We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +420 210012971 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
One of the biggest frustrations for software developers is when an application they've poured so much time into fails to deliver the expected results. It's back to square one when that happens! But how can organisations ensure their software is error-free before launch? The answer: By doing comprehensive Software Testing. But What is Software Testing exactly.
This process is about delivering a flawless software product to the client after thoroughly checking its functionality, from squashing bugs to perfecting its performance. So, wait no more and dive into this blog to learn What is Software Testing and how it ensures your favourite apps run without a glitch!
Table of Contents
1) What is Software Testing?
2) Importance of Software Testing
3) Software Testing Life Cycle
4) Types of Software Testing
5) Software Testing Techniques
6) Best Practices for Software Testing
7) Popular Software Testing Models
8) Software Testing Tools
9) Conclusion
What is Software Testing?
Software Testing is a methodology of assuring that a software application is of the highest possible quality for end users and testing a product to safeguard any issues from becoming a hurdle at any point in time. It’s a systematic process that involves evaluating and validating a software application to identify and remove all possible bugs.
The first goal of Software Testing is to meet industry requirements and operate as expected, providing users with a seamless experience. By uncovering issues in the early stages of development, Software Testing saves time and resources and avoids potential future threats.
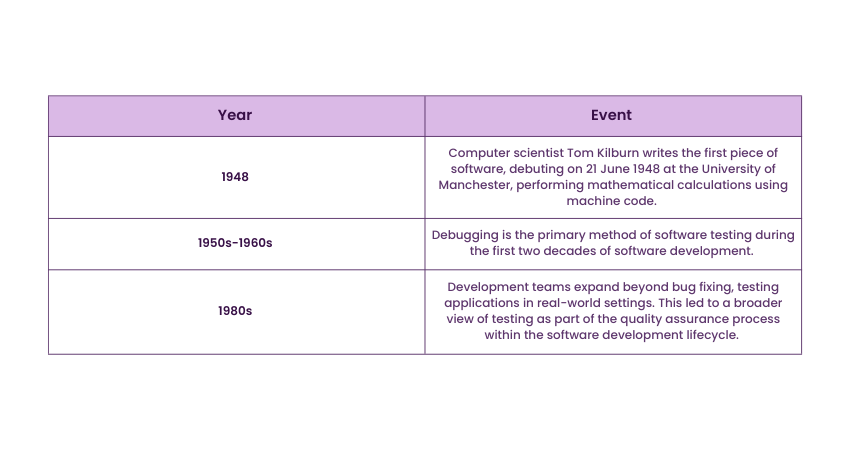
History of Software Testing
Here’s a brief timeline of the history of Software Testing:
Who needs it?
Software Testing has become an indispensable part of every industry and every organisation, big or small. Companies focus highly on the quality of the product before they roll it out to their clients or customers. Here are some instances where Software Testing is crucial:

a)Automobile: The automobile industry is one of the most complex and change-driven industries that must be equipped with all the latest technological advancements. They need a testing team to constantly refine the software by applying the correct testing methods. For instance, many automobile companies use chip-based technology to enhance safety measures.
Master the skills of Automated software testing with our comprehensive course. Start learning today!
b) Energy: It is one of the fastest-growing industries that focuses on channelling power supplies with technological support. Embracing alternative energy sources such as electric vehicle manufacturing and solar systems requires a software-driven approach. Alternative energy sources, like manufacturing electric vehicles and solar systems, require a software-driven approach. An in-house testing team can help an organisation use mobile applications to pay energy bills.
c) Banking: Banking and financial services play a vital role in the economic development of a country, and it is paramount that the software tools and techniques they use are well-tested and deliver high performance. Any banking software or service needs to be highly secure. If the services are secure, then they will be able to maintain security during monetary transactions. For example, the banking system needs a secure web network to process monetary transactions globally.
d) Healthcare: The healthcare industry has gone through a lot in the past few years, facing new challenges every day. It now depends heavily on software and robotics to keep themselves functioning all the time. The role of a Software Testing team is to build a robust mechanism that helps produce bug-free medical software to provide the best healthcare services within the stipulated time frame. For instance, automation in the pharmaceutical and healthcare industry has enabled drug manufacturers to make informed decisions.
e) Logistics: The expansion of every single economy depends heavily on transportation and logistics. To assist any logistics and transportation business, companies must be updated with modern software capable enough to perform day-to-day operational tasks. For instance, mobile applications are being made to track down the delivery of a product.
f) E-commerce: E-commerce caters to many visitors and buyers and empowers them to make well-informed decisions before buying a product or service online. This commodity-driven business needs the help of Software Testing Techniques to prevent bugs in the system and add value in prepositions to provide a smoother usability experience to its visitors.
Learn ISTQB Software Testing Foundation Course today and start your Software Testing career!
Importance of Software Testing
Since we got to know the industries where it is necessary, let’s now look at some of these points to understand in detail why Software Testing is important:
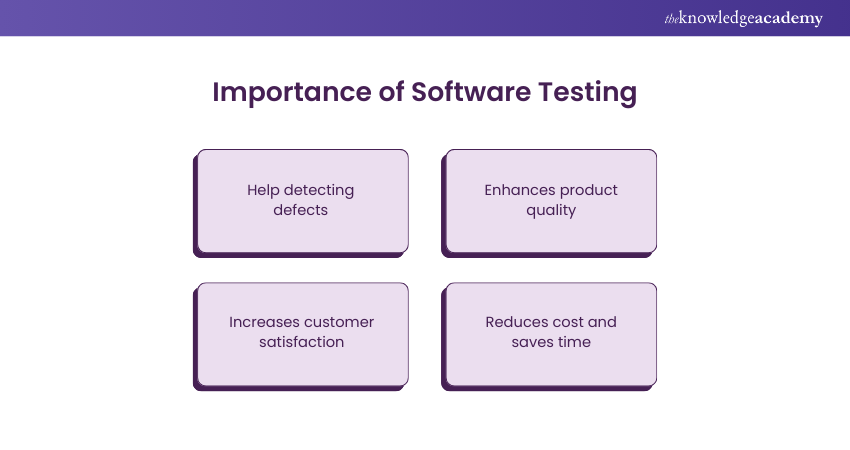
a) Help Detecting Defects: With the help of Software Testing, bugs and defects can be detected. Nowadays, they are built in such a way that they work seamlessly while they are interconnected with other devices or components. If there are any gaps between them or a component breaks down, then it causes a chain reaction of errors, which leads to faulty software products. With the help of the Software Testing process, these gaps can be discovered and fixed, which allows the organisation to deliver the product on time.
b) Enhances Product Qality: When the Software Testers identify the gaps or any possible errors in the software product, they automatically fix it without any delay. This improves the product quality and helps the organisation meet the customer expectations. With Software Testing, organisations can maintain the quality, compatibility, and security of the software applications.
c) Increases Customer Satisfaction: With rigorous Software Testing, businesses can increase customer satisfaction because it creates bug-free software that makes the product stable, secure and reliable. Maintaining these aspects helps the organisation to meet customer demands and create a positive and seamless User Experience (UX) for them, even in the long term. Moreover, when the customer gets to know that the software application has been tested repeatedly, they can maintain their trust in the product for a longer period.
d) Reduces Cost and Saves Time: When a software is getting tested repeatedly, the Software Testers can fix those bugs quickly without wasting any time. Software products in industries such as financial, medical, and legal need to be working without any default. The organisations cannot take the risk of this product failing while functioning as it may cause a huge revenue and even life loss. Therefore, Software Testing can prevent such damages from occurring without putting the company at risk.
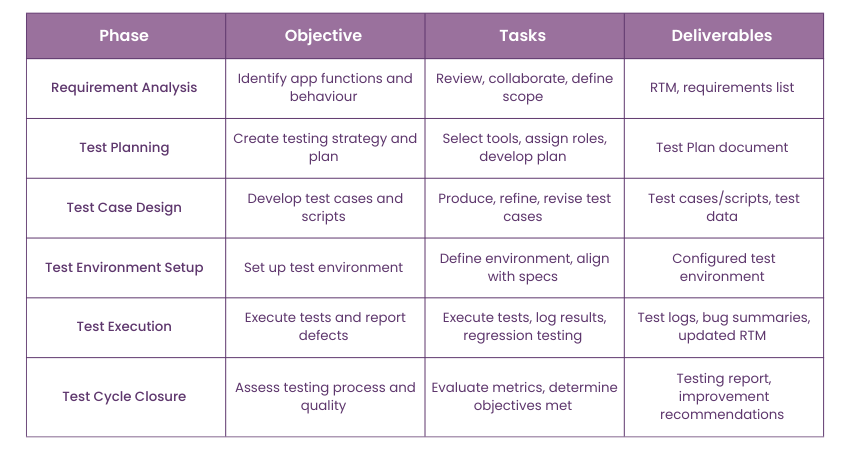
Software Testing Life Cycle
There are several stages involved in the Software Testing Life Cycle as summarised by the table below:
Master the art of seamless software quality with our Software Testing Automation Course – Sign up now!
Types of Software Testing
Software Testing can be broadly classified into three types:
a) Functional Testing: It’s a type of software testing that validates software systems against functional requirements. It's performed to check whether the application works according to the software’s requirements. There are various types of functional testing, including unit testing, integration testing, system testing, smoke testing, and so on.
b) Non-functional Testing: This checks the application for non-functional requirements like performance, portability, scalability, etc. Non-functional testing includes performance testing, stress testing, usability Testing, and so on.
c) Maintenance Testing: It’s the process of changing, modifying, and updating the software to align with the customer’s needs. It involves regression testing to verify that recent changes to the code have not adversely affected other previously working parts of the software.
Unlock your dream job with essential Software Testing Interview Questions!
Software Testing Techniques
Software Testing as a technique helps companies in odd situations and saves a great deal of time, cost and other valuable resources. These techniques detect threats and errors effectively, helping developers and testers deliver robust, bug-free software products. Incorporating automation testing into the testing process further enhances efficiency by automating repetitive test cases. Let us now explore some popular Software Testing Techniques and their significance.
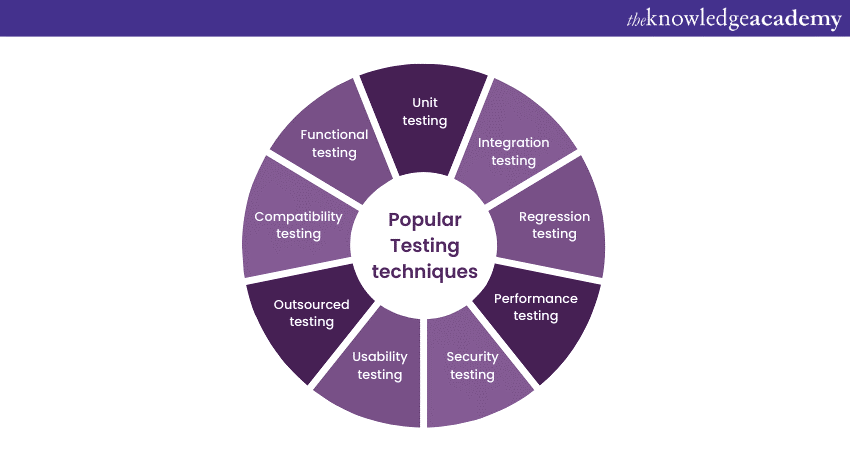
Unit Testing
Manual testing involves examining individual components or units of a software application. Developers conduct this type of testing to ensure that each unit functions correctly and to detect and fix any bugs early. Test cases are written to validate the functionality of units, making it easier to identify issues in specific coding sections.
Example: In a banking application, unit testing would involve testing individual functions like deposit, withdrawal, and balance inquiries to confirm that they perform their designated tasks accurately.
Integration Testing
Integration testing checks how different units or modules of a software application work together when compiled together. The primary aim of the integration method is to expose any interface issues between components and ensure the seamless interaction of integrated units. It helps identify defects that may arise due to the integration process.
Example: For web-enabled e-commerce applications, integration testing would involve testing the interactions between buyers and sellers and regulating database and updates accordingly.
Regression Testing
Regression testing is performed to verify that new code changes or updates to the software do not adversely impact existing functionalities. It resets the entire application or specific parts to ensure that any modifications have not introduced new defects or prevent previously fixed issues from reappearing.
Example: After fixing a bug and processing the application, retesting would be carried out to verify that the bug fix will not come back to the system, causing another problem for the user.
Performance Testing
Performance testing evaluates the software's performance under different conditions. It aims to determine the application’s responsiveness, speed, and stability under varying workloads and stress levels, as well as scalability testing to make sure the software is ready to perform in real-world scenarios.
Example: In this testing scenario, a website's delivery capacity can be checked thoroughly, analysing its scalability and responsiveness in absorbing the web traffic load etc.
Security Testing
Security testing is about identifying vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the software’s security measures. It aims to protect the application from threats and breaches, protecting sensitive data and user information. The whole idea of having security testing in place is to figure out any loophole in the system and fix it before the deployment.
Example: In a Healthcare Management System, testing would involve end-to-end scenarios, such as registering new patients, scheduling appointments, and generating medical reports to ensure the application functions correctly throughout the workflow.
Usability Testing
Usability testing evaluates the software's user-friendliness and User Experience (UX). It helps identify potential roadblocks or difficulties users may encounter when interacting with the application regularly. This testing is vital for ensuring a smooth and intuitive User Experience.
Example: A mobile app development project would involve a group of selected users testing the application to ensure it provides a satisfactory user experience and meets the business objective.
Outsourced Testing
This is where companies play smartly to save costs and resources by handing it over to an independent organisation or a bunch of Software Testers outside the company's limits. This form of testing is known as outsourced testing methodology resulting in higher quality outcomes. On the other hand, the organisation may lose control over the entire process compared to the in-house quality check team.
Example: A small company with a limited budget can outsource its Software Testing project to a third party; this can safeguard their interest, reducing the project's cost.
Compatibility Testing
Compatibility testing endorses an application that can be installed and run on different platforms, which includes hardware, network, operating system and other software. This testing emphasises more end-user satisfaction and reduces it. However, it is a time-consuming and costly method of testing software that is unrecommended for small-scale organisations with budget issues.
Example: Organisations developing software and likely to face compatibility issues amounting to conflict of interest between users and makers can go for compatibility testing before the deployment.
Functional Testing
Functional testing evaluates the software application against specified functional requirements. Testers verify whether the application functions and features work as intended. It ensures that the software meets the end users’ needs and adheres to the stated business requirements.
Example: A grocery store needs an application to check the customer's list without a server. The developer would create a test to determine the “check to customers” function, other than “customer number” or “customer name”, would also go under the testing process.
Try our course on Software Testing Black Belt today and start your testing career!
Best Practices for Software Testing
Developers must consider the following best practices regarding software testing:
1) Continuous Testing: Project teams must test each build as it becomes available. This enables software to be validated in real environments quite early in the development cycle, reducing risks and improving functionality and design.
2) Involve Users: The developers need to involve users in the process and ask open-ended questions about the application's functionality. This will help them develop and test the software from the perspective of customers.
3) Divide Tests into Smaller Parts: Fragmenting tests into smaller fractions saves time and resources in environments where frequent testing is needed. This also helps teams better analyse the tests and test results.
4) Metrics and Reporting: Reporting enables team members to share goals and test results. Advanced tools help integrate the project metrics and showcase an integrated report in the dashboard that team members can quickly review to assess the project's overall health.
5) Don’t Skip Regression Testing: Regression testing is among the most critical steps, as it encourages the application's validation. Thus, it should not be skipped.
6) Service Virtualisation: Service virtualisation simulates systems and services that have yet to be developed, enabling teams to reduce dependency and start testing sooner. This process can enable modification and reusability of the configuration to test diverse scenarios without altering the original environment.
7) Programmers Should Avoid Writing Tests: Generally, test cases are written before the start of the coding phase. So it's considered best practice for programmers to avoid writing test cases, as they might be biased towards their code and application.
Popular Software Testing Models
Popular Software Testing models include:
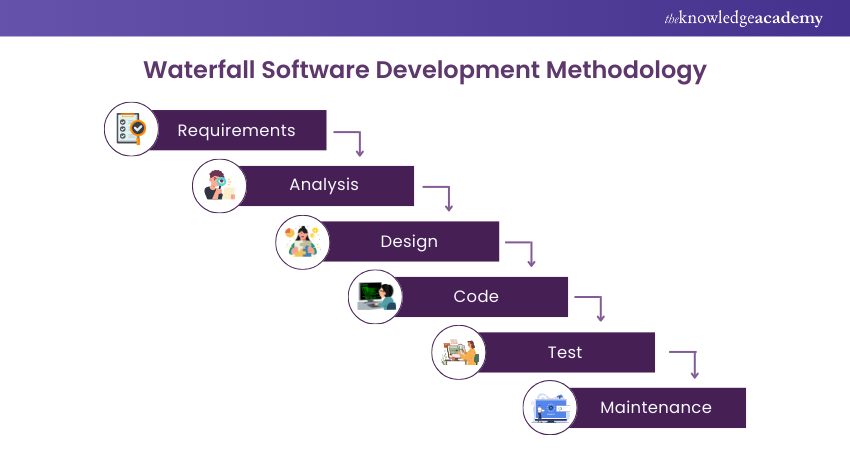
a) Waterfall Model: Stages of test runs following the development of the leading application.
b) V-Model: In some respect, the Waterfall model has proven effective, especially in its verification and validation features.
c) Agile Model: It adopts a humane approach of the development and testing cycles being interchangeable to a continuous iteration.
d) Spiral Model: Entwines consequential development with risk management and control.
e) Iterative Model: Writes software in small and focused modules to better be tested within incremental iterations in this process.
f) Big Bang Model: Minimum planning, which is testing that happens before, throughout, or after a development phase.
Software Testing Tools
Automated Software Testing Tools allow for quicker and more efficient testing cycles that are more likely to result in a high-quality product.
a) Test Management Tools (e.g., JIRA, TestRail): Create a test plan, run the tests, and produce a report.
b) Functional Testing Tools (e.g., Selenium, QTP/UFT): Automated execution of software functions tests.
c) Performance Testing Tools (e.g., LoadRunner, JMeter): Explore the software under various conditions.
d) Security Testing Tools (e.g., OWASP ZAP, Fortify): Find which software applications are vulnerable.
e) API Testing Tools (e.g., Postman, SoapUI): Put APIs to the test and verify their functionality and reliability.
Explore advanced Software Testing Techniques to enhance your skills and deliver top-notch results. Start mastering your craft today!
Conclusion
Understanding What is Software Testing is a fundamental process in software development, ensuring that applications are reliable, efficient, and secure. Employing various testing methodologies and types of testing, developers and Quality Assurance teams work together to detect and resolve defects at every stage of development.
Advance your Automation Testing skills with JUnit 5 by registering in Automation Testing With JUnit 5 Course
Frequently Asked Questions

Yes, Software Testers must have basic coding knowledge as it helps them understand the codebase, write test scripts, and collaborate effectively with developers.

Yes, Software Testing is a promising career path, and there's continually growing demand for Software Testers in diverse industries.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Software Testing Courses, including Unit Testing, Software Testing Black Belt and Software Testing Green Belt Courses. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Software Tester Roles and Responsibilities.
Our Business Analysis Blogs cover a range of topics related to Software Testing, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your knowledge on Software Testing, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Software Testing Automation Course
Software Testing Automation Course
Thu 9th Jan 2025
Thu 3rd Apr 2025
Thu 31st Jul 2025
Thu 6th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


