We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +49 8000101090 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Imagine trying to manage a big change in your organisation—like launching a new service or improving public systems. It can feel overwhelming, right? That’s where Managing Successful Programmes helps. MSP is a simple and clear way to handle large changes by breaking them into manageable parts. It keeps everything organised, on track, and focused on real results. Understanding MSP Roles and Responsibilities is crucial to fully grasp how MSP functions. Additionally, being aware of its key elements and benefits further enhances this understanding. A Technical Programme Manager may play an important role in MSP by overseeing technical projects that align with the broader programme strategy and ensuring the delivery of technical solutions within the programme scope.
Whether you are leading a team or planning major updates, MSP gives you the tools and steps to succeed. In this blog, we will discuss what Managing Successful Programmes is, why it matters, and how it can help your organisation reach its goals. Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
1) What is Managing Successful Programmes?
2) Why Use MSP?
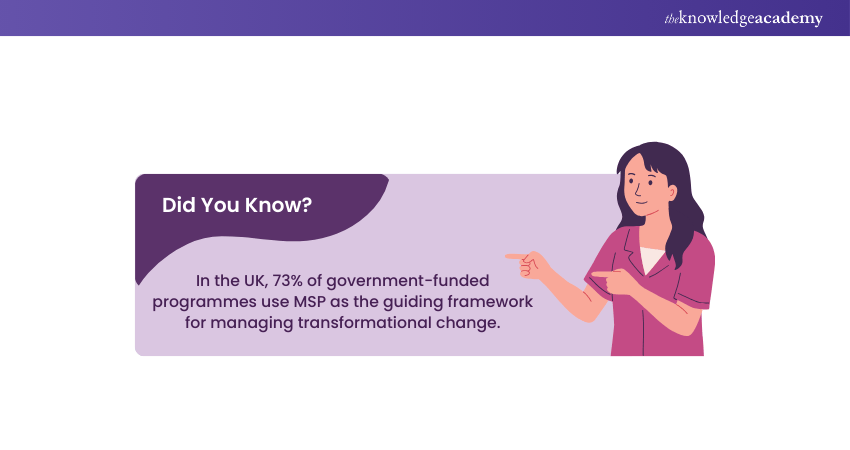
3) How Does MSP Work?
4) Managing Successful Programmes Framework
5) Conclusion
What is Managing Successful Programmes?
Managing Successful Programmes is a best-practice framework used to manage and deliver large and complex change through multiple related projects. It helps organisations break down big changes into smaller parts, making it easier to plan, control, and deliver results. MSP gives a clear structure and roles to help ensure success.
For example, a government wants to improve public transport across a city. Instead of doing everything in one go, they split the work into smaller projects—new buses, updated train services, and better ticketing systems. MSP helps manage all these projects together, making sure they stay on track, support each other, and meet the overall goal. It allows leaders to handle risks, monitor progress, and adapt when needed to ensure the programme succeeds.
Key Components
The key elements of MSP include:

1) Programme Governance: MSP emphasises the need for effective programme governance structures that define roles, responsibilities, and decision-making processes. This ensures the programme remains on track, aligned with strategic objectives, and delivers the intended benefits.
2) Vision: A clear programme vision statement is essential in MSP. It sets out the programme's desired outcomes, benefits, and strategic alignment. The vision is a guiding principle, providing a shared understanding and direction for all stakeholders.
3) Blueprint Design: MSP involves developing a blueprint or roadmap that outlines the programme's activities, projects, and dependencies. MSP blueprint serves as a comprehensive plan, guiding the programme's implementation and ensuring that all projects work together towards achieving the desired outcomes.
4) Benefits Realisation: MSP places significant emphasis on benefits realisation. It involves identifying, tracking, and measuring the expected benefits of the programme. By actively managing benefits throughout the programme's lifecycle, organisations can ensure that the desired value is achieved.
5) Risk Management: Effective MSP Risk Management is vital for a programme. Programmes often face uncertainties and potential challenges that can hinder success. MSP incorporates risk management processes to identify, assess, and mitigate risks, ensuring they are proactively managed to minimise their impact on the programme's objectives.
6) Stakeholder Engagement: Engaging stakeholders is crucial in MSP. It involves identifying and involving individuals or groups affected by the programme. MSP emphasises the need for effective communication, collaboration, and managing stakeholder expectations to gain their support and ensure programme success.
Why Use MSP?
Here are the main reasons why organisations choose to use MSP for managing change and improvement:

1) Structured Approach: MSP provides a clear methodology for managing programmes, ensuring that all projects are coordinated and contribute to the overall strategic goals.
2) Benefit Realisation: The framework emphasises identifying, tracking, and realising benefits throughout the programme lifecycle, ensuring that the intended value is delivered.
3) Risk Management: MSP incorporates robust risk management processes, enabling organisations to identify, assess, and mitigate risks that could impact programme success.
4) Stakeholder Engagement: Effective stakeholder communication and engagement are key to MSP, ensuring their needs and expectations are consistently managed.
Learn to navigate complex projects with our MSP® Practitioner Course – Join today!
How Does MSP Work?
Here are the key steps that show how MSP works:
a) Breaks big changes into smaller, manageable parts called projects
b) Focuses on delivering benefits and value throughout the programme
c) Uses clear roles and responsibilities to keep everyone on track
d) Follows a structured process from start to finish
e) Keeps risks and problems under control with proper planning
f) Encourages learning and improvement as the programme moves forward
g) Allows teams to stay aligned with business goals and long-term success
h) Involves key people at every stage to ensure the programme runs smoothly
i) Makes sure each project supports the overall programme goals
Learn to handle change initiatives with our MSP® Foundation Course – Join today!
Managing Successful Programmes Framework
Here are the three main parts of the MSP framework that help manage change and deliver strong results:
Principles
The MSP principles are the basic rules that guide every programme. They are based on real experiences and lessons from past projects. These principles help teams stay focused, make good choices, and learn along the way. Every programme using MSP should follow these principles to succeed.
a) Based on real project experiences
b) Helps teams stay on track
c) Encourages learning and improvement
d) Builds a strong foundation for decision-making
e) Supports better programme outcomes
Governance Themes
This provides a structure for managing people, resources, and risks. They make sure everyone knows their roles and what needs to be done. These themes support strong leadership and clear decision-making. They help keep the programme safe, organised, and effective.
a) Sets rules for how things are done
b) Defines roles and responsibilities
c) Supports strong leadership
d) Ensures resources are used wisely
e) Helps avoid confusion and delays
Transformational Flow
This shows the step-by-step journey of the programme. It starts with planning and moves through delivery to closing. This flow helps manage change smoothly and in the right order. It ensures that the programme moves forward with clear goals and steady progress.
a) Guides the programme from start to end
b) Helps manage each stage of change
c) Supports clear planning and delivery
d) Keeps the team focused at each step
e) Makes tracking progress easier
Conclusion
Managing Successful Programmes helps organisations manage complex change by breaking big goals into manageable parts. It improves planning, clarifies roles, and keeps teams aligned. By using MSP, you can deliver change more confidently, reduce confusion, and achieve better results. Start using MSP to make your projects smoother, smarter, and more successful.
Learn to manage programme transformations with our MSP® Foundation & Practitioner Course – Join today!
Frequently Asked Questions
How to Pass the MSP Practitioner Exam?

To pass the MSP Practitioner exam, study the MSP guide and understand each part well. Practise using sample questions to get used to the exam format. Focus on how MSP is used in real projects to answer questions better.
What is the Difference Between PMP and MSP?

PMP is about managing single projects from start to end. MSP is used to manage multiple projects as one programme to deliver bigger change. PMP focuses on tasks and timelines, while MSP focuses on benefits and long-term goals.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various MSP® Training, including MSP® Foundation & Practitioner Course, MSP® Foundation Course, and MSP® Practitioner Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into MSP Process.
Our Project Management Blogs cover a range of topics related to MSP, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Project Management knowledge, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Project Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 MSP® Foundation & Practitioner
MSP® Foundation & Practitioner
Mon 28th Apr 2025
Tue 6th May 2025
Mon 12th May 2025
Mon 19th May 2025
Tue 27th May 2025
Mon 2nd Jun 2025
Sat 7th Jun 2025, Sun 8th Jun 2025
Mon 9th Jun 2025
Mon 16th Jun 2025
Mon 23rd Jun 2025
Mon 30th Jun 2025
Mon 7th Jul 2025
Mon 14th Jul 2025
Mon 21st Jul 2025
Mon 28th Jul 2025
Sat 2nd Aug 2025, Sun 3rd Aug 2025
Mon 4th Aug 2025
Mon 11th Aug 2025
Mon 18th Aug 2025
Tue 26th Aug 2025
Mon 1st Sep 2025
Mon 8th Sep 2025
Mon 15th Sep 2025
Mon 22nd Sep 2025
Mon 29th Sep 2025
Sat 4th Oct 2025, Sun 5th Oct 2025
Mon 6th Oct 2025
Mon 13th Oct 2025
Mon 20th Oct 2025
Mon 27th Oct 2025
Mon 3rd Nov 2025
Mon 10th Nov 2025
Mon 17th Nov 2025
Mon 24th Nov 2025
Mon 1st Dec 2025
Sat 6th Dec 2025, Sun 7th Dec 2025
Mon 8th Dec 2025
Mon 15th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


