan outlines steps for handling emergencies. It identifies key roles, tasks, and procedures to ensure safety and protect property. An EAP helps organisations manage emergencies effectively, reducing disruptions and safeguarding employees. It's crucial for maintaining a secure and prepared workplace.
Prepare for any emergency and become an effective leader with our OPITO's Incident Commander Training – Register today!
Frequently Asked Questions

The four basic principles that need to be followed in an emergency situation include:
1) Stay calm
2) Assess the situation
3) Call for help
4) Provide care until help arrives

The six requirements for reporting emergencies are:
1) Procedures for reporting emergencies
2) Evacuation routes and procedures
3) Procedures for critical operations
4) Accounting for all employees
5) Rescue and medical duties
6) Contact information

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Leadership Courses, including OPITO Incident Commander Training, Leadership Skills Training and Agile Leadership Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into the Behavioural Theory of Leadership.
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to EAP, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Leadership skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 OPITO Incident Commander Training
OPITO Incident Commander Training
Fri 27th Dec 2024
Fri 24th Jan 2025
Fri 28th Mar 2025
Fri 23rd May 2025
Fri 25th Jul 2025
Fri 26th Sep 2025
Fri 28th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


