We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +34 932716793 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Have you ever wondered how our planet maintains its optimal temperature to support life, which is neither too cold nor too hot for us to survive? The answer lies in a natural phenomenon widely known as the Greenhouse Effect. You may have heard of this phenomenon a lot in light of the eco-sustainability. But have you ever wondered what exactly it is and why it is so crucial for our existence?
This blog will shed light on this intriguing and happening topic to help you understand exactly What is the Greenhouse Effect, including its causes, effects, and ways to mitigate it. Moreover, we will also help you with how you can work to keep our planet habitable against the growing concerns that threaten it in a catastrophic way. Let’s dive in!
Table of Contents
1) What is the Greenhouse Effect?
2) What Are Greenhouse Gases?
3) How Does the Greenhouse Effect Work?
4) Causes of the Greenhouse Effect
5) Effects of the Greenhouse Effect
6) Conclusion
What is the Greenhouse Effect?
The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon that helps regulate Earth's temperature, making it suitable for the survival of humans, plants, animals, and bacteria. This can be achieved through certain heat-trapping gases. These include Carbon Dioxide (CO2), water vapour and Methane.
When the Sun’s energy reaches the Earth, some of this energy is reflected back to the atmosphere and then to space, while the rest of the energy is absorbed. The one that is absorbed warms our planet. However, the energy that is absorbed is also radiated back to the atmosphere.
What Are Greenhouse Gases?
Greenhouse gases are primarily the atmospheric gases that impact the balancing of energy of the earth by causing the Greenhouse Effect to occur. The most well-known greenhouse gases, such as Carbon Dioxide (CO₂), Methane, and Nitrous Oxide occur in a natural state in low concentrations. However, scientists have noticed a significant rise in their levels since the early 20th century due to human activities.
While these trace gases are present in minimal amounts, water vapour is the most significant Greenhouse gas. It primarily influences the natural Greenhouse effect because its absorption capacity is directly related to temperature. Consequently, water vapour has a limited impact on human-induced climate change.
Start your ISO 14001 Foundation Certification Training today and enhance your Environmental Management skills!
How Does the Greenhouse Effect Work?
The Greenhouse Effect works through a series of steps:
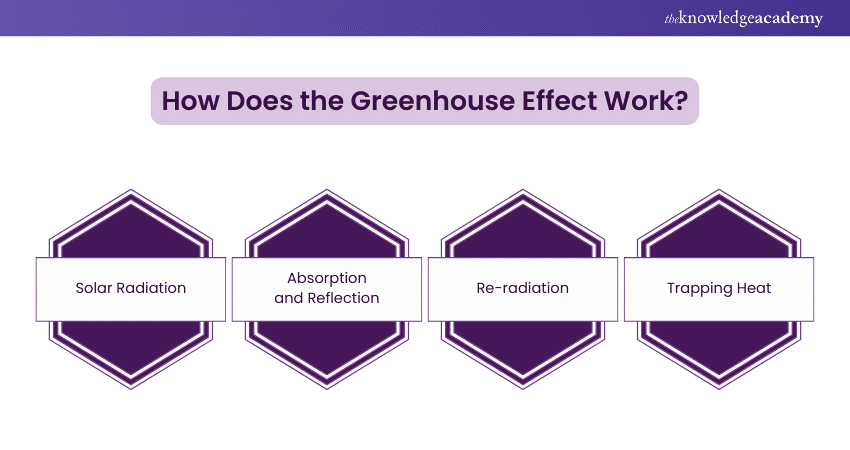
a) Solar Radiation: The Sun releases energy in the form of solar radiation. This radiation reaches the Earth’s atmosphere.
b) Absorption and Reflection: Some of the solar energy is absorbed by the Earth’s surface, warming it, while the rest is reflected back into space by clouds, ice, and other reflective surfaces.
c) Re-radiation: The Earth’s surface, now warm, emits energy in the form of infrared radiation.
d) Trapping Heat: Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb much of this infrared radiation and re-radiate it in all directions, including back towards the Earth’s surface. This trapping of heat is what keeps our planet warm.
Achieve ISO 14001 Certification for sustainable business practices - join our ISO 14001 Certification Training to make a positive environmental impact!
Causes of the Greenhouse Effect
The Greenhouse Effect is driven by various factors that influence our climate. The following are the major causes of the Greenhouse Effect are:
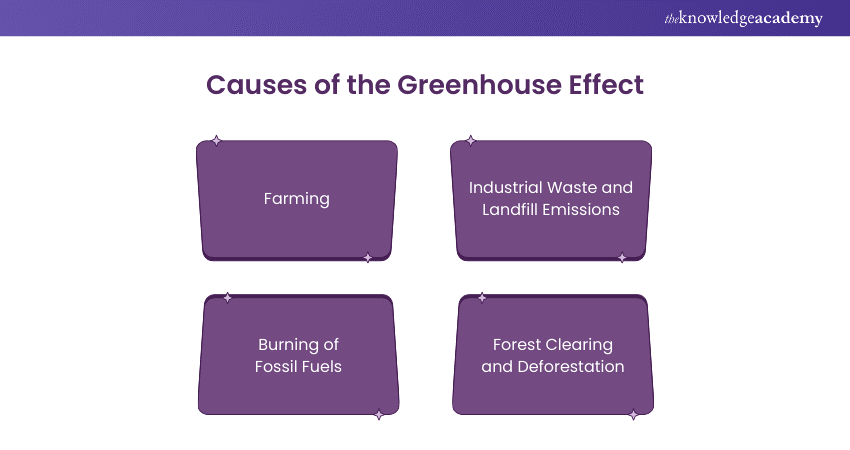
1) Farming
a) Animals like Cows and Sheep produce large amounts of Methane gas during their digestive-driven properties. This can be achieved through a process known as Enteric Fermentation.
b) Certain agricultural practices, particularly rice cultivation in waterlogged soils, results in forming of the Anaerobic conditions. This phenomenon results in the significant release of Methane, a powerful Greenhouse gas.
c) The use of Nitrogen-based fertilisers in agriculture also contributes to Greenhouse gas emissions. This can be achieved through the release of Nitrous Oxide, a highly potent and sustainable gas, into the atmosphere.
2) Industrial Waste and Landfill Emissions
a) Various industries produce waste materials, including chemical byproducts and gases. This releases Greenhouse gases into the atmosphere during disposal or processing.
b) Landfills generate Methane as organic waste decomposes without Oxygen in Anaerobic conditions.
c) Industrial processes, such as manufacturing and chemical production, emit a mix of Greenhouse gases. These include Carbon Dioxide (CO2), Methane, and Nitrous Oxide, which further intensify global warming.
3) Burning of Fossil Fuels
a) The primary source of CO2 emissions is the combustion of fossil fuels.
b) Using petroleum, coal, and natural gas emits enormous amounts of CO2, enhancing the Greenhouse Effect.
4) Forest Clearing and Deforestation
a) The main source of CO2 emissions is burning Fossil Fuels for releasing energy, transportation, and industrial processes.
b) The use of petroleum, coal, and natural gas releases large quantities of CO2 into the atmosphere. This further intensifies the Greenhouse Effect and global warming.
Gain expertise in ISO 14001 Lead Auditor Course - sign up now and become a Certified Lead Auditor!
Effects of the Greenhouse Effect
The enhanced Greenhouse effect has far catastrophic consequences on our planet. It can impact our environment, climate, and human health in several ways. Below, we have listed some of its key harmful effects:
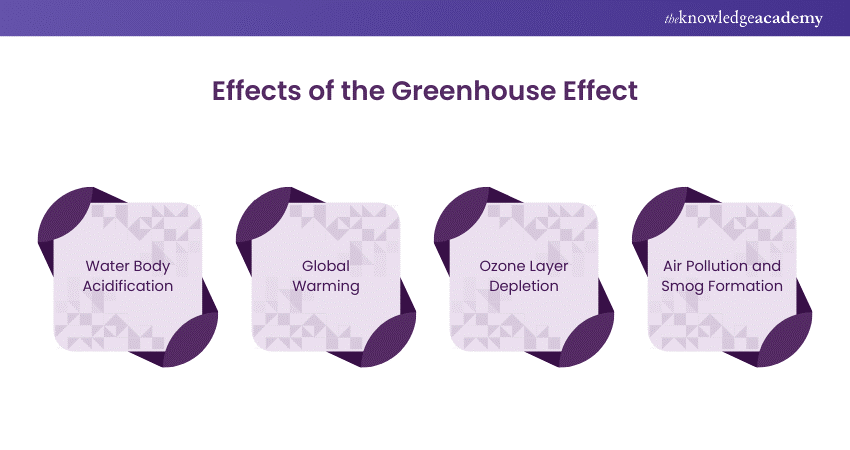
1) Water Body Acidification
The increase in Greenhouse gases has led to the Acidification of several global water bodies. These gases mix with rainwater, causing Acid Rain, which in turn acidifies rivers, streams, and lakes. Additionally, this rainwater can carry contaminants into these water bodies, further contributing to their Acidification.
2) Global Warming
Global Warming refers to the sudden surge (typically takes around hundredths to thousandths years) in the Earth’s average Atmospheric Temperature. This phenomenon is mostly caused by the release of huge amounts of Greenhouse gases like CO2 and Methane.
3) Ozone Layer Depletion
The Ozone layer, located in the Stratosphere's uppermost layer, protects the Earth from the sun's harmful Ultraviolet (UV) rays. Depletion of this layer allows more UV rays to reach the Earth’s surface. This further can potentially cause Skin Cancer and significant climate changes. The primary causes of ozone depletion are Greenhouse Gases, including Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), Carbon Dioxide, and Methane.
4) Air Pollution and Smog Formation
Smog, which is a combination of smoke and fog, can be caused through the occurrence of result both natural as well as human activities. It is typically formed by the accumulation of Greenhouse gases, including Nitrogen and Sulphur Oxides. A few of the major contributors to Smog are emissions from vehicles and industries, agricultural fires, and the chemical reactions among these catastrophic pollutants.
Master Environmental Management with expert ISO 14097 Training – register now!
Conclusion
Understanding What is the Greenhouse Effect is critical for everyone for tackling climate change in a safe and sustainable manner. By knowing about its causes, effects, and solutions, we can motivate ourselves to take impactful and efficient actions for contributing to the well-being of our planet. Are you ready, then? Remember, every single drop contributes to the vast ocean. Let's become that drop and join that ocean to protect our planet for future generations to come.
Transform with ISO 14097 - start your ISO 14097 Greenhouse Gas Management Training journey today!
Frequently Asked Questions

Greenhouse gases are created through various human activities, such as burning Fossil Fuels, cutting trees, industrial processes, agriculture, and waste decomposition. These activities release a huge number of gases, including Carbon Dioxide and Nitrous Oxide, into the atmosphere.

Joseph Fourier first proposed in 1824 that the Earth's atmosphere traps heat, acting like a blanket. Later, John Tyndall, in 1859, expanded on this idea by identifying specific gases. These include Carbon Dioxide and water vapour, which contribute to the Greenhouse Effect by absorbing and radiating Infrared radiation.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various ISO 14097 Training, including ISO 14097 Greenhouse Gas Management Training. This course caters to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Environmental Aspects and Impacts Register.
Our Health & Safety Blogs cover a range of topics related to Greenhouse Effect, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Health and Safety skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Health & Safety Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 ISO 14097 Greenhouse Gas Management Training
ISO 14097 Greenhouse Gas Management Training
Thu 1st Jan 1970







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


