We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Report Writing is a structured and systematic process that involves gathering, analysing, and presenting information clearly and concisely. There are several Features of Report Writing which make it effective. Understanding these features is essential for producing Reports that are clear, organised, and impactful. In this blog, you will learn about the different Features of Report Writing and some steps to take to create effective Reports for your organisation. Read more!
Table of Contents
1) What is Report Writing?
2) Features of Report Writing
a) Clarity
b) Accuracy
c) Visual aids
d) Evidence
e) Structure
f) Recommendations
g) Objectivity
3) Steps to write a Report
4) Conclusion
What is Report Writing?
Report Writing is a systematic and structured process of gathering, analysing, and presenting information in a formal document. It is a vital communication tool used across various fields, including academia, business, government, and research. Reports serve the purpose of informing, analysing, and making recommendations based on gathered data and research findings.
The process typically involves:
a) Defining the purpose and scope of the Report
b) Conducting thorough research
c) Organising the collected data
d) Presenting the information clearly and concisely
Reports can vary in complexity, from simple one-page documents to extensive research papers, business proposals, or technical manuals. Effective Report Writing requires a keen understanding of the target audience, as well as the ability to convey complex ideas understandably.
It involves structuring the content logically, ensuring coherence and consistency, and providing evidence-based conclusions or recommendations. Well-written Reports facilitate informed decision-making, problem-solving, and knowledge dissemination within organisations, making them invaluable tools for conveying critical information and contributing to the overall success of various endeavours.
Features of Report Writing
To help you create an effective Report, here are some of its Features of Report Writing:
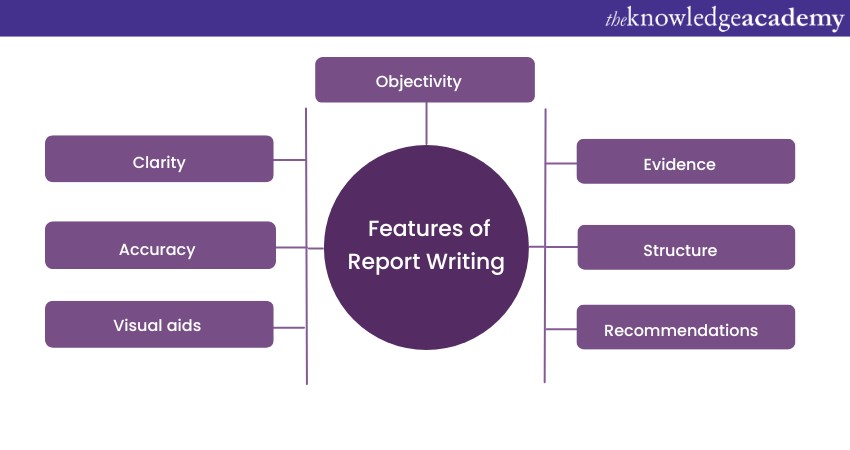
Clarity
Clarity in Report Writing is crucial. It ensures that complex ideas and data are presented straightforwardly and understandably. A clear Report leaves no room for ambiguity, allowing readers to grasp the information effortlessly. Achieving clarity involves:
a) Using simple and precise language
b) Structuring sentences and paragraphs logically
c) Employing visuals like charts or graphs for better comprehension
When a Report is clear, readers can quickly discern the key points, making it an effective tool for conveying information, aiding decision-making, and facilitating meaningful communication in various professional and academic contexts.
Accuracy
Accuracy is a pivotal feature in Report Writing, ensuring the information presented is precise, reliable, and error-free. It demands thorough research, attention to detail, and fact-checking to substantiate claims and findings. Inaccurate data can mislead readers and compromise the Report's credibility.
Writers must verify sources, use reliable data collection methods, and cross-verify information to maintain the Report's accuracy. Precision in language, adherence to established methodologies, and rigorous analysis contribute to the overall accuracy of the Report. A meticulously accurate Report enhances its reliability and builds trust, making it an invaluable tool for informed decision-making and academic discourse.
Visual aids
Visual aids are essential components of effective Report Writing, enhancing understanding and retention of information. Graphs, charts, tables, and images simplify complex data, making it accessible to a broad audience. These visuals provide a clear visual representation of trends, comparisons, and patterns, supplementing textual information.
They are potent tools for emphasising key points, supporting arguments, and enhancing comprehension. Well-designed visuals make the Report visually appealing and help readers absorb information more efficiently. By presenting data visually, Report writers can engage their audience, simplify complex concepts, and reinforce the main ideas, ensuring the Report's message is communicated effectively.
Evidence
Evidence in Report Writing refers to factual data, examples, or expert opinions supporting the document's claims and conclusions. It serves as the foundation upon which reliable arguments and analyses are built. Strong evidence enhances the Report's credibility, persuading readers of the validity of the presented information.
Researchers often rely on empirical studies, statistical data, surveys, or credible sources to substantiate their findings. They have correctly cited evidence not only validates the Report's assertions but also demonstrates the writer's thorough research and expertise on the topic. Evidence strengthens the Report's integrity, assuring readers that the information presented is well-grounded and trustworthy.
Structure
Structure in Report Writing refers to the organised framework that guides the presentation of information. A well-defined structure ensures logical flow, enabling readers to navigate the content seamlessly. It typically includes sections such as introduction, methodology, findings, analysis, conclusions, and recommendations.
Each section has a specific purpose, contributing to the overall coherence of the Report. The structure provides a roadmap for the writer, ensuring that essential points are covered systematically. Clear headings and subheadings delineate different topics, enhancing readability. A structured Report improves comprehension and reflects the writer's professionalism and attention to detail, making the document more impactful and persuasive to its intended audience.
Recommendations
Recommendations in Report Writing are crucial suggestions based on the findings and analysis. These actionable insights offer practical solutions, strategies, or actions that address the issues highlighted in the Report. Recommendations are grounded in evidence, making them credible and valuable for decision-makers.
Well-crafted recommendations are specific, feasible, and tailored to the context, providing a clear pathway for implementing changes or improvements. They serve as a guide for stakeholders, helping them make informed choices and take adequate measures. The quality and relevance of recommendations often determine the Report's impact, as they empower organisations and individuals to make positive changes based on the Report's insights.
Objectivity
Objectivity in Report Writing refers to presenting information and analysis in an unbiased, impartial, and fair manner. It demands writers separate personal opinions or emotions from presenting facts and findings. Objective Reports rely on empirical evidence, verifiable data, and expert opinions, ensuring the content is reliable and credible.
By maintaining objectivity, the writer establishes trust with the readers, enabling them to form opinions based on the presented information. Objectivity is essential in research and professional contexts, allowing for an accurate representation of reality and fostering a balanced, rational discussion of the topic.
Are you interested in improving your Report Writing skills? Register now for our Report Writing Training!
Steps to write a Report
Writing a comprehensive Report involves structured steps that ensure the document is well-organised, informative, and coherent. Here's a detailed overview of the essential steps to write a Report:
a) Define purpose: Clarify the Report's objectives and scope.
b) Research: Gather relevant information from credible sources.
c) Organise: Structure the Report with clear sections and headings.
d) Write introduction: Provide context, purpose, and research questions.
e) Methodology: Explain research methods and data collection processes.
f) Present findings: Display data using visuals, charts, or tables.
g) Analysis: Interpret results, discuss trends, and draw connections.
h) Conclusions: Summarise critical points, answering research questions.
i) Recommendations: Suggest actionable solutions based on findings.
j) Edit and proofread: Revise for clarity, coherence, and accuracy.
Do you want to show your creativity and hone your writing talents? Sign up now for our Creative Writing Training!
Conclusion
Understanding the art of Report Writing is essential for effective communication. There are some Features of Report Writing which, when followed, can be efficiently prepared. These features include following a structured approach, defining clear objectives, conducting thorough research, and presenting findings logically and objectively.
Elevate your personal and professional growth with our Personal Development Training. Join now!
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Organisational Skills
Organisational Skills
Fri 24th Jan 2025
Fri 28th Feb 2025
Fri 30th May 2025
Fri 15th Aug 2025
Fri 26th Sep 2025
Fri 31st Oct 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


