We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +34 932716793 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

We have come to the age where data has become the new currency, driving decision-making, innovation, and growth across industries. Big Data, with its promise of insights and competitive advantages, has captured the attention of businesses and organisations worldwide. However, with its potential benefits comes a critical aspect that often remains hidden beneath the surface: Big Data Cost.
As per Statista, the Big Data Analytics market will reach a value of around £95.99 billion by 2027. Though the market is expected to grow high, the implementation and maintenance of Big Data solutions come with a range of costs that organisations must navigate. Want to know how? Read this blog to explore how much is the Big Data Cost, exploring both financial and non-financial aspects that organisations need to consider.
Table of Contents
1) Financial Costs of Big Data
2) Non-financial Costs of Big Data
3) Importance of Managing Big Data Costs
4) Big Data Cost Management
5) Strategies to Reduce Costs with Data Analytics
6) Conclusion
Financial Costs of Big Data
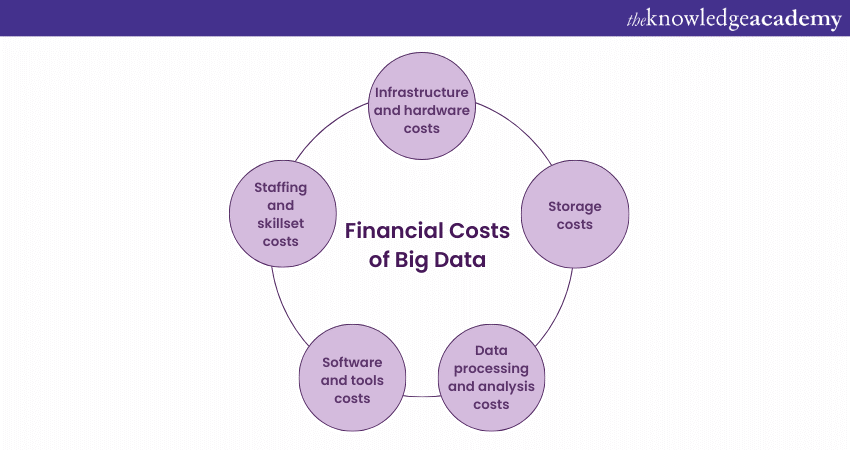
In the pursuit of harnessing the vast potential of Big Data, organisations encounter a range of Financial Costs that are integral to developing, implementing, and maintaining their initiatives. Thus, understanding these Costs of Big Data is important for effective budgeting, resource allocation, and overall project success. Financial Costs can include the following
1) Infrastructure and Hardware Costs
Implementing a Big Data infrastructure requires significant hardware, software, and cloud services investments. Organisations must build robust systems to store, manage, and process massive volumes of data, often resulting in substantial upfront and ongoing expenses.

2) Storage Costs
The accumulation of massive datasets requires significant storage capacity, both for active and archival data. Organisations can choose between on-premises storage solutions or cloud-based storage services, each with its own cost structure.
Cloud storage offers scalability and flexibility, allowing businesses to pay for the storage they use, while on-premises solutions involve upfront investments in hardware and maintenance. Spark and Hadoop are the main Big Data platforms for storage.
Data Processing and Analysis Costs
The real value of data lies in its analysis, which can provide insights into driving strategic decisions. Complex algorithms and Machine Learning models are employed to extract meaningful patterns and correlations from data.
Implementing and fine-tuning these models require expertise and computational power, contributing to the overall costs. High-performance computing clusters and specialised hardware, such as Graphics Processing Units (GPUs), are often employed to expedite the processing of intricate computations.
Become a Hadoop expert today – Register in our expert-led Hadoop Big Data Certification Course and master Big Data processing.
Software and Tools Costs
The realm of Data Analytics is populated with numerous software tools and platforms designed to handle diverse data types and analysis tasks. While open-source options offer cost-effective alternatives, they may require additional customisation, integration efforts, and ongoing support.
Proprietary software solutions, on the other hand, come with licensing and subscription fees. Selecting the right mix of tools that align with an organisation's data strategy is crucial to optimising costs.
Staffing and Skillset Costs
Building and maintaining a competent data team capable of handling Big Data projects is crucial. Skilled Data Scientists, Engineers, Analysts, and Administrators come at a premium, adding to operational costs.
Non-financial Costs of Big Data

While the Financial Costs of implementing and maintaining Big Data initiatives are significant, the Non-financial Costs associated with such endeavours are equally important to consider. They are as follows:
Data privacy and Security
As organisations collect and analyse huge volumes of sensitive data, concerns about data privacy and security become paramount. Mishandling or data breaches can lead to legal and financial repercussions. This can damage the brand's reputation and erode customer trust. Thus, establishing stringent data privacy measures and regular security audits are essential to safeguarding the confidentiality of the data.
Ethical Considerations
The ethical implications of using consumer data for profit require careful consideration. Organisations must navigate the fine line between leveraging data to enhance customer experiences and respecting individual privacy rights. Misuse of data can damage reputation and customer trust, leading to long-term costs.
Regulatory Compliance
The evolving landscape of data protection regulations, including the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), adds another layer of complexity to Big Data projects. Not following these regulations can result in hefty penalties and legal repercussions.
Opportunity Costs
While investing in Big Data projects can yield significant benefits, organisations must also consider the opportunity costs incurred. Resources allocated to data initiatives may be diverted from other strategic projects, potentially hindering growth and innovation in other areas. Balancing these opportunity costs requires careful prioritisation and strategic resource allocation to maximise overall organisational impact.
Supercharge your skills in Big Data Analysis – Join now and elevate your expertise with our specialised Big Data Analysis Course.
Importance of Managing Big Data Costs
While Big Data offers unprecedented opportunities for insights and innovation, it comes with substantial financial implications. Managing these costs effectively is crucial as it directly impacts an organisation's profitability and competitiveness.
Overspending on Big Data infrastructure and operations can strain budgets and hinder growth while underspending may lead to missed opportunities and compromised data quality. Hence, by understanding and managing the Costs of Big Data, businesses can strike the delicate balance between extracting value from their data assets and maintaining financial sustainability. As a result, they can ensure that Big Data remains an asset rather than a financial burden.
Big Data Cost Management
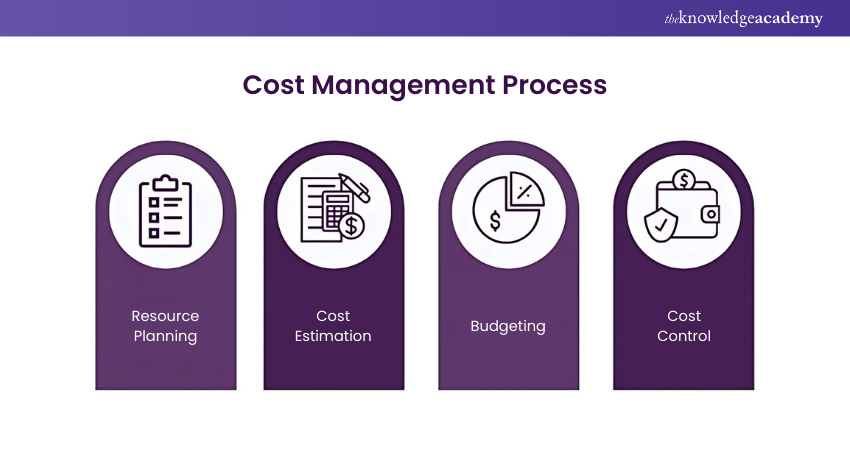
Big Data Cost management is a multifaceted process that involves resource planning, cost estimation, budgeting, and cost control to ensure that organisations can effectively leverage data while keeping expenses in check. Here’s the process:
a) Resource Planning: Effective Big Data Cost management begins with meticulous resource planning. This entails determining the computing power, storage capacity, and data processing capabilities required to meet an organisation's objectives. It involves assessing current and future data needs, as well as understanding the scalability requirements to accommodate data growth.
b) Cost Estimation: Once resource needs are identified, organisations must estimate the associated costs. This includes calculating expenses for hardware, software, cloud services, data storage, and personnel. It's essential to consider both upfront and ongoing costs, ensuring that the budget aligns with the organisation's financial capabilities.
c) Budgeting: Budgeting in Cost management involves allocating financial resources in a way that optimally supports data initiatives. It necessitates setting clear spending limits for various aspects of data operations, such as infrastructure procurement, data acquisition, analytics tools, and personnel expenses. A well-structured budget ensures that funds are allocated efficiently and prevents overspending.
d) Cost Control: Cost control is an ongoing process aimed at monitoring and managing Big Data expenses throughout their lifecycle. It involves tracking actual spending against the budget, identifying cost overruns, and implementing corrective actions. Organisations may employ cost-monitoring tools, implement cost-saving measures, and regularly review and adjust their strategies to maintain the financial field.
Strategies to Reduce Costs with Data Analytics
As companies increasingly rely on data to make critical decisions, the speed at which they can analyse that data becomes a key factor in reducing costs. Faster Big Data Analytics not only provides valuable insights into trends but also helps improve efficiency, cut operational costs, and direct investments to where they matter most.
Here’s a closer look at six ways faster Data Analytics can significantly lower business expenses:
1) Target Ad Campaigns for Fewer Wasted Marketing Dollars
Big Data allows businesses to transition from broad, mass-marketing strategies to more targeted, personalised campaigns. By analysing customer behaviour and intent, companies can centre their focus on marketing efforts on specific customer segments that are more likely to respond, reducing wasted ad spend.
This leads to more efficient use of trade and marketing budgets, helping to drive down overall marketing costs while boosting return on investment.
2) Avoid Financial Impact of Supply Chain Disruptions
Supply chains generate vast amounts of data, and Big Data Analytics can transform this information into actionable insights. By analysing this data in real time, businesses can predict and prevent potential disruptions, minimise bottlenecks, and optimise the flow of goods.
This not only enhances operational efficiency but also reduces the financial burden of delayed shipments, supply shortages, or other costly disruptions.
3) Prevent Loss with Better Fraud Detection
Fraud is a significant cost for many industries, but faster Data Analytics can help identify unusual or suspicious activities early. By analysing transaction patterns and customer behaviour, businesses can flag potential fraud before it escalates, preventing substantial financial losses.
This proactive approach to fraud detection will make sure that businesses stay one step ahead of fraudulent activities.
4) Enhance Log Analytics for Resource Management
Log analytics offers valuable insights into system performance, user behaviour, and resource utilisation. Faster analysis of this data allows businesses to quickly identify areas of inefficiency, such as underutilised resources or system bottlenecks.
By optimising the use of resources and eliminating waste, companies can significantly reduce operational costs and improve productivity.
5) Make Better Customer Service a Priority
Providing exceptional customer service is crucial for holding loyal customers. Faster analytics can help businesses track customer interactions and feedback, enabling them to improve service quality and resolve issues more quickly.
By enhancing customer satisfaction, companies can reduce churn, and avoid the high costs associated with acquiring new customers, instead of focusing on retaining the existing ones, which is more cost-effective in the long run.
6) Drive Productivity and Efficiency with Real-Time Data
Real-time Data Analytics enables businesses to make quicker, more informed decisions, leading to higher productivity and efficiency. By providing actionable insights when they are needed most, companies can streamline processes, improve employee performance, and optimise operations.
This ultimately results in lower operational costs, as resources are used more efficiently, and decision-making becomes more agile.
Become a Hadoop expert today – Register in our expert-led Hadoop Big Data Certification Course and master Big Data processing.
Conclusion
While Big Data offers unparalleled opportunities for insights and innovation, it's essential to recognise and manage the actual costs involved. By understanding Big Data Costs and adopting strategic approaches to manage them, organisations can harness the power of Big Data while minimising its impact on their bottom line and reputation.
Master the latest Big Data tools with our comprehensive Big Data and Analytics Training. Register today!
Frequently Asked Questions

The cost of Big Data depends on various factors, including the size of the dataset, the tools and technologies used, and the complexity of the analysis. Expenses can range from a few thousand to millions of pounds annually for businesses, depending on their needs and scale.

Companies typically spend between £800,000 to over £8 million annually on Big Data initiatives, depending on their industry, project scope, and data infrastructure. Larger enterprises with advanced analytics may have even higher expenditures.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Big Data and Analytics Trainings, including the Big Data Analysis Course, Data Science Analytics Training, and Big Data Architecture Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Big Data Analyst Job Description.
Our Data, Analytics & AI Blogs cover a range of topics related to Big Data Analytics, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Data Analytics skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Data, Analytics & AI Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Hadoop Big Data Certification
Hadoop Big Data Certification
Thu 12th Dec 2024
Thu 23rd Jan 2025
Thu 20th Mar 2025
Thu 22nd May 2025
Thu 17th Jul 2025
Thu 18th Sep 2025
Thu 20th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


