We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +49 8000101090 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

The Importance of Project Planning cannot be emphasised enough in effective Project Management. It serves as the fundamental cornerstone upon which successful endeavours are built. In a world where businesses are constantly evolving, competition is fierce, and resources are finite, the significance of meticulous Project Planning becomes even more pronounced.
Moreover, it minimises uncertainties, optimises resource allocation, and ensures that teams are aligned with Project objectives. It is impossible to underline the Importance of Project Planning. Learn why effective Project Planning is essential for Project success and business success.
Table of Contents
1) Project Planning- an overview
2) Discussing the Importance of Project Planning
3) Exploring the key components of Project Planning
4) Looking at the five phases of a Project’s life cycle
5) The key tools you need for Project Planning
6) Steps you can take to create an effective Project Plan
7) Conclusion
Project Planning- an overview
Project Planning is a fundamental process in Project Management, serving as the compass that guides an endeavour from its conceptualisation to successful completion. Project Planning is the systematic and strategic process of defining, organising, and outlining all the essential components and activities required to achieve a specific goal or objective within a predetermined timeframe and budget.
Furthermore, Project Planners meticulously outline the Project's scope, objectives, tasks, and resources, breaking down complex endeavours into manageable units. They establish a clear roadmap that not only serves as a reference for team members but also helps in managing expectations among stakeholders, as detailed in the Project Planning and Control Guide.
Project Planning encompasses several key elements:
a) Scope definition: Clearly delineating the Project's boundaries and what it aims to accomplish, thus preventing scope creep.
b) Objective setting: Establishing Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART) goals that guide the Project's direction.
c) Resource allocation: Determining the necessary resources, whether they be human, financial, or material, and allocating them efficiently.
d) Timelines: Creating detailed schedules, often visualised through Gantt charts or Project Management Software, to manage deadlines and dependencies.
Discussing the Importance of Project Planning
Project Planning is the cornerstone of effective Project Management, and its importance cannot be overstated in today's dynamic and competitive business landscape. It serves as the essential blueprint that lays the foundation for a Project’s success. Here are key reasons why Project Planning is of Importance:
Minimising uncertainty
Project Planning allows teams to identify potential risks, uncertainties, and challenges early in the process. By conducting a thorough risk assessment, Project Managers can develop mitigation strategies and contingency plans, reducing the likelihood of unexpected setbacks during Project Execution.
Resource allocation
A well-structured Project Plan helps allocate resources efficiently. It ensures that human resources, budgets, and materials are distributed optimally to support Project objectives. Effective resource allocation prevents overburdening team members and minimises wastage, ultimately leading to cost savings.
Stakeholder alignment
Clear Project Planning documents, including scope statements, objectives, and timelines, align stakeholders' expectations. This alignment fosters collaboration, reduces misunderstandings, and minimises conflicts among Project participants. When everyone understands the Project's direction, it's easier to work together toward a common goal.
Time management
Project Planning establishes realistic timelines and deadlines for each Project phase and task. This helps teams prioritise their activities, set milestones, and monitor progress. Effective Time Management ensures that Projects stay on track, preventing delays that could impact delivery dates.
Budget control
A well-defined Project Plan includes a detailed budget breakdown. This budget provides a financial roadmap for the Project, allowing for the allocation of funds to specific tasks and activities. By closely monitoring budget expenditures throughout the Project's life cycle, organisations can control costs and prevent budget overruns.
Quality assurance
Project Planning encompasses quality assurance measures, ensuring that deliverables meet predefined standards and quality criteria. By proactively addressing quality issues in the planning phase, teams can avoid costly rework and enhance the overall Project outcome.
Client satisfaction
Effective Project Planning leads to successful Project outcomes. When Projects are delivered on time, within budget, and in line with stakeholders' expectations, client satisfaction increases. Satisfied clients are more likely to become repeat customers and provide positive referrals.
Continuous improvement
Post-project evaluations often reveal areas where improvements can be made. A structured Project Plan includes mechanisms for monitoring and evaluating Project performance. These insights can inform future Projects, enabling organisations to refine their processes and achieve even better results.
Monitor Projects effectively by signing up for our Project Planning and Control™ (PPC) Foundation now!
Exploring the key components of Project Planning
Project Planning is a systematic process that involves several key components, each playing a crucial role in ensuring the success of a Project. These components collectively form the blueprint for Project execution, guiding the Project team from initiation to completion. Here are the key components of Project Planning:
Project scope
Defining the Project scope is the first and foremost step in Project Planning. It involves clarifying what the Project will accomplish, its boundaries, and what it will not include. A well-defined scope prevents scope creep, ensuring the Project stays on track and within its intended parameters.
Project objectives
Project Planning sets clear, Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART) objectives. These objectives serve as the Project's goals and help align efforts toward a common purpose.
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
The WBS is a hierarchical breakdown of the Project into smaller, manageable tasks and activities. It provides a detailed view of the Project's components, helping in resource allocation and task assignment.
Resource allocation
Project Planning involves identifying and allocating the necessary resources, including human resources, budgets, materials, and equipment. Efficient resource allocation ensures that the Project has the required support to achieve its goals.
Project schedule
Creating a timeline or Project schedule is critical. This component outlines the sequence of tasks, their dependencies, and deadlines. Project Managers often use tools like Gantt charts to visualise and manage schedules effectively.
Risk assessment and mitigation
Identifying potential risks and uncertainties is essential. Project Planning includes a risk assessment that outlines the potential challenges and their impacts. Strategies for risk mitigation and contingency plans are developed to address these challenges.
Quality standards
Establishing and documenting quality standards ensures that Project deliverables meet the required level of quality. Quality planning outlines the criteria and metrics for measuring quality throughout the Project.
Communication plan
Effective Communication is vital for Project success. A communication plan defines how Project information will be disseminated, who the stakeholders are, and what channels and frequency will be used for communication.
Procurement plan
In Projects involving external suppliers or vendors, a procurement plan is developed. It outlines the procurement strategy, selection criteria for vendors, and the procurement process.
Change management
Project Planning includes provisions for Change Management. It addresses how changes to Project scope, objectives, or requirements will be managed, ensuring that changes are documented, evaluated, and approved before implementation.
Cost estimate and budget
Project Planning includes the estimation of Project costs and the creation of a detailed budget. This budget serves as a financial roadmap for the Project, guiding financial decisions throughout the Project lifecycle.
Stakeholder analysis
Identifying and analysing stakeholders is crucial for managing expectations and addressing their concerns. A stakeholder analysis helps in tailoring communication and engagement strategies for different stakeholder groups.
Legal and regulatory considerations
Depending on the Project's nature and location, there may be legal and regulatory requirements that need to be considered during planning. Compliance with these requirements is crucial to avoid legal issues.
Monitoring and evaluation
Project Planning should include mechanisms for monitoring and evaluating Project performance against the defined objectives and milestones. This component ensures that the Project stays on track and allows for adjustments as needed.
Identify and implement actions for stakeholders by signing up for our Creative Effective Stakeholder Engagement Training now!
Looking at the five phases of a Project’s life cycle
A Project life cycle is a structured framework that defines the phases a Project goes through, from initiation to completion. It typically includes stages like initiation, planning, execution, monitoring and controlling, and closure. Each phase has specific goals and tasks, ensuring organised and efficient Project Management. Here is each phase described in further detail as follows:
Initiation
The Project Initiation Phase marks the beginning of a Project’s life cycle. It's a critical step where the Project's feasibility, purpose, and objectives are defined. During this phase, key stakeholders identify the Project's scope, its potential benefits, and assess whether it aligns with the organisation's goals.
Furthermore, a Project Charter or initiation document is often created to outline the Project's key details, such as its objectives, scope, budget, and initial timeline. Additionally, the initiation phase involves appointing a Project Manager and assembling a Project team, setting the foundation for comprehensive planning and successful Project execution in subsequent phases.
Planning
The planning phase is the pivotal stage in the Project life cycle. This phase comprises of the detailed strategies that are developed to achieve Project objectives. It encompasses defining Project scope, setting clear goals, creating a comprehensive work breakdown structure (WBS), allocating resources, establishing timelines, and formulating Risk Management plans.
Furthermore, Project Managers and teams collaborate to produce a detailed Project Plan, including tasks, dependencies, and milestones. Budgets, quality standards, and Project Communication Plans are refined.
Moreover, this phase ensures that everyone involved understands their roles and responsibilities, laying a solid foundation for efficient Project execution. Effective planning minimises risks and increases the likelihood of on-time, on-budget Project completion.
Execution
The execution phase is where the Project Plan comes to life. It involves putting the meticulously crafted plans into action. Project teams carry out assigned tasks, utilising allocated resources and adhering to the established timelines.
Additionally, clear communication and collaboration among team members are crucial during this phase to ensure seamless progress. The Project Manager plays a pivotal role in coordinating efforts, monitoring progress, and addressing issues as they arise.
Furthermore, quality control measures are applied to maintain the Project's integrity, and any necessary changes are managed according to the change control process. Successful execution brings the Project closer to its objectives and delivers tangible results.
Monitoring and managing
The monitoring and managing phase is the stage where Project Managers and teams continuously track progress against the Project Plan. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), milestones, and quality standards are rigorously evaluated.
Moreover, any deviations from the plan are identified, and corrective actions are taken to keep the Project on course. Risk Management remains a focus, with proactive risk mitigation strategies applied as necessary.
Furthermore, communication with stakeholders is ongoing to provide updates and address concerns. This phase ensures that the Project remains aligned with its objectives, budgets, and timelines, allowing for effective Decision-making and the successful delivery of the Project.
Closure
The closure phase represents the culmination of the Project life cycle. It involves the systematic and organised closure of all Project activities. This includes verifying that all Project deliverables are met, finalising documentation, conducting a thorough review to ensure that Project objectives are achieved, and obtaining client or stakeholder acceptance.
Furthermore, financial and administrative closure tasks are executed, including settling outstanding bills, releasing Project resources, and archiving Project-related documents. Additionally, lessons learned are documented to facilitate future improvements.
Moreover, the closure phase ensures that the Project concludes smoothly, with all loose ends tied up, resources released, and stakeholders satisfied, marking a successful conclusion to the Project.
Learn the process of resourcing Project schedules by signing up for our Project Planning and Control Certification now!
The key tools you need for Project Planning
Effective Project Planning is crucial for business success, and having the right tools can greatly enhance the process. Here are key tools that businesses need for Project Planning:
a) Project Management software: This is the cornerstone of Project Planning. Tools like Microsoft Project, Asana, Trello, or Jira help teams create Project schedules, track progress, manage tasks, and collaborate efficiently. They provide a centralised platform for team communication and task management.
b) Gantt charts: Gantt Charts are visual tools that display Project tasks and their timelines in a bar chart format. They help Project Managers and teams visualise task dependencies and the overall Project Management Timeline, aiding in efficient scheduling and resource allocation.
c) Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) software: WBS software helps in creating and organising a hierarchical breakdown of Project tasks, allowing for a clear understanding of the Project's components and their relationships.
d) Communication tools: Collaboration and communication tools like Slack, Microsoft Teams, or Basecamp facilitate real-time communication among Project team members. They enable document sharing, instant messaging, and video conferencing, enhancing team collaboration regardless of location.
e) Risk Management software: Tools such as risk register software help in identifying, assessing, and managing Project risks. They assist in developing mitigation strategies and contingency plans to minimise the impact of potential issues.
f) Resource management software: These tools assist in allocating and managing Project resources efficiently. They provide insights into resource availability, workload, and allocation, preventing overallocation and ensuring optimal resource utilisation.
g) Financial and budgeting software: Financial tools help in creating Project budgets, tracking expenses, and managing financial resources. They allow for accurate cost estimation and control throughout the Project.
h) Document management systems: Systems like SharePoint or Google Workspace facilitate document storage, version control, and collaborative editing, ensuring that Project documentation is organised and accessible to all team members.
i) Risk analysis software: For complex Projects, specialised risk analysis software can help in modelling and simulating various scenarios to assess potential risks and their impact on the Project.
j) Reporting and analytics tools: Reporting tools like Tableau or Power BI enable Project managers to create and share performance dashboards and reports. These tools provide insights into Project progress, KPIs, and areas requiring attention.
k) Time tracking software: Time tracking tools help in monitoring the time spent on Project tasks and activities. This data is valuable for assessing productivity, estimating future Projects, and managing billable hours for client Projects.
l) Integration platforms: Integration tools like Zapier or Integromat can connect various software applications, automating data transfer and reducing manual data entry between different Project Management tools.
Learn to estimate Project durations by signing up for our Project Planning and Control™ (PPC) Foundation and Practitioner now!
Steps you can take to create an effective Project Plan
Creating an effective Project Plan is vital for achieving Project success. Here are five key steps to guide you through the process:
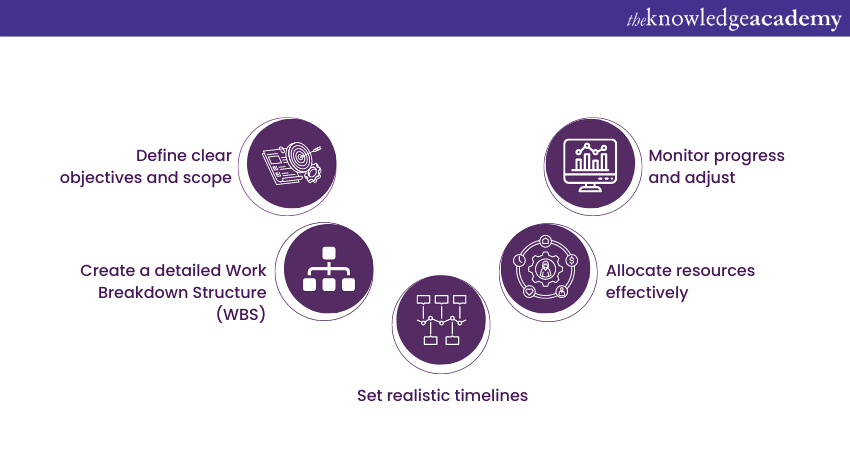
a) Define clear objectives and scope: Clearly articulate the project's objectives, goals, and deliverables. Define what the project will achieve and what it won't.
b) Create a detailed Work Breakdown Structure (WBS): Develop a hierarchical breakdown of all Project tasks and deliverables using a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS). This visual roadmap helps organise Project components, making them easier to manage and assign.
c) Set realistic timelines: Establish a Project schedule with clear timelines for each task and milestone. Use tools like Gantt charts to visualise dependencies and critical paths. Ensure that your timelines are achievable and consider potential constraints.
d) Allocate resources effectively: Identify the resources required for each task, including personnel, budgets, materials, and equipment. Efficient resource allocation prevents overburdening teams and helps maintain cost control.
d) Monitor progress and adjust: Regularly track Project progress against your plan. Implement a monitoring and controlling process to identify issues early and take corrective actions. Be prepared to adapt the plan when unforeseen challenges arise, maintaining flexibility and agility throughout the Project's lifecycle.
Conclusion
The Importance of Project Planning cannot be overstated. A well-crafted Project Plan serves as the guiding compass, minimising risks, optimising resources, and ensuring successful Project outcomes. By diligently following the steps outlined and utilising the right tools, businesses can navigate the complexities of Project Management and achieve their goals with confidence.
Handle risks during Project implementation by signing up for our Project Planning and Control™ Cours
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Project Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Project Planning and Control™ (PPC) Foundation
Project Planning and Control™ (PPC) Foundation
Mon 3rd Mar 2025
Tue 6th May 2025
Mon 14th Jul 2025
Mon 8th Sep 2025
Mon 10th Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


