We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +34 932716793 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

When it comes to surfing the internet, security and privacy are primary concerns for many users. Hackers, advertisers, and even governments can track your online activity, collect your personal data, and censor your access to certain websites. Using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) can help you overcome these challenges effectively. But What is a VPN, and how does it work?
If you are curious to learn more about VPNs, then this blog will help you learn What is a VPN, how it works, its pros and cons, as well as its alternatives. Let's dive in to learn more!
Table of Contents
1) What is a VPN?
2) How does a VPN work?
3) How to use a VPN?
4) The evolution of VPNs
5) Installing a VPN on your computer
6) Considerations when selecting a VPN
7) Advantages and disadvantages of VPN
8) VPN alternatives for business
9) Conclusion
What is a VPN?
A Virtual Private Network is a technology crafted to bolster internet security and confidentiality. At its core, it forms a secure network connection, which is especially vital when utilising public networks. By encrypting your internet data and masking your digital identity, VPNs significantly reduce the likelihood of third-party tracking and data theft.
Its primary role is to create a connection that is not only secure but also encrypted, offering a level of privacy that surpasses even that of a protected Wi-Fi hotspot. In essence, VPN serves as an indispensable resource for those prioritising their online privacy and security, ensuring a protected and discreet browsing experience on the internet.
How does a VPN work?
A Virtual Private Network functions as a tunnel between your device and the internet, ensuring private and secure web browsing. Here's a breakdown of how it operates:
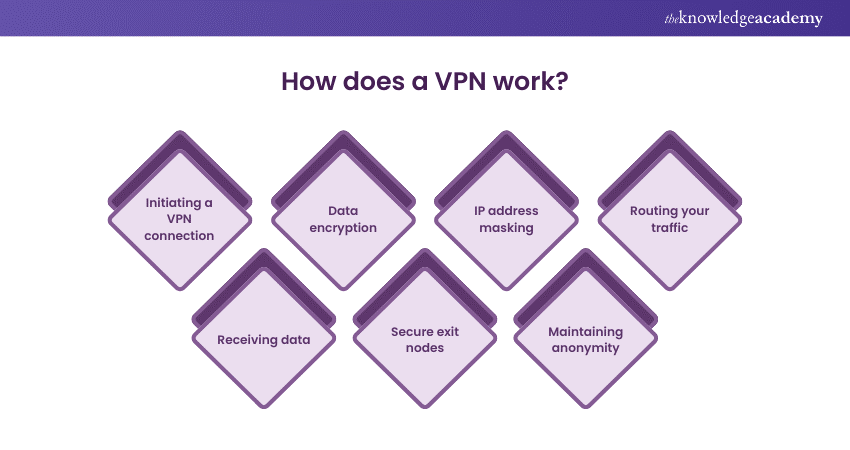
1) Initiating a VPN connection: When you activate your VPN software, it communicates with your chosen VPN server. This connection is encrypted, creating a secure 'tunnel' through which your data travels to and from your device.
2) Data encryption: Once the connection is established, your data is encrypted before leaving your device. This encryption converts the data into a complex code that can only be decoded with the right key. Even if intercepted, the data remains unreadable and secure.
3) IP address masking: The VPN assigns your device a new IP address, usually corresponding to the server's location. This masks your actual IP address, so it will seem as if you are using the internet from the physical location of the VPN server, not your real location.
4) Routing your traffic: Your encrypted data is transmitted to the VPN's server, where it is decrypted and sent to the intended internet destination, like a website or an online service. To that website or service, it appears as though the traffic is coming from the VPN server and its location, not from your device and your actual location.
5) Receiving data: When the website or online service sends data back to you, the process is reversed. The data is sent to the VPN server, where it is encrypted and then sent to your device through the secure tunnel. Upon arrival, the VPN client software decrypts the data so you can use it.
6) Secure exit nodes: This encrypted tunnel ensures that your internet activity is concealed from your internet service provider, network administrator, and potential eavesdroppers. It's particularly useful when using public Wi-Fi networks, where the risk of unsecured data being intercepted is higher.
7) Maintaining anonymity: By using a VPN, your browsing history, location, IP address, and other personal data are kept private and secure. This is beneficial for maintaining anonymity online, especially against tracking and surveillance.
A VPN works by encrypting your data, masking your IP address, and securely routing your internet traffic through a VPN server, which enhances your overall internet privacy and security.
How to use a VPN?
Using a VPN can significantly enhance your internet privacy and security. Here are five key steps to effectively use a VPN:
1) Choose a reliable VPN provider: Start by picking a reputable VPN provider. Look for providers with a good track record of privacy, a no-logs policy, robust encryption standards, and good reviews. Consider factors like speed, server locations, compatibility with your devices, and price.
2) Download and install the VPN software: After choosing a provider, download their VPN software or app onto your device. Most VPNs are compatible with various devices and operating systems, including Windows, macOS, iOS, Android, and sometimes even Linux.
3) Configure your VPN settings: Once installed, open the application and log in with your credentials. Some VPNs will require you to configure settings according to your needs. You can usually select preferences like auto-connect on startup, choose default servers, or adjust security protocols.
4) Connect to a VPN server: Pick a VPN server with less latency. Many VPNs offer servers in multiple countries around the world. Your choice of server can depend on several factors, such as your location, the content you want to access, or your desired level of privacy. Some VPNs also offer specialised servers for activities like streaming or torrenting.
5) Browse securely and privately: Once connected, all your internet traffic will be routed through the VPN’s encrypted tunnel. You can now browse, stream, or conduct any online activity with enhanced security and privacy. Remember that while a VPN provides increased privacy and security, it’s still important to use safe browsing practices.
By following these steps, you can effectively use a VPN to protect your online privacy and access content that might be restricted in your geographic location. Remember, the effectiveness of a VPN largely depends on the quality of the provider and how diligently you use it.
The evolution of VPNs
The evolution of Virtual Private Networks has been shaped by increasing concerns for internet privacy and security. Here's a look at how VPNs have developed over the years:
1) Early development: Created in the 1990s, VPNs were first developed for business and government use to create secure network paths for remote access to private networks. This was essential for secure communication and data sharing.
2) Rise in the corporate world: VPNs became essential in the corporate sector, primarily for connecting remote employees to company networks. They ensured that remote access to sensitive company resources was secure and private.
3) Shift to personal use: With growing internet surveillance and data privacy concerns, VPNs expanded into personal use. They became popular for enhancing privacy, especially on public Wi-Fi, and for bypassing geo-restrictions on content.
4) Technological advancements: VPN technology evolved to offer stronger encryption and additional features like kill switches. These advancements made VPNs more reliable and secure for both personal and business use.
5) Mainstream awareness and future trends: High-profile data breaches and increased awareness of digital privacy issues have made VPNs popular among the general public. VPNs are likely to see further integration with other technologies, making privacy protection more accessible across various devices.
This progression reflects the transition of VPNs from a niche business tool to a crucial component of online security and privacy for individuals and businesses alike.
Build a strong IT foundation with our IT Fundamentals Training – Sign up now!
Installing a VPN on your computer
To enhance your online privacy and security, installing a Virtual Private Network on your computer can be done in several ways. Each method suits different needs and offers varying levels of protection. Let's explore how to install the different Types of VPNs:
VPN clients
Installing a standalone VPN client involves a few critical steps to ensure a secure and efficient setup. Let's explore the steps involved:
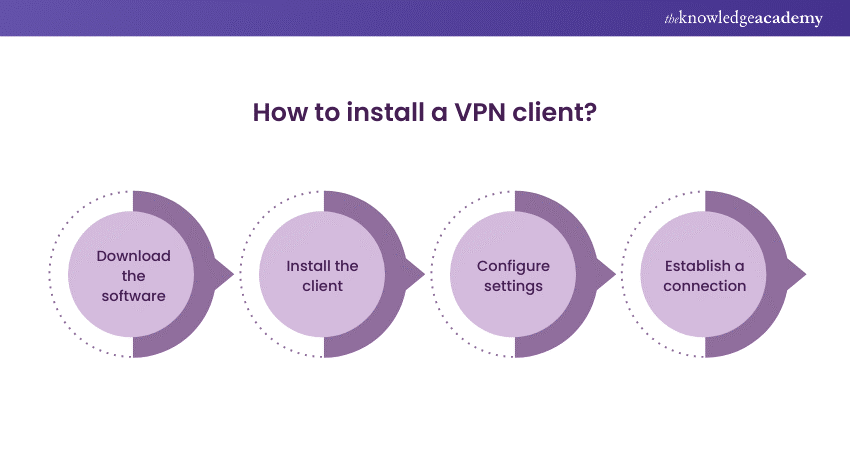
1) Download the software: Get the VPN client software from your VPN provider's website, ensuring it's compatible with your computer's operating system.
2) Install the client: Execute the downloaded file and follow the on-screen instructions for installation.
3) Configure settings: Open the VPN client after installation. You might need to enter your subscription details and choose settings like server preferences and security protocols.
4) Establish a connection: Connect to a VPN server by selecting one from the list provided and clicking 'connect'. This encrypts and routes your internet traffic through the VPN server.
Browser extensions
For a more browser-focused VPN experience, extensions can be a convenient option. They can be installed from the browser's web store. Here are the steps:
1) Find the extension: Search for your VPN provider's extension in your browser's extension store.
2) Install the extension: Insert the extension into your browser, which usually doesn't require restarting the browser.
3) Log in and customise: Open the extension, log in with your VPN account, and adjust settings like server location.
4) Activate the VPN: Turn on the VPN in the extension to start encrypting your browser traffic. Note that this only secures traffic within that browser.
Router VPN
Installing a VPN on your router is an effective way to secure your entire network, so let's explore the steps:
1) Check router compatibility: Make sure your router can handle VPN connections. Some routers may need additional firmware like DD-WRT.
2) Configure the router: Access the router's settings and enter the VPN configuration details from your VPN service.
3) Connect and secure: After configuration, any device connected to your router will use the VPN connection.
Corporate VPN
For those in a corporate environment, a company-provided VPN is the norm. Here are the steps involved in installing it:
1) Receive instructions: Your company will provide specific instructions or software for the VPN.
2) Install and configure: Follow the provided steps to install and configure the VPN client, which might involve entering credentials or installing certificates.
3) Connect to the network: Use the VPN client to connect to your company's network for secure access to internal resources.
Each method caters to different needs, offering various levels of convenience and security. Whether you’re an individual user, a remote worker, or looking to secure multiple devices at home, these steps will help you set up your VPN correctly.
Considerations when selecting a VPN
When selecting a Virtual Private Network (VPN), it's crucial to weigh various factors that affect its performance and suitability for your needs. Let's delve into six key considerations:
1) Speed: Speed is a vital aspect of a VPN's performance. A good VPN should offer fast connection speeds to minimise the impact on your internet browsing, streaming, and downloading activities.
2) Reputation: The reputation of a VPN provider is essential for trust and reliability. Researching the provider's history, user reviews, and industry standing can give insights into its credibility and service quality.
3) Shared IP addresses: Shared IP addresses in a VPN enhance your anonymity online. This feature makes it more challenging to trace online activity back to an individual user, but it may have implications for accessibility to some websites.
4) Server infrastructure: The infrastructure of VPN servers plays a crucial role in determining overall performance. A robust network with various servers can offer better speed, stability, and options for geo-spoofing.
5) Encryption: Encryption strength is key to the security offered by a VPN. Strong encryption protocols ensure your data is protected, but the level of encryption can also affect the speed of your connection.
6) Protocol: The choice of VPN protocol impacts both security and performance. Different protocols offer varying balances between encryption strength, speed, and compatibility with different devices and networks.
Enhance your online defence with our Cloudflare Training – Sign up today!
Advantages and disadvantages of VPN
Using a VPN offers a range of benefits but also comes with certain limitations. Let’s explore both the positive aspects and the potential downsides.
Advantages of VPN
VPNs provide enhanced online privacy and security, making them a valuable tool for internet users. Here are the key benefits of VPN:
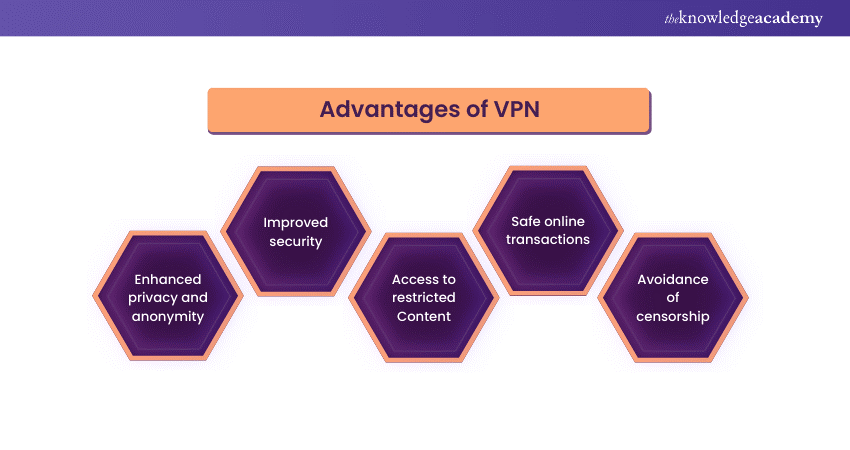
1) Enhanced privacy and anonymity: VPNs hide your IP address, reducing the ability of websites, advertisers, and potential intruders to track your online activities.
2) Improved security: They encrypt your data, safeguarding it from eavesdroppers, especially on insecure public Wi-Fi networks.
3) Access to restricted Content: VPNs can bypass geographical restrictions, allowing access to content and websites that might be unavailable in your region.
4) Safe online transactions: Encryption provided by VPNs offers a safer environment for conducting sensitive online transactions.
5) Avoidance of censorship: VPNs can get around government censorship, granting access to a more open and freer internet, particularly in countries with restricted web access.
Disadvantages of VPN
While VPNs are highly beneficial, they also have some drawbacks that users should be aware of. Here are the main disadvantages of using a VPN:
1) Potential Slowdown in Internet Speed: The encryption process and rerouting of data through VPN servers can sometimes slow down your internet connection.
2) Limited Free Options: Free VPN versions are often restricted in speed, available servers, and data usage and may offer lower security.
3) Complexity for Novices: For those less familiar with technology, setting up and managing a VPN can be a complex task.
4) Blocked by Some Services: Some online services, such as streaming platforms, actively block known VPN IPs, which can restrict access to their content.
5) Legal and Policy Compliance: The use of VPNs is regulated or restricted in some countries, and not all VPNs adhere to specific regional laws.
6)Trust in the VPN Provider: You need to trust your VPN provider with your data, making it crucial to choose one with a strong reputation and a strict no-logs policy.
Understanding these pros and cons is critical for making an informed decision about how to use a VPN. This will ensure you get the most out of your online experience while being aware of the limitations.
Learn the fundamentals of networking with our Introduction to Networking Training – Sign up now!
VPN alternatives for business
For businesses seeking to secure their digital environments, there are alternatives to traditional VPNs that focus on specific aspects of security and access management. Here are three key alternatives:
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Identity and Access Management systems are created to manage user identities and regulate access to company resources. They ensure that the right people have access to the right resources at the right times and for the right reasons.
Benefits for businesses: IAM systems provide improved security by controlling access to delicate data and systems. They also improve efficiency by automating user provisioning and de-provisioning, and they can offer insights into user activities and potential security risks.
Privileged Access Management (PAM)
Privileged Access Management focuses on monitoring and securing access to critical resources within an organisation. It's designed to protect against threats posed by users with elevated privileges or administrative access.
Advantages for organisations: PAM provides a higher level of security for sensitive systems by managing and monitoring privileged accounts. It helps in preventing data breaches that could occur due to compromised privileged accounts and ensures compliance with various regulatory requirements.
Vendor Privileged Access Management (VPAM)
VPAM is an extension of PAM that specifically deals with access given to vendors or third-party service providers. It controls and monitors their access to the organisation's critical systems and data.
Importance in business ecosystems: This approach is crucial for businesses that rely on external vendors for services and support. VPAM ensures that vendor access is secure and compliant and does not pose a threat to the organisation's security posture.
Each of these alternatives serves a specific purpose in the broader context of business security and can be used alongside or instead of traditional VPNs, depending on the organisation's specific security needs and infrastructure.
Conclusion
We hope you have understood What is a VPN with this blog. Understanding VPNs and their alternatives is essential for boosting online security and privacy for both personal and business use. VPNs provide strong encryption and anonymity, while options like IAM, PAM, and VPAM cater to more specific security requirements. Navigating these choices effectively ensures a safer and more secure online experience in our increasingly digital world.
Empower your online freedom with our VPN Training – Sign up today!
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I set up a VPN?

To set up a VPN, first select a trustworthy VPN provider. Download and install their VPN application on your device. Open the application, log in with your credentials, and then select a server to connect to. Once connected to the server, your internet traffic will be encoded and routed through the VPN.
Are VPNs legal?

VPNs are legal in most countries and are widely used for enhancing online privacy and security. However, the legality can vary based on your location and the specific use of the VPN. In some countries, VPN use is restricted or regulated. Always ensure that you're compliant with local laws when using a VPN.
What are the other resources and offers provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is the Knowledge Pass, and how does it work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are related IT Support and Solution Courses and blogs provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various IT Support and Solution Courses, including VPN Training, IT Fundamentals Training, and Introduction to Networking Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into IT Support and Solution methodologies.
Our IT Support and Solution blogs cover a range of topics related to VPNs, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your IT Support and Solution skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming IT Infrastructure & Networking Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 VPN Training
VPN Training
Fri 2nd May 2025
Fri 4th Jul 2025
Fri 5th Sep 2025
Fri 7th Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


