We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +358 942454206 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
In an increasingly digitised world where information is as valuable as currency and data is gold, the need for security has never been more urgent. For malicious actors, your private information is just a few clicks or codes away. This is where Data Encryption comes in as the trusty guardian, safeguarding corporate and personal data by transforming plain text into unreadable code accessible only to those with the correct keys.
This comprehensive blog dives into the essentials of Data Encryption, detailing its benefits, practical applications, examples and future trends. So read on and choose the gold standard in fortifying your digital life!
Table of Contents
1) What is Data Encryption?
2) How Encryption Works?
3) The Importance of Data Encryption
4) Types of Data Encryption
5) Challenges to Contemporary Encryption
6) Examples of Encryption Algorithms
7) Emerging Trends in Data Encryption
8) Conclusion
What is Data Encryption?
Data Encryption is a security technique that translates data into code (or ciphertext) that can be read only by people with access to a password or secret key. Cryptography is the science involving encryption and decryption of information. Data Encryption shields data from being changed, stolen or compromised.
However, to protect data, the decryption key must be kept secret from unauthorised access. Every data can be encrypted, including data at rest (stored in fixed locations like a hard drive) or in transit (being transferred over a network).
How Encryption Works?
Data is encrypted using algorithms and cryptography, resulting in ciphertext. Ciphertext is the end result of encryption performed on plaintext. It can only be read when it has been decrypted with a key, which converts it back to plaintext.
In the case of data at rest, such as information on laptops, whole disk encryption can ensure that every sensitive data is encrypted. Additionally, data can be encrypted file by file, or if a vast amount of data needs to be encrypted, databases can be encrypted through database server software.
The Importance of Data Encryption
With the digital landscape inundated with data, data is more accessible and desirable to attackers than ever, thus increasing the need for protection. Additionally, numerous businesses face data protection regulation requirements, which explicitly require encryption. Here are the benefits of Data Encryption:
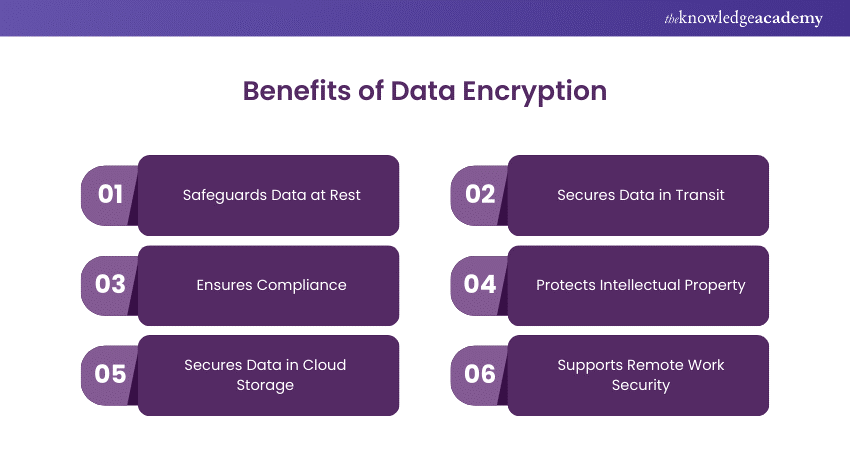
Safeguards Data at Rest
Data stored on a fixed location, such as a server, device, or database, is referred to as “data at rest.” Unauthorised individuals can physically or remotely gain access and retrieve the stored data. Thanks to decryption, encrypting data at rest, without the decryption key, malicious actors won’t be able to interpret the data even if they obtain the storage medium.
This helps ensure that confidential corporate information, personal data, and other sensitive records remain inaccessible and useless to anyone without authorisation.
Secures Data in Transit
Data transferred between systems or devices over a network is particularly vulnerable to unauthorised access and tampering. Encryption protects data in transit by ensuring only authorised parties with the right decryption keys can access the information.
As more employees use mobile devices for accessing company data, the risk of data breaches rises. Data Encryption can protect the sensitive information stored on the devices and the data transmitted between these devices and company networks.
Ensures Compliance
A lot of industries are subject to strict regulations regarding the data protection. For example, financial institutions must adhere to Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). By implementing Data Encryption, businesses can ensure they meet regulatory requirements and avoid penalties or fines penalties for non-compliance.
Protects Intellectual Property
Intellectual property, including proprietary algorithms, trade secrets, and product designs, is often a business's lifeblood. Protecting such information is essential for maintaining a competitive edge and avoid corporate espionage. Encryption can help fortify intellectual property by ensuring that even if an unauthorised party gains access, they cannot decipher the encrypted information.
Secures Data in Cloud Storage
While cloud storage offers plenty of benefits, including reduced infrastructure costs and increased accessibility, it also presents some security challenges. One of the main concerns for businesses that use cloud storage is the security of their data stored on cloud servers.
Data Encryption delivers an additional layer of protection, ensuring that unauthorised parties can't access the encrypted data without the correct decryption keys.
Supports Remote Work Security
With more employees choosing to work from home or other remote locations, the risk of security incidents such as data breaches has increased. Data Encryption ensures that the encrypted data remains secure even if the remote employees' devices or connections are compromised.
Stay ahead of digital manipulators by signing up for our comprehensive Social Engineering Training!
Types of Data Encryption
When it comes to the main categories of Data Encryption, you can find in-transit-based encryption and Data Encryption at rest. These two types are explored below:
Encryption in Transit
Data Encryption in transit refers to the process of encrypting data while it's being transported over a network between two systems or devices. You must ensure both in-transit and at-rest Data Encryption for the best results. Things can go wrong if you have encryption on your disk but not the network.
Encryption at Rest
This is a type of Data Encryption when it's being “at rest” or stored in a device or system, such as database, hard disk, or cloud storage. This technique guarantees that the data is secure from theft and unauthorised access, even if a system is compromised.
Challenges to Contemporary Encryption
The primary method of attack on encryption today involves trying random keys until the right one is found. However, the length of the key determines affects the plausibility of this type of attack. While encryption strength is directly proportional to key size, the number of resources to perform the computation increases with the key size increases.
Alternative methods of breaking a cipher include:
1) Side-channel Attacks: These attacks target the cipher's implementation rather than the cipher itself. These attacks succeed if there's an error in system design or execution.
2) Cryptanalysis: Cryptanalysis means detecting a weakness in the cipher and exploiting it. This type of attack is more likely to occur when there's a flaw in the cipher itself.
Examples of Encryption Algorithms
Encryption algorithms turn data into ciphertext. These algorithms use the encryption key to predictably alter the data so that, even though the encrypted data appears random, it can be turned back into plaintext using the decryption key. Some of the best-known encryption algorithms include the following:

1) 3DES Encryption: 3DES, short for Triple Data Encryption Standard, is a symmetric key algorithm, where data is passed through the original DES algorithm three times throughout the encryption process. Triple DES is a reliable hardware encryption solution for financial services and other industries.
2) AES encryption: AES, short for Advanced Encryption Standard, was created to update the original DES algorithm. Some of the more common applications of this algorithm include messaging apps such as WhatsApp or Signal and the file archiver program called WinZip.
3) RSA Encryption: RSA, short for Rivest, Shamir, and Adleman (surnames of the mathematicians who described this algorithm), was the first asymmetric encryption algorithm available to the public. RSA's popularity is due to its key length.
4) Twofish Encryption: Used in software and hardware, Twofish is deemed one of the fastest of its kind. Since Twofish is not patented, it's freely available to anyone and can be found bundled in encryption programs such as GPG, PhotoEncrypt, and the open-source software TrueCrypt.
5) RC4 Encryption: This one is used in WPA and WEP, which are encryption protocols used in wireless routers.
Want to become a pro in identifying and mitigating digital threats? Sign up for our Cyber Security Risk Management Course now!
Emerging Trends in Data Encryption
Now that we have explored the benefits and examples of Data Encryption, let's explore a few trends that are likely to drive the development of this technology in the future
Field-level Encryption
This refers to the ability to encrypt data in fields on a web page, such as social security numbers, credit card numbers, bank account numbers and health information.
Sequential Link Encryption
This method encrypts data as it leaves a host, then decrypts it on the next network link (a relay point or a host), and re-encrypts it again before sending it to the next link. Every link can utilise a different algorithm or key to encrypt data, which repeats until the data reaches the receiver.
Network-level Encryption
This applies cryptographic services at the network forwarding layer, which is above the data link layer but below the application layer. Level 3 encryption is accomplished through Internet Protocol security (IPsec). Combined with IETF standards, it forms a framework for private communications in IP networks.
Bring Your Own Encryption (BYOE)
This Cloud Computing security model, also known as Bring Your Own Key (BYOK), enables cloud service customers to manage their encryption keys using their very own encryption software. it allows customers to deploy virtualised instances of the encryption software alongside cloud-hosted business applications.
Encryption as a Service (EaaS)
This is a subscription model in which cloud providers deliver encryption on a pay-per-use basis. This approach addresses concerns regarding compliance and equips customers with the capabilities to secure data in multi-tenant environments. This model typically involves full disk encryption (FDE), file encryption or database encryption.
Cloud Storage Encryption
This is a service in which cloud storage providers leverage encryption algorithms to safeguard data saved to cloud storage. Cloud customers must take the time to understand the provider procedures and policies regarding key management to match the confidentiality level of their self-managed encrypted data.

End-to-end Encryption (E2EE)
E2EE ensures an attacker cannot see the data transmitted across a communication channel. Transport Layer Security (TLS) creates an encrypted channel between web servers and clients. However, it does not always guarantee E2EE, because attackers can still access the content before it is encrypted and just after the server decrypts it.
Conclusion
In a world where digital threats are slowly but surely overshadowing every other kind of threat, Data Encryption is the ultimate defence against unauthorised access. This process ensures privacy and security by transforming sensitive information into unreadable code. More than just a smart choice, embracing the powers of encryption as detailed in this blog is essential for fortifying your digital life.
Become more effective in responding to cyber threats with our up-to-date Cyber Security Awareness Course - Sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions

Yes, encrypted data can be deleted. Encryption doesn’t prevent data from being deletion; it only prevents unauthorised access to its contents. Yes, encrypted data can be deleted. Encryption doesn’t prevent data from being deletion; it only prevents unauthorised access to its contents.

When your data is encrypted, it transforms its original, readable form into an unreadable format called ciphertext. This process ensures that only authorised parties with the right decryption key can access sensitive data.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Cyber Security Courses, including the Cyber Security Awareness Course and the Fraud Analytics Training Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Cyber Resilience Framework.
Our IT Security & Data Protection Blogs cover a range of topics related to data security, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your data protection skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Introduction to System and Network Security
Introduction to System and Network Security
Fri 17th Jan 2025
Fri 21st Mar 2025
Fri 16th May 2025
Fri 18th Jul 2025
Fri 19th Sep 2025
Fri 21st Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


