We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +420 210012971 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

The success of Six Sigma has emerged as a powerful lies in its powerful and impactful metric named Defects Per Million Opportunities (DPMO). But do you know What is DPMO in Six Sigma?
DPMO in Six Sigma quantifies the number of defects or errors that occur in a process for every one million opportunities or chances for a defect to occur. However, many organisations leveraging Six Sigma are still unfamiliar with how to calculate this metric. Therefore, they often struggle to upscale their Project Management game.
If you, too, are unfamiliar with Six Sigma DPMO and how it fits into this powerful methodology, you've come to the right place. Read this blog to learn about What is DPMO in Six Sigma. Also, explore its calculation methods and benefits to achieve near-perfect performance in your organisation.
Table of contents
1) What is DPMO in Six Sigma?
2) How to calculate DPMO? Step-by-step guide
3) Importance of DPMO in Six Sigma
4) What to think about when utilising DPMO?
5) What can be some DPMO examples?
6) Best Practices for Managing DPMO
7) Conclusion
What is DPMO in Six Sigma?
Defects Per Million Opportunities (DPMO) is a fundamental metric used in the field of Six Sigma. It plays a crucial role in measuring the performance and quality of various processes within an organisation.
The ultimate objective of this metric is to minimise defects and reduce variations in processes. Therefore, it helps organisations enhance efficiency, increase customer satisfaction, and drive overall business success.
The concept behind DPMO is simple yet powerful. It involves calculating the number of defects in a process. Further, relating them to the number of opportunities for defects that exist within that process. The resulting value represents the number of defects that would occur in one million opportunities. Therefore, organisations can compare their performance against established benchmarks and industry standards.
Furthermore, the metric provides a common language and framework for discussions and decision-making within the realm of Six Sigma. It assists organisations in the following:
a) Facilitating communication among team members and stakeholders
b) Allowing them to align their efforts towards reducing defects
c) Enhancing process efficiency
d) Identifying areas that require improvement
e) Setting realistic quality goals
f) Monitoring their progress towards achieving those goals
g) Enabling organisations to focus their resources and efforts on the areas that will have the most significant impact
How to calculate DPMO? Step-by-step guide
After learning What is DPMO in Six Sigma, it’s time to understand how to calculate it. Calculating Defects Per Million Opportunities (DPMO) is a crucial step in measuring the performance and quality of a process within the Six Sigma Methodology. Follow this step-by-step guide to learn about the process of calculating DPMO:
Step 1: Sampling
To begin, it's essential to select a representative sample from the process you want to evaluate. The sample should adequately reflect the overall process and provide a reliable basis for calculating DPMO. Ensure that the sample size is sufficient to provide statistically significant results.
Step 2: Determine the number of opportunities for defects per unit
Identify the various opportunities for defects within the process. These opportunities represent the specific points or steps where defects can occur.
For example, if you are assessing a manufacturing process, the opportunities for defects could be the number of components in a product or the number of assembly steps.
Step 3: Determine the total number of defects in your sample
Next, carefully examine each unit in your sample and identify the number of defects present. A defect is any non-conformity or deviation from the desired specifications or requirements. Count and record the total number of defects across the entire sample.
Step 4: Counting the actual defects within the sample group
In this step, you will have to count the actual number of defects for each unit in your sample. By doing so, you obtain accurate data on the defects present in the sample, which will be used in the subsequent calculations.
Step 5: Calculate the DPMO
Once you have the total number of defects and the number of opportunities for defects, you can calculate the DPMO using the following formula:
DPMO = (Number of Defects / (Number of Opportunities per unit × Number of Units in Sample)) × 1,000,000
Let's break down the formula:
Number of Defects: The total number of defects identified in the sample.
a) Number of opportunities per unit: The total number of opportunities for defects within each unit of the process.
b) Number of units in sample: The size of the sample, i.e., the number of units assessed.
c) 1,000,000: A scaling factor to convert the DPMO value into per million.
By substituting the values from your sample into the formula, you can calculate the DPMO, which represents the number of defects that would occur in one million opportunities.
It provides a standardised measure of process performance and quality. The calculation also allows you to compare different processes or track improvement efforts over time. The lower the DPMO value, the better the process performance, indicating fewer defects and higher efficiency.
Importance of DPMO in Six Sigma
This metric holds significant importance within the Six Sigma Methodology. It is vital for measuring process performance, quantifying defects, and driving Process Improvement efforts. So, let’s explore the key reasons why DPMO is crucial in the context of Six Sigma:
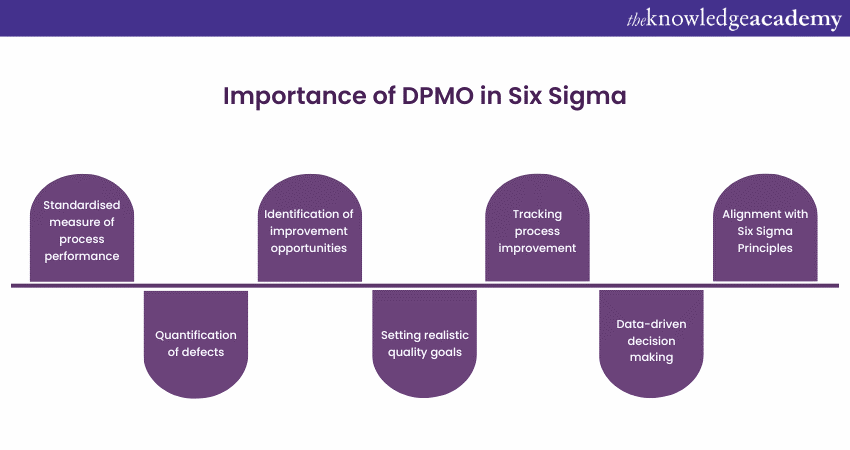
Standardised measure of process performance
DPMO in Six Sigma allows organisations to assess and compare the performance of different processes within their operations. By calculating it, companies can establish a common benchmark to evaluate the quality and efficiency of their processes, regardless of their scale or complexity.
Quantification of defects
Quantification of defects enables organisations to gain a clear understanding of the extent of defects occurring within their processes. It also provides a tangible figure that can be tracked, analysed, and used as a basis for Process Improvement initiatives.
Identification of improvement opportunities
By analysing the DPMO data, organisations can pinpoint specific steps or stages where defects are most prevalent. This identification of improvement opportunities also enables companies to focus their resources and efforts. Further, they can also implement targeted process enhancements.
Setting realistic quality goals
By analysing the current values in DPMO and industry benchmarks, companies can establish achievable targets for defect reduction. These goals provide a clear direction and enable teams to align their efforts towards attaining higher process performance and delivering superior quality products or services.
Tracking Process Improvement
The metric also acts as a key performance indicator for Process Improvement efforts. It helps organisations track the effectiveness of their improvement initiatives. Further, they can also assess whether the implemented changes have resulted in a reduction in defects and improved performance.
Data-driven decision making
It supports organisations in the decision-making processes by basing decisions on quantified defects and process performance data. Therefore, organisations can make informed choices regarding resource allocation, prioritisation of improvement projects, and the implementation of corrective actions.
Alignment with Six Sigma Principles
The metric also aligns perfectly with the Six Sigma Principles, which aim to minimise defects and reduce process variations. It enables organisations to demonstrate their progress towards achieving Six Sigma’s ultimate goal (3.4 defects per million opportunities). Therefore, DPMO guides organisations on their journey towards operational excellence and customer satisfaction.
What to think about when utilising DPMO?
When utilising DPMO, there are several crucial factors to keep in mind. These factors are as follows:
Definition of a 'Defect'
Before calculating DPMO, it's essential to clearly define what constitutes a 'Defect' within the context of your process or product. A Defect can vary from one process to another, and it's crucial that everyone involved has a shared understanding to ensure accuracy in your calculations.
Identification of opportunities
An 'opportunity' in DPMO refers to any chance for a Defect to occur. It’s important to accurately count all possible opportunities for defects to ensure a proper DPMO calculation. Miscounting opportunities can lead to skewed results, potentially hiding issues or magnifying minor ones.
Sample size and consistency
Ensure that the sample size you're evaluating is large enough to provide an accurate representation of the process. A small sample might give skewed results, either painting a too rosy or too dire picture of process performance.
Use DPMO in conjunction with other metrics
While DPMO is a powerful metric, it shouldn't be used in isolation. Combining DPMO with other Six Sigma or quality metrics, like process sigma or yield, can provide a more comprehensive view of process performance.
External factors
Be aware of external factors that might affect the defect rate temporarily. For instance, if a machine breaks down or there's an unexpected material shortage, these external factors can influence the DPMO but aren't indicative of the process's overall quality.
Continual review
Processes change and evolve. As a result, the definition of defects, opportunities, or even the process flow might change over time. It’s important to review and recalibrate the DPMO calculations periodically to ensure they remain relevant and accurate.
Interpretation and action
Knowing your DPMO number is just the start. The real value comes from interpreting this metric in the context of your business goals and taking actionable steps to improve. This could mean investing in training, implementing new technologies, or redesigning a process.
Avoid over-reliance
While DPMO is a valuable metric, it’s essential not to become too fixated on achieving a particular number. The ultimate goal should be processing improvement and customer satisfaction, and while DPMO can guide you in this, it shouldn't overshadow the bigger picture.
Training and expertise
Calculating and interpreting DPMO requires some expertise. Those tasked with this should have adequate training, ideally in Six Sigma methodology, to ensure that they're using and interpreting DPMO correctly.
Communication
The insights gained from DPMO should be communicated across relevant teams and departments. This not only ensures transparency but also promotes a culture of continuous improvement. When everyone is aware of process performance, it fosters collective responsibility and motivation to improve.
What can be some DPMO examples?
After you have read about What is DPMO in Six Sigma in detail, it’s time to understand this metric with the help of some examples. These examples will provide you with a concrete illustration of how this metric is calculated and applied in real-world scenarios.
So, let's explore a few examples to better understand how DPMO in Six Sigma is used to measure process performance and quantify defects:
Example 1: Manufacturing process
Consider a manufacturing process that involves assembling electronic devices. The opportunities for defects in this process may include soldering joints, component placement, and final product testing.
Suppose you assess a sample of 1,000 units and identify a total of 15 defects. To calculate the DPMO, follow these steps:
1) Number of Defects: 15
2) Number of opportunities per unit: 10 opportunities for defects in each unit (assumption)
3) Number of units in sample: 1,000
Use the formula:
DPMO = (Number of Defects / (Number of Opportunities per unit × Number of Units in Sample)) × 1,000,000
DPMO = (15 / (10 × 1,000)) × 1,000,000
DPMO = 150 × 1,000
DPMO = 150,000
In this example, the DPMO is calculated as 150,000. This means that within this manufacturing process, there are 150,000 defects that would occur per one million opportunities.
Equip yourself with the tools and techniques needed to drive Process Improvement with our Six Sigma Black Belt Course.
Example 2: Customer-service process
Now, let’s consider a customer service process that handles incoming customer queries and complaints. The opportunities for defects in this process may include response time, accuracy of information provided, and customer satisfaction.
Suppose you evaluate a sample of 500 customer interactions and find 7 instances where customers received incorrect information. The calculation of DPMO would be as follows:
1) Number of Defects: 7
2) Number of opportunities per unit: Let's assume there are 5 opportunities for defects in each customer interaction.
3) Number of units in sample: 500
Use the formula:
DPMO = (Number of Defects / (Number of Opportunities per unit × Number of Units in Sample)) × 1,000,000
DPMO = (7 / (5 × 500)) × 1,000,000
DPMO = (7 / 2500) × 1,000,000
DPMO = 2,800
In this example, the DPMO is calculated as approximately 2,800. This indicates that within the customer service process, there are 2,800 defects that would occur per one million opportunities.
Best practices for managing DPMO
Effectively managing this metric in Six Sigma is crucial for organisations aiming to improve process performance and drive continuous quality enhancement. So, before implementing DPMO, it’s important to understand its best practices. The following best practices for managing DPMO:

a) Establish clear definitions for defects and opportunities for defects within the processes.
b) Ensure that everyone involved understands and follows these definitions consistently.
c) Implement robust data collection processes and ensure that data is consistently and accurately recorded.
d) Leverage appropriate data collection methods such as sampling techniques or automated data capture systems to minimise errors and biases.
e) Establishing a baseline DPMO allows you to gauge the initial performance of the processes.
f) Calculate the metric for your existing processes and use it as a starting point for setting improvement goals and tracking progress.
g) Analyse the data to identify the areas with the highest defect rates or opportunities for improvement.
h) Prioritise improvement opportunities based on their impact on overall process performance, customer satisfaction, or business objectives.
i) Employ root cause analysis techniques to identify the underlying causes of defects.
j) Investigate the contributing factors that lead to defects and dig deeper to identify the root causes.
k) Based on the findings from root cause analysis, develop and implement corrective and preventive actions to reduce defects.
l) Regularly monitor the effectiveness of these actions and adjust as necessary.
m) Regularly measure and analyse DPMO to assess the impact of improvement initiatives.
n) Identify any emerging trends or areas requiring further attention.
Conclusion
We hope after reading this blog you have understood What is DPMO in Six Sigma. It is a vital metric that allows organisations to quantify defects and measure process performance. By understanding and effectively managing DPMO, organisations can drive Process Improvement, reduce defects, and deliver higher-quality products or services.
Take the first step towards professional growth in Project Management with our Six Sigma Certification Training.
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Business Improvement Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Six Sigma Green Belt
Six Sigma Green Belt
Mon 6th Jan 2025
Mon 13th Jan 2025
Mon 20th Jan 2025
Mon 27th Jan 2025
Mon 3rd Feb 2025
Mon 10th Feb 2025
Mon 17th Feb 2025
Mon 24th Feb 2025
Mon 3rd Mar 2025
Mon 10th Mar 2025
Mon 17th Mar 2025
Mon 24th Mar 2025
Mon 31st Mar 2025
Mon 7th Apr 2025
Mon 14th Apr 2025
Tue 22nd Apr 2025
Mon 28th Apr 2025
Tue 6th May 2025
Mon 12th May 2025
Mon 19th May 2025
Tue 27th May 2025
Mon 2nd Jun 2025
Mon 9th Jun 2025
Mon 16th Jun 2025
Mon 23rd Jun 2025
Mon 30th Jun 2025
Mon 7th Jul 2025
Mon 14th Jul 2025
Mon 21st Jul 2025
Mon 28th Jul 2025
Mon 4th Aug 2025
Mon 11th Aug 2025
Mon 18th Aug 2025
Tue 26th Aug 2025
Mon 1st Sep 2025
Mon 8th Sep 2025
Mon 15th Sep 2025
Mon 22nd Sep 2025
Mon 29th Sep 2025
Mon 6th Oct 2025
Mon 13th Oct 2025
Mon 20th Oct 2025
Mon 27th Oct 2025
Mon 3rd Nov 2025
Mon 10th Nov 2025
Mon 17th Nov 2025
Mon 24th Nov 2025
Mon 1st Dec 2025
Mon 8th Dec 2025
Mon 15th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


