We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +45 89870423 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

In today’s digital age, data is a priceless asset for any organisation. Cyber Security plays a crucial role in safeguarding this sensitive information. Equally important is Cyber Resilience, which not only helps maintain trust with customers and partners but also ensures compliance with data protection regulations.
By enhancing Cyber Resilience, organisations can rebuild trust with customers and stakeholders following any incidents. In this blog, we’ll guide you through the essential steps to Improve Cyber Resilience, along with the Cyber Security strategies and technologies that can help you achieve this goal.
Table of contents
1) What is Cyber Resilience?
2) Importance of Cyber Resilience
3) The Pillars of Cyber Resilience
4) Developing a Cyber Resilience Strategy
5) Technologies for Enhancing Cyber Resilience
6) Implementing and Monitoring Cyber Resilience
7) Fostering a Cyber-Resilient Organisation
8) Case studies: Real-world Examples
9) Conclusion
What is Cyber Resilience?
Cyber Resilience is a proactive approach that helps organisations handle and reduce cyber risks. Instead of just trying to block attacks, it focuses on staying prepared to keep things running and recover quickly if an attack does happen. While Cyber Security aims to prevent threats, Cyber Resilience works on the idea that some attacks are unavoidable.
This approach includes having plans for responding to incidents, ensuring business can continue, managing risks, and training employees. By focusing on resilience, companies strengthen their ability to respond to threats, recover from incidents, and create a culture where everyone understands and helps with cyber safety.

Types of Cyber Threats
Before we explore how to Improve Cyber Resilience, we will look into different Types of Cyber Security Breaches and threats. Cyber threats consist of various forms of malicious activities that can compromise digital systems and data. These include:
a) Malware: Malicious software designed to enter and damage computer systems. Examples include viruses, worms, and ransomware.
b) Phishing: Deceptive emails or messages used to trick individuals into revealing sensitive and important information, such as passwords or financial details.
c) Cyber-espionage: Covert activities conducted by nation-states or entities to gather sensitive information or disrupt foreign systems.
d) Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks: In this cyber-attack, overwhelming a system with traffic makes it inaccessible to users.
e) Insider Threats: Attacks or data breaches originating from within an organisation, often perpetrated by employees or contractors.
f) Zero-day Exploits: Vulnerabilities in software or hardware unknown to the vendor, making them difficult to defend against.
g) Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): Long-term cyber-attacks by well-funded and organised adversaries, often targeting high-value assets.
h) Social Engineering: Manipulating individuals through psychological tactics to gain unauthorised access or information.
i) Supply Chain Attacks: Targeting vulnerabilities in an organisation's suppliers or partners to compromise the main target.
j) IoT Vulnerabilities: Security weaknesses in Internet of Things (IoT) devices that can be exploited for cyber-attacks.
Importance of Cyber Resilience
Cyber resilience is essential for ensuring that organisations can withstand, adapt to, and quickly recover from cyber incidents in today’s high-risk digital landscape.
1) Continuous Operations: Ensures that organisations can maintain essential functions even during and after a cyber incident.
2) Minimises Financial Loss: Reduces potential costs associated with data breaches, operational downtime, and recovery efforts.
3) Protects Reputation: Safeguards the organisation's reputation by ensuring quick recovery and minimal impact on customers and stakeholders.
4) Builds Trust: Enhances digital trust with clients, partners, and stakeholders by demonstrating strong security and response capabilities.
5) Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Helps organisations meet regulatory requirements related to data protection and cyber incident response.
6) Adapts to Evolving Threats: Prepares organisations for new and evolving cyber threats, helping them stay resilient in a constantly changing landscape.
7) Competitive Advantage: Provides a strategic edge, allowing businesses to grow and innovate securely in a digital environment.
8) Boosts Employee Confidence: Introduce a culture of security awareness and preparedness among employees, contributing to overall resilience.
The Pillars of Cyber Resilience
Let us now understand the four pillars of Cyber Resilience:
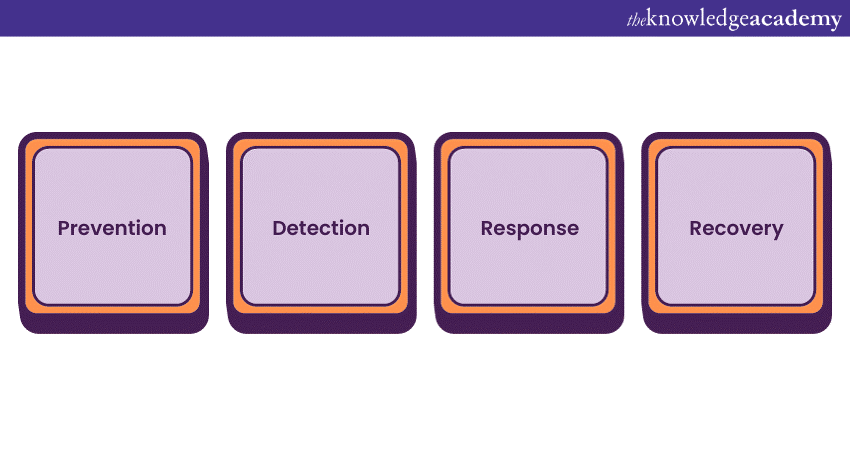
a) Prevention: The proactive measures taken to reduce vulnerabilities and prevent cyber-attacks. Prevention includes installing security software, regularly patching software, and configuring systems securely.
b) Detection: The ability to identify cyber threats and incidents as they occur. Detection relies on real-time monitoring, intrusion detection systems, and threat intelligence to recognise and alert about suspicious activities.
c) Response: The well-defined actions are taken when a cyber incident is detected. An effective response plan includes incident triage, containment, eradication, and recovery to minimise damage and prevent further compromise.
d) Recovery: The process of restoring normal operations after a cyber incident. Recovery includes data restoration, system cleanup, and continuous monitoring to ensure that vulnerabilities are addressed to prevent future incidents.
Developing a Cyber Resilience Strategy
Developing a Cyber Resilience strategy involves creating a comprehensive framework that prepares an organisation to withstand, respond to, and recover from cyber incidents.
a) Comprehensive framework: Prepares an organisation to withstand, respond to, and recover from cyber incidents.
b) Thorough risk assessment: Identifies vulnerabilities and prioritises critical assets that require protection.
c) Multi-layered security measures: Minimises entry points for potential threats.
d) Clear incident response protocol: Enables teams to act swiftly and effectively when a breach occurs.
e) Regular training and awareness programs: Empowers employees to recognise and avoid cyber risks.
f) Continuous monitoring: Ensures real-time threat detection.
g) Well-defined recovery plan: Ensures systems can be restored quickly, minimising disruption and financial impact.
h) Proactive, end-to-end approach: Protects assets, builds digital trust, and maintains continuity even in the face of unforeseen challenges.
Strategies to Improve Cyber Resilience
A strong Cyber Resilience strategy aims to achieve several key objectives:
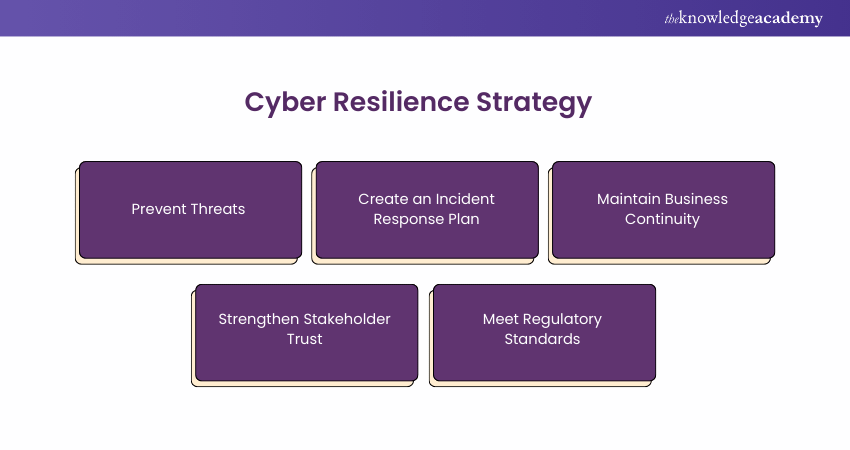
1) Prevent Threats: Actively identify and address cyber threats before they can take benefit of vulnerabilities in your system.
2) Create an Incident Response Plan: Establish a clear, structured plan to quickly detect, contain, and manage any cyber incidents that occur.
3) Maintain Business Continuity: Put fast, effective backup and recovery processes in place to ensure that operations continue smoothly, even in the face of a cyberattack.
4) Strengthen Stakeholder Trust: Show your dedication to Cyber Security and resilience, building confidence among customers, partners, and stakeholders.
5) Meet Regulatory Standards: Ensure your strategy aligns with regulations and standards of the industry to protect sensitive information and avoid possible legal and financial penalties.
By focusing on these goals, organisations can enhance their readiness and resilience, preparing for both the prevention of threats and effective responses when they occur.
Technologies for Enhancing Cyber Resilience
Technology plays a pivotal role in strengthening Cyber Resilience. From endpoint protection to security automation, we will shed light on the tools you can use to improve Cybersecurity.
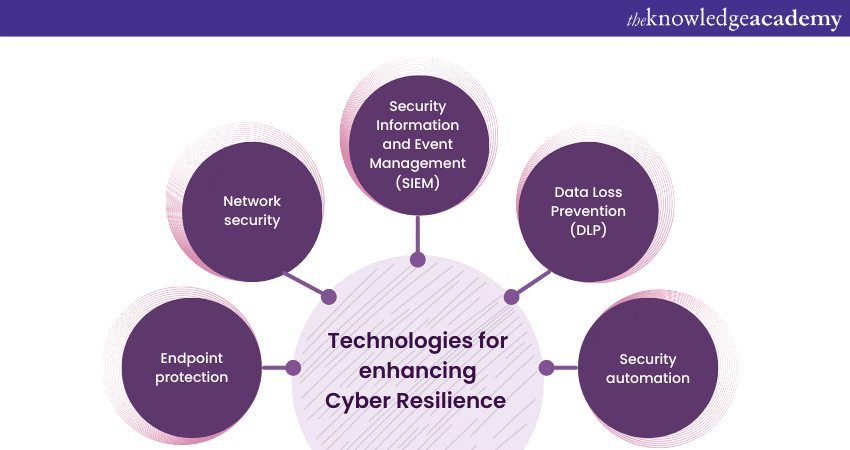
a) Endpoint Protection: Utilise endpoint security solutions to safeguard individual devices.
b) Network Security: Establish a strong network security infrastructure to prevent unauthorised access.
c) Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Incorporate SIEM systems for real-time analysis of security alerts.
d) Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Use DLP solutions to prevent unauthorised data disclosure.
e) Security Automation: Implement automation to accelerate response times and reduce human error.
Implementing and Monitoring Cyber Resilience
Implementing and monitoring Cyber Resilience involves putting in place the necessary tools, policies, and procedures to protect, detect, respond to, and recover from cyber threats while continuously assessing their effectiveness.
Once a Cyber Resilience strategy is developed, organisations need to deploy technology solutions such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and endpoint protection to safeguard their digital infrastructure.
Regular training for employees fosters a security-aware culture, equipping them to identify and respond to potential threats. Monitoring is equally crucial, as it provides real-time insights into network activity and alerts the organisation to any suspicious behaviour.
How to Measure Cyber Resilience?
Effective Cyber Resilience involves smoothly managing cyber incidents and bouncing back quickly. Here are a few key metrics to gauge your resilience:
1) Mean Time to Detect (MTTD): This measures how quickly you can recognise something unusual like a vulnerability being exploited or suspicious activity on a system.
2) Mean Time to Respond (MTTR): After detecting an issue, this metric tracks how swiftly you act, whether it’s removing malware from a device or restoring lost data.
3) Recovery Time Objective (RTO): If a cyber incident disrupts operations, RTO sets the target time for restoring normalcy. It reflects how fast you aim to get systems back up and running.
Keeping detailed logs is also crucial. Track how often incidents occur, how well your responses worked, and if your plan effectively prevented further harm. This helps assess the strength of your strategy, revealing any areas for improvement.
Continuous Improvement and Adaptation
Cyber threats evolve relentlessly, demanding constant adaptation. Let us delve into the importance of continuous improvement and adaptation, exploring the role of Cyber Resilience.
a) The Role of Cyber Resilience Frameworks: Cyber Resilience frameworks like NIST Cybersecurity Framework or ISO 27001 provide guidelines for continually assessing and improving Cybersecurity measures.
b) Compliance and Regulation: Adhering to industry regulations and standards ensures a basic level of Cyber Resilience, with regular updates to stay compliant.
c) Incident Post-mortems: After a cyber incident, conducting post-mortem analysis helps identify vulnerabilities and areas for improvement, contributing to ongoing adaptation.
d) Threat Intelligence Integration: Constantly monitoring threat intelligence sources helps organisations stay ahead of new threats and adapt their defences accordingly.
Fostering a Cyber-Resilient Organisation
Fostering a cyber-resilient organisation requires a culture where Cyber Security is integrated into every level of operations, from executive decision-making to daily tasks. It starts with strong leadership commitment to prioritise Cyber Resilience as a strategic business goal, ensuring that adequate resources and budget are allocated to safeguard critical assets.
Empowering employees through regular Cyber Security training and awareness programs helps cultivate a proactive workforce that can recognise and mitigate potential threats. Implementing layered security protocols and investing in cutting-edge technology for real-time threat detection are also essential components.
Additionally, fostering a mindset of resilience involves not only defensive measures but also a robust incident response and recovery plan, enabling rapid restoration of operations after an attack. By embedding Cyber Security into its core values, an organisation can build trust, reduce risk, and maintain a competitive edge in an increasingly digital world.
Building a Cyber-Resilient Culture
Creating a culture of Cyber Resilience is as essential as implementing technological defences. Let’s understand the critical role of nurturing a learning culture in boosting your organisation's Cyber Resilience.
a) Leadership Commitment: When leaders prioritise and champion Cybersecurity, it sets the tone for the whole organisation, demonstrating the importance of Cyber Resilience.
b) Employee Involvement: Engaging all employees in Cybersecurity efforts fosters a sense of collective responsibility for the organisation's digital safety.
c) Encouraging a Learning Culture: Promoting continuous learning and adaptation encourages employees to stay updated on the latest Cybersecurity best practices and threats, thus contributing to a resilient culture.
Elevate your Cyber Resilience skills with our RESILIA Training and secure your digital future now!
Assess Your Personal Cyber Resilience
Although Cyber Resilience is often discussed as an organisational strategy, reflecting on your own Cyber Resilience can be a valuable exercise. This can serve as a starting point for strengthening the digital security of your business, nonprofit, school, or any group you’re involved with.
Begin by assessing your personal digital habits, security practices, and awareness of potential threats. Consider asking yourself:
1) Do I use passwords that are long, complex, and unique for each account?
2) Is multi-factor authentication (MFA) enabled on all my accounts?
3) Do I consistently update my software to stay protected?
4) Am I cautious about avoiding suspicious links or unverified downloads?
5) Do I back up important data regularly and understand how to recover it if needed?
These questions can help you access your current Cyber Security practices and highlight areas where you could improve.
Case Studies : Real-world Examples
In this section of the blog, we will examine notable Cyber Security Incidents which highlight the need for strengthening Cybersecurity. These stories provide practical lessons and inspiration for your Cyber Resilience journey.
a) Sony Pictures Hack (2014): The cyber-attack on Sony Pictures Entertainment in 2014 highlighted the importance of robust incident response plans. Sony's experience demonstrated that even large corporations can fall victim to cyber-attacks, underlining the need for swift and coordinated responses.
b) WannaCry Ransomware Attack (2017): WannaCry infected hundreds of thousands of computers worldwide in 2017. This case showcased the significance of regularly updating software and patch management as a crucial part of Cyber Resilience.
c) Equifax Data Breach (2017): The Equifax data breach in 2017 emphasised the criticality of protecting sensitive customer data. It revealed the extensive financial and reputational damage that can result from a security incident, urging organisations to prioritise data protection.
d) SolarWinds Cyber-attack (2020): The SolarWinds attack, attributed to nation-state actors, demonstrated the sophistication of modern cyber threats. It underscored the need for robust supply chain security and ongoing threat monitoring.
e) Colonial Pipeline Ransomware Attack (2021): This incident disrupted fuel supplies along the U.S. East Coast, illustrating the real-world consequences of cyber-attacks on critical infrastructure. It emphasised the need for resilience measures in essential sectors.
Enhance your Cyber Resilience knowledge with RESILIA Foundation Training - strengthen your digital defences today!
Conclusion
Data loss can have long-lasting repercussions. When you Improve Cyber Resilience, it serves as a safeguard against data loss, ensuring the preservation and accessibility of vital information. In the unfortunate event of a cyber-attack or data breach, these measures are pivotal in mitigating damage, such as financial losses or unwanted loss of sensitive data.
Take the next step in mastering Cyber Resilience with RESILIA Practitioner Training - empower your Cybersecurity expertise today!
Frequently Asked Questions

To build Cyber Security resilience, focus on proactive threat detection, incident response planning, business continuity, employee training, regular updates, data backups, and compliance with industry standards. This holistic approach strengthens defence and recovery.

The seven steps are: 1) Identify critical assets, 2) Detect threats early, 3) Protect systems, 4) Respond to incidents, 5) Recover operations quickly, 6) Educate employees, and 7) Continuously improve based on incidents and feedback.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various RESILIA® Training, including the RESILIA® Foundation and Practitioner Course and RESILIA® Foundation Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into the What is Cyber Resilience.
Our IT Security & Data Protection Blogs cover a range of topics related to Cyber Resilience, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Cyber Security skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 RESILIA® Foundation and Practitioner
RESILIA® Foundation and Practitioner
Mon 3rd Feb 2025
Tue 6th May 2025
Mon 28th Jul 2025
Mon 20th Oct 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


