We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +34 932716793 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Imagine you’re at a family barbecue, enjoying a delicious meal. Suddenly, a guest falls ill due to improperly handled food. This scenario highlights the importance of understanding What is Food Safety. Guaranteeing Food Safety is crucial to prevent foodborne illnesses and protect public health. Ever wondered how to know if the food you’re eating is safe?
In this blog, you will learn What is Food Safety, why it matters, and how you can implement best practices in your daily life. It will cover everything from proper food handling and storage to recognising potential hazards. So, let’s dive in and make every meal a safe one!
Table of Contents
1) What is Food Safety?
2) Scope of Food Safety
3) Key Components of Food Safety
4) Importance of Food Safety
5) Global Initiatives for Food Safety
6) Who is Responsible to Ensure the Safety of Food?
7) Tips for Ensuring Food Safety at Home
8) Conclusion
What is Food Safety?
Food Safety can be defined as the ways and methods that are adopted to ensure that food is fit to be eaten. It aims at avoiding, minimising, and controlling risks that are biological, chemical and physical in nature and can cause illnesses or injuries associated with foods. Food hygiene and safety procedures should be practiced from the time a particular food item is procured to the time it is ready to be consumed, and it is imperative that this is put into practice, as emphasized in the Food Hygiene Guide.
It is therefore significantly more than an exercise of avoiding the obvious dangers. This concept is marked by a preventive outlook that continually looks for lurking risks and seeks to eliminate them at every point in the food chain, often by conducting a thorough food safety risk assessment.
This encompasses the food sector and especially the growers, horticulturists as well as the agricultural and food chain agents, including processors, transporters, handlers, retailers and preparers of food.
Scope of Food Safety
The scope of Food Safety is vast and multifaceted, covering various aspects of food production, distribution, and consumption. Here are some of the scopes of Food Safety:
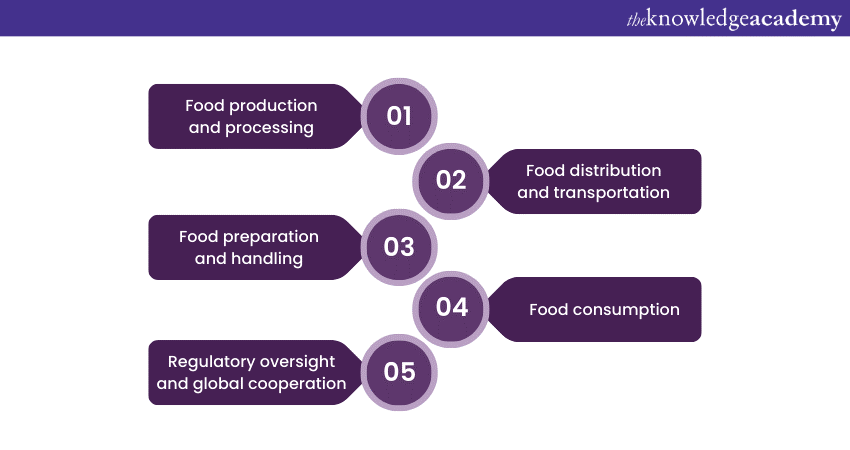
1) Food Production and Processing: Food Safety starts at the place where crops are grown and animals are reared. It entails the promotion of practices that reduce the consumption of toxic pesticides, chemicals, as well as antibiotics. Such farming practices are adhered to in order to minimise production of diseases that affect animals and in extension affect the health of humans.
Moreover, in industrial facilities measures are taken to restrict contamination during processing, packaging and labeling. Quality control procedures are exercised in order to ensure that the end products are safe and marketed with appropriate labels.
2) Food Distribution and Transportation: Control and Maintenance of food temperature during its distribution and transportation is very important to avoid temperature abuse. Refrigerated and frozen products must be transported at optimised temperatures with a view of preventing bacterial growth of microbes. This makes it important that the food undergo the right packaging and meet the right storage conditions to enhance their safety.
3) Food Preparation and Handling: The presentation of the foods is important to reduce cross contamination and the germs that will enhance the growth of bacteria. This includes proper handling of food in cooking; not using the same utensils for raw meat and the ready meals; cleanliness of the kitchen. It is mandatory for anyone in the food chain – from home to restaurants, cafes’, and other food business processes, to be trained in Food Safety.
4) Food Consumption: Consumers play a vital role in Food Safety by following guidelines for safe food handling and storage at home. Properly storing leftovers, reheating foods to appropriate temperatures, and avoiding consumption of foods that show signs of spoilage are essential practices.
5) Regulatory Oversight and Global Cooperation: It is always the work of the government or other organisations like the Food and Agricultural Organisation to provide and regulate Food Safety standards. These regulations set out rules governing food production and processing, labelling as well as handling of foods. Bodies such as the Codex Alimentarius Commission and the World Health Organisation have engaged in standardising Food Safety standards all over the world and encouraging all nations to tackle Food Safety issues.
Gain the knowledge to prevent foodborne illness by signing up for our Food Hygiene and Safety Training now!
Key Components of Food Safety
Some of the key components of Food Safety are:
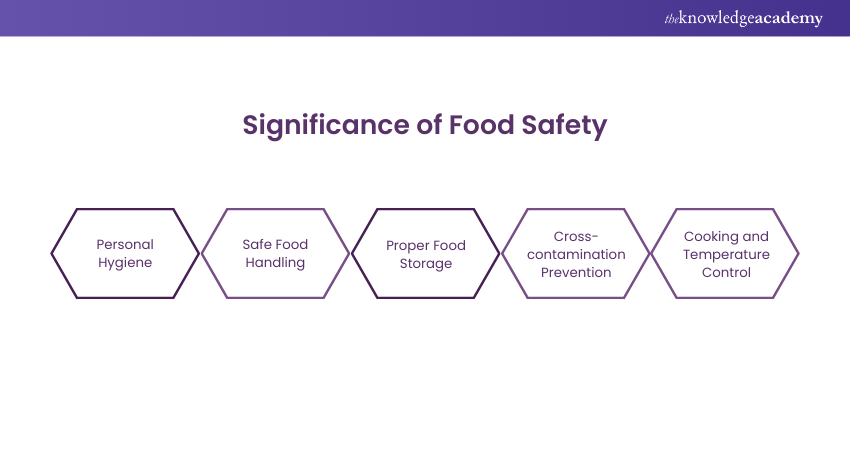
1) Proper personal hygiene is crucial for Food Safety. Food handlers must wash hands regularly, wear appropriate attire, and avoid handling food when ill to prevent contamination.
2) Properly storing, preparing, and serving food minimises contamination risks and prevents foodborne illnesses.
3) Correct storage conditions preserve food quality and safety, preventing spoilage and bacterial growth.
4) Separate raw meats, poultry, seafood, and eggs from ready-to-eat foods. Use different cutting boards, utensils, and containers for raw and cooked foods.
Cook food to the accurate internal temperature to destroy harmful bacteria. Use food thermometers and follow cooking guidelines to ensure safety.
Crack your Interview with Food Safety Questions and Answers Guide
Importance of Food Safety
Food Safety is not only a concern for the food industry but a fundamental aspect of public health and well-being. Hence, the significance of Food Safety cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts individuals, communities, and even economies. Let's explore why Food Safety is of utmost importance.

1) Preventing Foodborne llnesses
One of the most compelling reasons for prioritising Food Safety is the prevention of foodborne illnesses. Contaminated food can harbour a wide range of harmful microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, parasites, and fungi, which can cause human infections and diseases. These illnesses, often characterised by symptoms like nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhoea, and fever, can range from mild discomfort to severe and fatal or life-threatening conditions.
By implementing strict Food Safety measures, the risk of contamination is minimised, leading to a major reduction in the occurrence of foodborne illnesses. Proper handling, preparation, and storage of food help ensure that harmful microorganisms are destroyed or controlled before consumption.
2) Protecting Public Health
Food Safety directly impacts public health on a large scale. When contaminated food enters the food supply chain, it can lead to outbreaks of foodborne illnesses affecting a significant number of people. These outbreaks can overwhelm healthcare systems, leading to increased hospitalisations and medical costs.
However, in severe cases, they can result in long-term health complications and even fatalities, particularly among vulnerable populations such as children, the elderly, and people with weak immune systems. By prioritising Food Safety, communities can minimise the risks associated with foodborne illnesses, reduce the burden on healthcare systems, and promote overall well-being.
3) Building Consumer Trust
Consumer trust is the foundation of any successful food industry. When consumers believe the food they purchase and consume is safe, they are more likely to make smart choices and continue supporting food businesses. On the other hand, a single instance of foodborne illness outbreak linked to a particular brand or establishment can severely damage consumer trust and lead to reputational and financial losses.
By consistently adhering to Food Safety standards and transparently communicating about safety practices, businesses can establish themselves as reliable sources of safe and high-quality food. Once this trust is built, it can lead to customer loyalty and positive word-of-mouth recommendations.
Drive sustainability and compliance in your workplace with our Environmental Awareness Training – join now for a greener future!
4) Ensuring Legal Compliance
Regulatory bodies worldwide have developed strict guidelines and standards for Food Safety. These rules and regulations are made to protect consumers and ensure that food businesses operate in a responsible and ethical manner. Failing to adhere to Food Safety regulations can result in legal actions, fines, shutdowns, and damage to a company's reputation.
Businesses that prioritise Food Safety and invest in training their staff to adhere to these regulations demonstrate their commitment to legal compliance and their customers' well-
Global Initiatives for Food Safety
Several international organisations and initiatives play a pivotal role in setting guidelines, facilitating collaboration, and promoting awareness about Food Safety on a global scale. Here are some of the prominent global initiatives in the field of Food Safety:
1) Codex Alimentarius
The Codex Alimentarius Commission, established by the Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO) and the World Health Organisation (WHO), is a globally recognised body that develops international food standards, codes of practice, and guidelines to ensure the safety, quality, and fairness of food trade. These standards cover various topics, including food additives, contaminants, labelling, and hygiene.
Codex standards are not mandatory but serve as a reference for national regulatory authorities to develop their own regulations. By harmonising international Food Safety standards, Codex promotes consistency in Food Safety practices across countries, facilitating trade while safeguarding public health.
2) World Health Organisation (WHO)
The WHO is a leading authority in global public health. Regarding Food Safety, the WHO provides scientific expertise, research, and guidance to member states. It plays a major role in shaping policies, regulations, and strategies that promote Food Safety and prevent foodborne diseases. WHO's efforts include:
a) Conducting risk assessments.
b) Providing technical support to member states.
c) Collaborating with international partners to address emerging Food Safety challenges.
The organisation's dedication to promoting safe food consumption contributes significantly to improving global public health outcomes.
3) Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO)
The Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations works in collaboration with WHO to establish and promote Food Safety standards. FAO focuses on various aspects of Food Safety, including sustainable agriculture practices, food quality, and Food Safety management systems. It provides technical assistance, capacity-building programs, and knowledge dissemination to support countries in implementing effective Food Safety measures.
4) Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
Although not a global initiative, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is a crucial regulatory authority with a substantial impact on global Food Safety practices. The FDA sets and enforces regulations for Food Safety in the United States (US), including food labelling, inspection, and quality control. Its guidelines and standards often influence Food Safety practices in other countries due to the interconnected nature of the global food supply chain.
Ensure your remote workforce's safety with our comprehensive Health and Safety for Homeworkers Training.
Who is Responsible to Ensure the Safety of Food?
Food Safety is a collective effort that requires cooperation from all stakeholders in the food supply chain. Here are some insights into the roles of major food industry players in managing Food Safety:
1) Government Regulatory Bodies Develop Standards and Laws for Food Safety
Government regulatory bodies, such as the Food Standards Agency (FSA) in the UK, are responsible for establishing Food Safety standards related to food handling, hygiene, and distribution. These agencies ensure consumer rights are upheld and address Food Safety concerns. They create and enforce food laws and regulations to prevent foodborne illnesses, regulate imports and exports, and monitor the use of chemical additives. They also conduct inspections, provide certifications, and ensure compliance with Food Safety standards.
2) Food Safety Responsibility in a Food Business or Store
In a food business or store, the primary responsibility for Food Safety lies with the owners and managers. They must ensure that all food handling practices comply with regulatory standards. This includes training employees, implementing Food Safety protocols, and conducting regular audits. Managers must stay updated on Food Safety regulations and ensure their team is knowledgeable about potential hazards and control measures.
3) Customers Must Be Knowledgeable About Food Safety
Consumers also play an important role in maintaining Food Safety. They should demand safe food from manufacturers and handlers and be educated about Food Safety practices and foodborne illnesses. Once food products reach households, consumers must handle, process, and store them properly to prevent contamination. Basic knowledge about cross-contamination, proper handwashing, and safe food storage is essential for maintaining Food Safety.
Tips for Ensuring Food Safety at Home
Maintaining Food Safety doesn't end at the production and distribution stages; it's equally important at the consumer level. How food is handled, prepared, and stored in your own kitchen directly impacts your health and the health of your loved ones. Here are some essential tips for ensuring Food Safety at home:
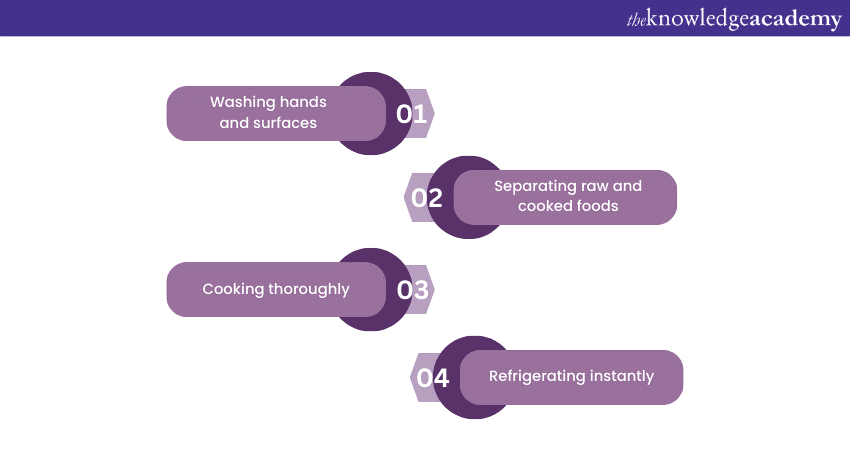
1) Washing hands and surfaces: Thoroughly washing hands before handling food and after handling raw meats, using the bathroom, or touching pets is crucial. Surfaces, utensils, and cutting boards should also be cleaned and sanitised regularly to prevent cross-contamination.
2) Separating raw and cooked foods: To prevent cross-contamination, keep raw meats, poultry, seafood, and eggs separate from ready-to-eat foods. Use separate cutting boards and containers for different food types and store them separately in the refrigerator.
3) Cooking thoroughly: Cooking food to the appropriate internal temperature is essential. Use a food thermometer to make sure that meats, poultry, seafood, and eggs are cooked thoroughly, killing any harmful bacteria that may be present.
4) Refrigerating instantly: Perishable foods should be refrigerated promptly to slow the growth of bacteria. Keep the refrigerator temperature at 4.4°C or below and the freezer at -17.8°C or below. Leftovers should be refrigerated within two hours of cooking.
Conclusion
We hope that our blog on "What is Food Safety" has helped you understand its fundamentals and the approaches to safeguarding your meals from contamination. Now, armed with this information, you can ensure that your every bite is safe and healthy. If you're interested in pursuing a career in food safety, exploring roles like a Food Safety Inspector and salary can provide valuable insights for your career planning.
Equip your team with essential knowledge through our Food Allergy Awareness Training – book your spot now!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Easiest way to Prevent Cross-contamination?

The Food Hygiene Guide recommends that the easiest way to prevent cross-contamination is by using separate cutting boards and utensils for raw and cooked foods and ensuring thorough handwashing before and after handling different food types.
What are the Principles of Food Safety?

The principles of Food Safety include proper cooking, cleaning, chilling, and avoiding cross-contamination to prevent foodborne illnesses.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Food Hygiene and Safety Trainings, including the Food Safety Manager Training, Food Allergy Awareness Training, and Food Safety and Hygiene Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into a Healthy Lifestyle.
Our Health & Safety Blogs cover a range of topics related to Food Safety, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Health and Safety knowledge, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Health & Safety Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Health and Safety in the Workplace Training
Health and Safety in the Workplace Training
Fri 28th Feb 2025
Fri 4th Apr 2025
Fri 27th Jun 2025
Fri 29th Aug 2025
Fri 24th Oct 2025
Fri 5th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


