We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +34 932716793 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
In the horizon of Networking, the adoption of IPv6 has ushered in a new era, providing an expansive solution to the limitations posed by its predecessor. A cornerstone of this evolution lies in understanding the intricacies of IPv6 Address Types. From unicast to multicast, anycast to special-purpose addresses, the Networking domain is rich with diversity.
Now, Networking enthusiasts must grasp the importance of IPv6 addresses as they navigate the evolving digital ecosystem. IPv6 ensures the continued growth of the internet by providing an expansive address space, addressing the exhaustion concerns of IPv4. Read this blog to learn more about how IPv6 Address Types are numerical labels assigned to each device participating in a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication.
Table of Contents
1) Types of IPv6 addresses
a) Unicast
b) Multicast
c) Anycast
2) Conclusion
Types of IPv6 addresses
IPv6, or Internet Protocol version 6, represents the next evolutionary step in networking to overcome the limitations of its predecessor, IPv4. As the demand for unique IP addresses grows exponentially with the proliferation of devices, IPv6 provides a robust solution with its expanded 128-bit address space.
Now, unlike IPv4's 32-bit addresses, IPv6 offers an almost infinite pool of unique identifiers, facilitating the continued growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) and ensuring sustainable address allocation. IPv6 addresses are 128-bit numerical labels written in hexadecimal notation, featuring a vastly expanded range of possibilities.
More importantly, these addresses serve to uniquely identify and locate devices on a network. The addressing architecture includes unicast, multicast, anycast, and special-purpose addresses, each designed to fulfil specific communication needs, making IPv6 a foundational element for the seamless and secure connectivity of our increasingly interconnected world.
Moreover, different types of IPv6 addresses exist to cater to various communication scenarios in the digital world. Unicast addresses facilitate one-to-one communication, multicast addresses enable efficient group communication, anycast addresses optimise communication with the nearest node, and special-purpose addresses address unique network requirements. This diversity ensures flexibility, efficiency, and security in IPv6 networking.
Here is a list describing the three key types of IPv6 addresses:
IPv4 vs. IPv6: Is Your Network Ready for the Future? Find Out Now!
Unicast
Unicast addresses, a fundamental component of IPv6, enable point-to-point communication between two devices on a network. These addresses ensure the direct delivery of data from a single source to a specific destination. Have a look:
a) Global unicast addresses: Similar to public IPv4 addresses, they are routable on the internet, while link-local addresses facilitate communication within a specific network segment. Site-local addresses serve communication within an organisation or site. Furthermore, Global unicast addresses in IPv6 serve as the equivalent of public IPv4 addresses, facilitating communication across the global internet.
With a unique 48-bit global routing prefix assigned by Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) and a 16-bit subnet ID determined by the network administrator, global unicast addresses offer a vast and globally unique identifier for devices.
b) Unique-local addresses: Unique Local Addresses (ULA) in IPv6 provide a private and secure addressing solution for internal network communication within an organisation. With the prefix "fc00::/7" and a 40-bit Global ID, ULAs ensure localised connectivity, preserving privacy and security in internal networks while avoiding conflicts with globally routable addresses.
Furthermore, Unique Local Addresses (ULA) in IPv6 serve as private addresses for localised communication within an organisation or network. Prefixed with "fc00::/7," ULAs offer a substantial address space for internal use, allowing organisations to create secure, private networks without relying on globally routable addresses.
The 40-bit Global ID within the ULA ensures uniqueness, preventing address collisions. ULAs enhance network security and privacy by facilitating internal communication without exposing devices to the global internet. This addressing scheme is crucial for maintaining a separation between internal and external communication, providing a robust solution for private network configurations in the IPv6 ecosystem.
Discover the Key Advantages of IPv6 – Boost Your Network's Performance and Security Today!
c) Link-local addresses: Link-local addresses in IPv6 serve as identifiers for communication within a specific network segment. Prefixed with "fe80::," these addresses are automatically configured and enable devices on the same local network to communicate without the need for external routers. Link-local addresses facilitate efficient and localized network operations.
Link-local addresses in IPv6 are crucial for communication within a specific network segment, such as a local area network (LAN). Identified by the prefix "fe80::," these addresses are automatically configured by devices and allow direct communication without the need for external routers.
Link-local addresses are crucial for local network operations, enabling devices on the same segment to exchange information efficiently. They play a pivotal role in Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) and are often used in scenarios where immediate, localised communication is essential, contributing to the seamless functioning of devices within the confines of a specific network or link.
Attain the fundamental knowledge of IP protocol by signing up for our IPv6 Basics Course now!
Multicast
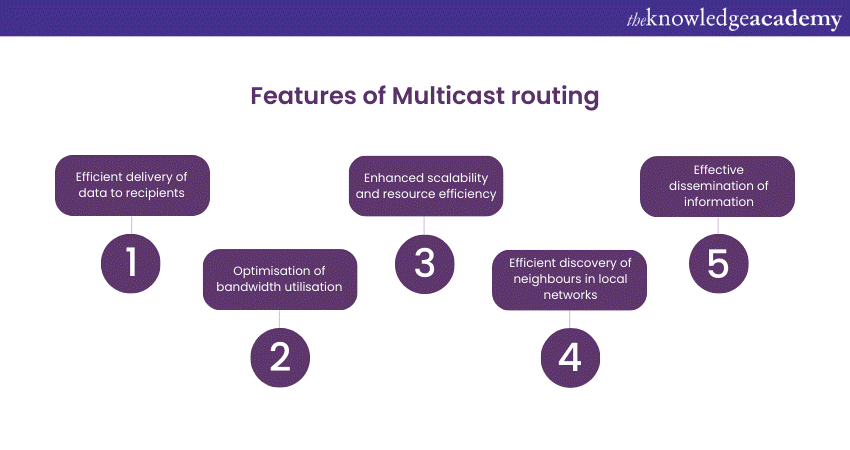
Multicast IP Routing is a communication paradigm in networking that enables the efficient delivery of data from one sender to multiple recipients. Unlike unicast, which is one-to-one communication, multicast allows a sender to address a specific group of recipients simultaneously.
Multicast addresses start with the prefix "ff00::/8" in IPv6, signalling their dedicated role in group communication. This routing method optimises bandwidth utilisation by avoiding unnecessary replication of data, making it ideal for applications like multimedia streaming, collaborative projects, and network management.
Furthermore, Multicast IP routing enhances scalability and resource efficiency, enabling streamlined content distribution to multiple destinations without overburdening the network infrastructure. As networks continue to evolve, multicast routing remains a key technology, contributing to the seamless and effective dissemination of information to diverse audiences.
Now, the solicited-node multicast address is a specific type of multicast address used in IPv6 for efficient neighbour discovery in local networks. It plays a crucial role in the Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP), part of the IPv6 protocol suite.
Ace Your Network Security Interview! Explore Top Network Security Interview Questions and Answers to Boost Your Confidence and Secure the Job!
The structure of a solicited-node multicast address is derived from the lower 24 bits of a device's unicast IPv6 address. Specifically, it takes the well-known multicast prefix "ff02::1:ff00:0/104" and appends the lower 24 bits of the unicast address in question. This process ensures that each device generates a solicited-node multicast address unique to its unicast address.
For example, if a unicast address is "2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334," the corresponding solicited-node multicast address would be "ff02::1:ff70:7334." These addresses are instrumental in Neighbor Solicitation messages, allowing devices to efficiently discover and communicate with their neighbours on the local network without flooding the entire segment with unnecessary multicast traffic.
Master the basics of networking concepts by signing up for our Cisco Certified Network Professional Boot Camp Week 1 Course now!
Anycast
Anycast IP routing in IPv6 introduces a unique communication paradigm where a single destination address is shared by multiple nodes, and the data is sent to the nearest or most optimal member of the anycast group. Unlike unicast, which involves one-to-one communication, anycast allows multiple nodes to share the same address, distributing traffic to the closest available server or network node.
Anycast routing enhances efficiency, load balancing, and fault tolerance, as traffic is directed to the nearest node in the anycast group, minimising latency and optimising resource utilisation. This method is particularly advantageous in distributed systems, content delivery networks (CDNs), and services where redundancy and load distribution are critical.
Master IPv6 Protocols with These Essential Interview Questions! Prepare for Your Next IT Interview with Our Expert-Compiled IPv6 Questions and Answers!
Anycast IP routing in IPv6 contributes to the resilience and scalability of modern networks, offering a powerful tool for improving the performance and reliability of internet services.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a nuanced understanding of the Different Types of IPv6 Addresses is indispensable for navigating the intricate landscape of modern networking. From the versatility of unicast addresses to the efficiency of multicast and anycast, the diversity within IPv6 address types shapes the robust and interconnected fabric of the internet. Mastering IPv6 Address Types is pivotal for network administrators and engineers embracing the future of digital connectivity.
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming IT Infrastructure & Networking Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 IPv6 Basics
IPv6 Basics
Thu 9th Jan 2025
Thu 6th Mar 2025
Thu 8th May 2025
Thu 3rd Jul 2025
Thu 4th Sep 2025
Thu 6th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


