We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on + 1-866 272 8822 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Have you ever pondered the intricate world of Software Testing and Software Tester Roles and Responsibilities? It's not just about running tests and finding bugs. In this dynamic realm, every role, from junior testers to seasoned Managers, shapes software quality and reliability. But what exactly do these roles include?
Let's explore the world of Software Testing, where every role, big or small, plays a vital role in crafting Software that works seamlessly. We'll explore the ins and outs of Software Tester Roles and Responsibilities, uncovering what it takes to excel in this fast-paced and ever-changing industry.
Table of Contents
1) Software Tester Roles and Responsibilities
2) Critical skills for hiring Software Testers
3) Advantages of Software Testing
4) Disadvantages of Software Testing
5) Conclusion
Software Tester Roles and Responsibilities
Listed below are the key aspects of Software Tester Roles and Responsibilities. Let’s have a look:
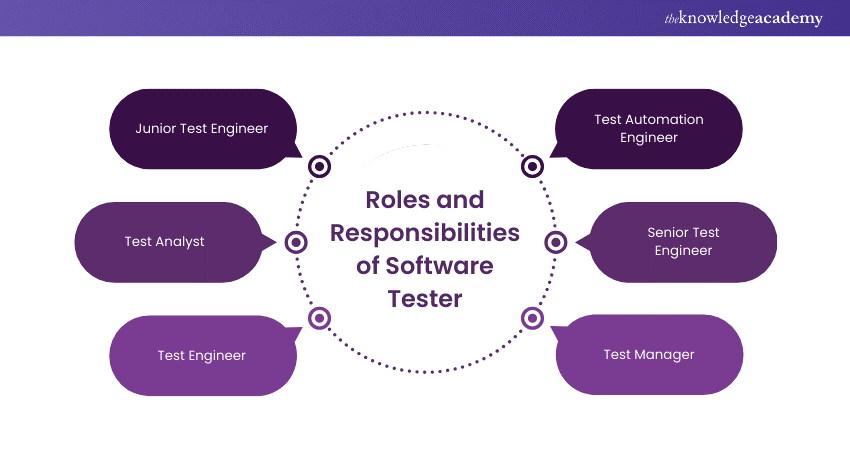
1) Junior Test Engineer
Junior Test Engineers generally work under the guidance of senior members of the testing team. Their primary role involves carrying out test cases, recording the outcomes of these tests, and pinpointing any issues or defects that arise during testing. Additionally, they might be involved in the initial phases of test planning and offer insights to improve testing procedures. Overall, they support the senior members in ensuring the quality and effectiveness of the testing process.
2) Test Analyst
Test Analysts are responsible for analysing software requirements, designing test cases, and executing tests to ensure that software products meet specified requirements. They also play a crucial role in identifying defects and collaborating with development teams to resolve issues.
3) Test Engineer
Test Engineers are involved in the design, development, and execution of test cases to evaluate the functionality and performance of software applications. They work closely with developers to understand product requirements and ensure comprehensive test coverage.
4) Test Automation Engineer
Test Automation Engineers specialise in developing automated test scripts and frameworks to streamline the testing process and improve efficiency. They are proficient in scripting languages and automation tools and play a crucial role in continuous integration and delivery pipelines.
Unlock your potential with ISTQB Software Testing certification! Gain recognized skills and advance your career in software testing today!
5) Senior Test Engineer
Senior Test Engineers lead testing efforts, develop test strategies, and mentor junior members of the testing team. They possess extensive knowledge of testing methodologies and tools and are responsible for ensuring the overall quality of software products.
6) Test Manager
Test Managers oversee testing activities, allocate resources, and define testing strategies to meet project objectives. They collaborate with stakeholders to prioritise testing efforts and ensure that testing processes align with project timelines and goals.
Unlock your potential with ISTQB Software Testing Foundation Training and certification. Join now to boost your career in Software Testing!
Critical skills for hiring Software Testers
Here are the essential attributes required to recruit top-notch Software Testers. Skim through the following to learn more about it:

1) Automation tests
Automation tests, facilitated by mastery of test automation tools and frameworks, streamline testing processes and broaden test coverage. They expedite repetitive test execution, relieving testers of manual tasks to focus on complex scenarios. This accelerates testing cycles, ensuring thorough examination of critical software aspects for higher-quality releases.
2) Understanding of Agile and DevOps methodologies
Testers need a strong understanding of Agile and DevOps methodologies to collaborate effectively with development teams. This involves active participation in sprint planning and stand-up meetings, as well as seamless integration of testing into the continuous delivery pipeline. By aligning with Agile and DevOps principles, testers promote collaboration and rapid delivery of quality software.
3) Familiarity with Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
Testers must grasp the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) phases, encompassing requirements analysis, design, implementation, testing, and maintenance. Understanding testing alignment with each phase ensures comprehensive coverage and early defect detection. This knowledge fosters collaboration with developers and stakeholders, facilitating smoother project execution and delivery of high-quality software products.
4) Effective communication skills
Effective communication skills are vital for testers to engage with team members, stakeholders, and clients proficiently. Clear and concise communication ensures accurate transmission of testing status, defect reports, and resolutions. This fosters collaboration and alignment among project stakeholders, facilitating smoother project execution.
Testers need to convey complex technical information in a manner understandable to non-technical stakeholders, fostering transparency and trust in the testing process. Strong communication abilities enable testers to articulate testing strategies, discuss findings, and address concerns promptly.
Dive into essential software testing principles to ensure top-notch product quality. Build your expertise and enhance software reliability today!
5) Test preparation abilities
Testers need the capability to craft thorough test plans, cases, and scenarios aligned with software requirements and user stories. This entails a deep understanding of the application's functionality and goals, enabling testers to define precise test objectives. They must design test cases encompassing diverse usage scenarios and edge cases to ensure robust software validation.
This rigorous method ensures thorough test coverage and assists in identifying possible problems early in the development phase. Testers significantly enhance the overall quality of the product by contributing to the software's reliability and customer satisfaction through rigorous testing planning.
6) Logical and rational thinking
Logical and rational thinking are essential attributes for Software Testers. They entail the ability to methodically analyse intricate systems, discern potential risks, and devise effective test strategies. Testers must critically evaluate software requirements to ensure they align with system functionalities.
Understanding how various components interact within the system aids in identifying vulnerabilities and potential failure points. By formulating comprehensive test strategies, testers can proactively mitigate risks and uphold the overall quality of the software product. This approach fosters a systematic and thorough testing process, eventually improving the performance and dependability of the software.
Explore Software Tester Salary: Know Your Worth Today!
Advantages of Software Testing
Software testing offers several advantages, including:
1) Identification of defects and issues before software deployment.
2) Assurance of software quality and reliability.
3) Validation of software functionality and compliance with specified requirements.
4) Reduction of overall development costs by detecting and fixing defects early in the development process.
5) Improved customer satisfaction through the delivery of high-quality software products.
6) Minimisation of business risks associated with software failures, such as financial consequences as well as reputational harm.
7) Enhancement of product competitiveness by ensuring superior quality and performance compared to competitors.
8) Facilitate regulatory compliance by ensuring adherence to industry standards and regulations.
9) Optimisation of software performance and scalability through thorough testing of various usage scenarios and load conditions.
Elevate your career with Certified Software Testing Professional (CSTP) Training. Sign up now to become a certified testing expert!
Disadvantages of Software Testing
Despite its benefits, Software Testing also has some limitations, such as:
1) Time and resource limitations might limit the depth and scope of testing.
2) Over-reliance on automated testing may cause certain aspects of software behaviour to be overlooked.
3) Testing cannot guarantee the absence of defects; it can only reduce their likelihood.
4) Increased complexity of software systems may lead to challenges in test case design and execution.
5) Inadequate documentation or incomplete requirements may hinder the effectiveness of testing efforts.
6) Limited access to real-world testing environments may impact the accuracy of test results.
Master your skills with Certified Software Testing Manager (CSTM) Training. Sign up now to become a certified testing manager!
Conclusion
Understanding Software Tester Roles and Responsibilities is paramount for ensuring the success of software projects. From Junior Test Engineers to Test Managers, each role contributes uniquely to the testing process, fostering collaboration, efficiency, and quality. Embracing these roles and responsibilities empowers testers to uphold software quality standards.
Advance your career with the ISTQB Advanced Level Test Manager Course. Join now to excel in Software Testing management!
Frequently Asked Questions

A career in Software Testing is lucrative and full of possibilities for growth. As our dependency on technology expands, there is a need for skilled testers in numerous industries to ensure the quality of software.

A job in Software Testing can be quite profitable, particularly for experienced professionals with specialised training. Factors like industry, region, experience level, and degree of skill affect salary variations.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Software Testing Courses, including ISTQB Advanced Level Test Manager, ISTQB Advanced Level Test Analyst, Certified Software Testing Professional (CSTP) and more. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Programming Fundamentals.
Our Programming & DevOps cover a range of topics related to Software Testing, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Business Analysis Skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Analysis Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 ISTQB Certified Tester Advanced Level Test Management Course
ISTQB Certified Tester Advanced Level Test Management Course
Mon 13th Jan 2025
Mon 10th Mar 2025
Mon 19th May 2025
Mon 21st Jul 2025
Mon 15th Sep 2025
Mon 17th Nov 2025
Mon 15th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


