We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +49 8000101090 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Modern organisations leverage user data to their advantage to improve efficiency and increase the revenue generated, and hence data resources are of paramount importance to the organisation. This importance of data has resulted in an increase in the need for information security, which has, in turn, resulted in a prevalence of information security standards such as ISO 27001. However, to comply with ISO 27001, one must file in an ISO 27001 Risk Assessment.
To gain compliance with ISO 27001, an organisation must fulfil a set of requirements as per the ISO 27001 Compliance Framework – one of which is filing in anISO 27001 Risk Assessment. However, not many organisations are aware of this standard. As per Statista, 21 per cent of all businesses and 57% of large businesses in the United Kingdom are aware of ISO 27001.If your organisation too wants to secure your user data but are unaware how, then this blog is for you. Read this blog to learn everything about an ISO 27001 Risk Assessment, including a step-by-step guide to the Risk Assessment procedure.
Table of Contents
1) What is ISO 27001 Risk Assessment?
2) Measures to take after ISO 27001 Risk Assessment
3) A step-by-step guide to the Risk Assessment procedure
4) Examples of Risk Treatment
5) Risk Management procedure for small or medium sized organisations
6) Conclusion
What is ISO 27001 Risk Assessment?
An ISO 27001 Risk Assessment helps organisations to assess and manage incidents that have the potential to harm their sensitive data. The process involves the identification of vulnerabilities that a cyber-criminal may exploit to their advantage or mistakes that employees could make. One then determines the level of risk and decides the best course of action to help prevent them from reoccurring and causing any further damage.
An ISO 27001 Risk Assessment finds, evaluates, and applies important application security measures. The assessment also focuses on preventing security flaws and vulnerabilities in applications. Risk Assessments are usually conducted across the whole organisation. Once the assessment has been conducted, compliance ISO 27001 Requirements helps an organisation to determine how to manage the risks based on its allocated resources and budget. These cover all the possible risks to which the information could be exposed, balanced against the likelihood of materialising risks and their potential impact on the organisation.
Risk Assessments are necessary for validating that your Information Security Management System (ISMS) can handle the potential risks adequately.
Measures to take after ISO 27001 Risk Assessment
Under ISO 27001, businesses must establish a series of measures to reduce recognised risks. ISO 27001 suggested measures comprising not just technological remedies but also human elements and organisational procedures. The Annex A of 27001 comprises 114 measures that span the spectrum of Information Security Management, consisting of areas such as regulating physical access, defining firewall policies, implementing security awareness initiatives for staff, establishing protocols for threat surveillance, managing incidents, and employing encryption. These measure listed in Annex A are categorised into 14 groups that are as follows:
a) Information security policies (A.5)
b) Organisation of information security (A.6)
c) Human resources security (A.7)
d) Asset management (A.8)
e) Access control (A.9)
f) Cryptography (A.10)
g) Physical and environmental security (A.11)
h) Operational security (A.12)
i) Communications security (A.13)
j) System acquisition, development, and maintenance (A.14)
k) Supplier relationships (A.15)
l) Information security incident management (A.16)
m) Information security aspects of business continuity management (A.17)
n) Compliance (A.18)
Risk Assessments are conducted comprehensively throughout the organisation, comprising all potential risks that could jeopardise information security. These assessments consider the likelihood of these risks manifesting and their potential impact. Subsequently, the organisation must determine how to manage and mitigate these risks, considering the available resources and budget allocation.
Want to elevate your organisation's cybersecurity practices? Make sure to register for our industry-leading ISO 27001 Training!
A step-by-step guide to the Risk Assessment procedure
Now that you know what an ISO 27001 Risk Assessment is, let's look at how you can create a Risk Assessment procedure. Though risks assessments can be challenging, the procedure can be simplified into the following six steps:
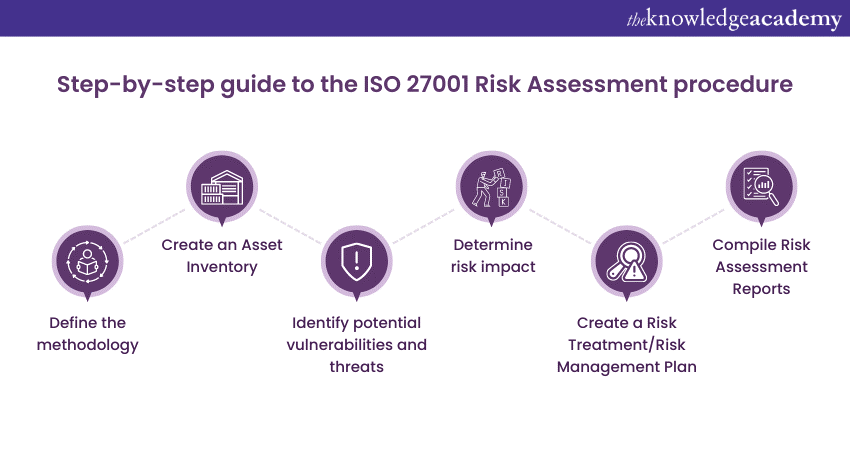
Define the methodology
As there is no standardised Risk Assessment methodology for ISO 27001, an organisation must define their methods clearly. To start, an organisation can review its unique profile by understanding the following:
1) The primary information security objectives that you aim to achieve with ISO 27001 Framework
2) Your organisation’s business, legal, and compliance obligations
3) The overall organisational goals and objectives
4) The stakeholders’ expectations and needs
One must determine whether to use a qualitative or a quantitative approach to assess risk. A qualitative approach to the assessment is subjective; it focuses on the identification of risks followed by the estimation of the risks’ likelihood of occurrence and potential impact.
On the other hand, a quantitative approach uses verifiable data to help analyse identified threats and assign a numerical value to them. One must use the method most relevant to their organisation’s unique information security goals.
Create an asset inventory
One can perform an ISO 27001 in one of two ways: one, focusing on assets (that is, the risk to information); and two, focusing on scenarios that may result in a data breach.
In a scenario-based Risk Assessment, users are more likely to identify risk situations, which often speeds up the risk identification process. However, the drawback is that users often need to catch up on some elements that might create risks. As a direct result, the risk identification process is incomplete and often results in a false (and often dangerous) sense of safety.
With the asset-based approach, the process of identification of relevant risks becomes more time-consuming. It also yields a complete review of risk posture – so this method should be considered. You should start by compiling their asset inventory, which should include their hardware, software, devices, information databases, removable devices, mobile devices and intellectual property. To compile the list, one must check with all the asset owners – the individuals responsible for controlling asset use, maintenance and security.
Identify potential vulnerabilities and threats
Next in the Risk Assessment procedure, you must identify and analyse the potential vulnerabilities and threats that might rise. Once you have the asset register, you must analyse the risk to each asset. Here's how you can assess vulnerabilities:
Firstly, any potential vulnerabilities – such as a weakness that a potential threat may exploit – must be identified. Then, you must make a list of the information assets across your organisation. These would include your software, hardware, databases, and intellectual property, only to name a few. Now you must identify the risks to every asset – risks that could impact on the confidentiality, integrity and availability of each listed asset.
Your threats and vulnerabilities for each asset could vary from unauthorised access to your database, stealing to inadequate data backup, and password management. It must be noted that the risks are subjective and dependent on the organisation’s scope of ISMS, its business type and operating environment. Any potential vulnerabilities must be identified – for example, a glitch or security vulnerability in a software or operating system can make your organisation vulnerable to any cyber criminals who could infiltrate your system and compromise your valuable information and data.
Determine risk impact
After you are done with identifying potential vulnerabilities and threats, it is time to analyse the risks that are associated with them. ISO 27001 Checklist does not define any specific way to analyse and score the risks, and hence it is essential to determine an organisation-wide standardised approach for the same. It must be noted that the risk analysis must be based on this pre-defined approach.
It must be noted that not all risks are equally severe – organisations may not want to implement extensive measures or controls to mitigate or eliminate risks that would cause little damage. This is why it is crucial to score risks based on the likelihood or probability of occurrence as well as the damage that they can cause.
You must create a Risk Assessment matrix based on different factors to compare risks, such as, risk against their risk appetite, and then identifyi and prioritisethe risks that require action.
Organisations can either analyse the identified risks by assigning a likelihood of occurrence and ranking its potential impact on a scale of 1 to 10, or from Low to Medium to High. You must also examine how the Confidentiality, Integrity and Availability of data (the “CIA” triad) could potentially be affected by every risk.
One must also consider different implications of every threat, including the legal, organisational, contractual and regulatory implications. To get going with the determination of risk impact, youcan ask questions like:
1) What may be the cost of replacing a compromised asset?
2) What is the potential for financial loss from a particular risk (such as lost income, fines and so forth)?
3) Could a security incident damage or hinder our reputation?
Create a Risk Treatment/Risk Management plan
Now that you have analysed the risks and assigned a potential impact to each of them, the next step of the process requires you to determine the way to treat every risk that has been identified. The risk treatment plan, in short, documents your responses to all the threats, vulnerabilities and risks that you have identified in your Risk Assessment.
A Risk Treatment Plan typically includes the following elements:
a) Risk identification: You need to include the identified vulnerabilities.
b) Risk analysis: Add information related to the risk's prevalence and severity. This is often expressed as a statement number or range.
c) Risk treatment options: You need to provide a strategy for every risk (dodge, reduce, shift or bear).
d) Selected controls: You must explain who will be responsible for controlling which risk.
e) Responsibilities: You must assign individuals who will work on design, and who will take the lead in each control.
f) Timeline: You need to set deadlines to implement these controls.
g) Budget/Resources: Establish adequate protection, considering funding, employees, and technology resources.
h) Monitoring and review plan: Establish a time when the plan is to be reviewed and its effectiveness will be evaluated.
Compile Risk Assessment reports
As the next step in the procedure, you must prepare reports about your findings and implement an appropriate action plan for ISO 27001 Audit and certification. You must prepare the following reports:
1) A Statement of Applicability: A Statement of Applicability must be prepared. This statement must document the various ISO 27001 controls that you will be implementing in order to tackle the identified risks. Every single control must have its own entry, and you should also explain why any controls were omitted.
2) A Risk Treatment Plan: A Risk Treatment Plan must also be prepared, which provides a comprehensive summary of each identified risk, the proposed actions to deal with each risk as well as all the parties responsible.
The certification auditor who oversees your ISO 27001 effort will use these reports as guidelines.
Want to gain the expertise to lead and conduct successful ISO 27001 audit? Sign up for our ISO 27001 Lead Auditor Course today!
Examples of Risk Treatment
The following are some examples of to treat a risk properly:
1) Example 1 - Treating unauthorised access to customer data
a) Risk: Unauthorised entry to customer data.
b) Threat: Malicious hackers.
c) Vulnerability: Inadequate password policy.
d) Impact: Financial ramifications and harm to reputation.
e) Treatment: Implement a robust password policy, mandating that users create passwords with a minimum length of 12 characters. The password should, comprise a blend of uppercase and lowercase letters, digits, and special symbols.
This risk mitigation strategy proves effective by addressing the fundamental issue, which is the weak password policy. By adopting a strong password policy, the organisation can heighten the challenge for malevolent hackers attempting to gain unauthorised access to customer data.
2) Example 2 - Treating data loss due to fire
a) Risk: Potential data loss caused by a fire.
b) Threat: Fire incidents.
c) Vulnerability: Absence of a fire suppression system.
d) Impact: Financial losses, harm to reputation, and disruption of business operations.
e) Treatment: Installation of a fire suppression system within the server room.
In this case, the Risk Treatment focuses on mitigating the risk of data loss in the event of a fire by proactively addressing the vulnerability.
Risk Management procedure for small or medium sized organisations
Smaller organisations undertaking ISO 27001 implementation projects often face challenges when adapting Risk Management procedures, which may be primarily designed for larger enterprises. To simplify Risk Management for small organisations, consider the following recommendations:
a) Choose the right framework: It is essential that you include all the five essential components that are required by ISO 27001.
b) Select the appropriate tool: Seek software or tools that align with your simplified approach. In some cases, a well-designed Excel template can be more effective than complex software solutions.
c) Involve relevant stakeholders: Avoid tackling Risk Management in isolation. Engage departmental leaders from all areas of your organisation since they possess valuable insights into their processes and potential challenges.
d) Embrace imperfection: Instead of striving for absolute perfection in identifying all risks initially, focus on completing your initial Risk Assessment and treatment. Later, revisit the process to incorporate any overlooked hazards.
Conclusion
We hope that from this blog you understood the importance of ISO 27001 Risk Assessment and how it can help an organisation identify any risk that may cause any major fatality in the future. This blog also discussed how by creating the Risk Treatment plan you can not only avoid major casualties, but also improve your organisation’s information security.
Take the first step towards securing your organisation's information with our comprehensive ISO 27001 Foundation course – Register now!
Frequently Asked Questions

ISO 27001's risk assessment is specific to information security within an Information Security Management System, focusing on confidentiality, integrity, and availability, requiring periodic ISMS reviews, distinguishing it from broader risk management frameworks.

Under ISO 27001, Risk Assessments should be conducted at regular intervals or when significant changes occur that could affect information security. This ensures the ISMS remains effective and responsive to new threats, aligning with the organization's evolving security posture and compliance requirements.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various ISO 27001 Training, including ISO 27001 Foundation Course, ISO 27001 Lead Auditor Course and ISO 27001 Internal Auditor Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into ISO 27001.
Our ISO & Compliance Blogs cover a range of topics related to ISO 27001 offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your knowledge on Information Security, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 ISO 27001 Foundation
ISO 27001 Foundation
Mon 27th Jan 2025
Tue 22nd Apr 2025
Mon 28th Jul 2025
Mon 27th Oct 2025
Mon 15th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


