We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +358 942454206 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Have you ever wondered How Virtual Reality Works? How can a headset make you feel like you’re flying around a city when you’re just sitting in your room? There’s more to this technology than just replacing what we can see with something more striking. In this blog, you will learn How Virtual Reality Works and the components and features of Virtual Reality systems. Read further to get a better understanding.
Table of Contents
1) What is Virtual Reality?
2) How Does Virtual Reality Work?
a) Hardware components
b) Software processing
c) Immersive environment
d) User interaction
3) Key features of Virtual Reality systems
4) Conclusion
What is Virtual Reality?
Virtual Reality is a computer-generated simulation that immerses users in a three-dimensional environment. This technology employs specialised hardware, such as VR headsets, to create a synthetic reality that users can interact with. By engaging multiple senses, including sight and sound, VR aims to replicate a lifelike experience. It is used in various fields, from gaming and entertainment to education, offering users a unique and immersive way to interact with digital environments.
How Does Virtual Reality Work?
Virtual Reality (VR) operates through a combination of advanced hardware and software, creating immersive digital experiences. Here's an expanded explanation:
Hardware components
Hardware components include the following:
a) Headset: Users wear VR headsets equipped with displays, lenses, and sensors.
b) Sensors: Track head and body movements for a responsive experience.
c) Controllers: Input devices that enable users to interact with the virtual environment.
Explore cutting-edge technologies with our Advanced Technologies Courses for a future-ready skill set. Elevate your expertise today!
Software processing
Software processing is another important step which includes:
a) Graphics rendering: Powerful computers process high-quality graphics to simulate realistic environments.
b) Stereoscopic display: VR presents two images, one for each eye, creating depth perception.
c) Head tracking: Sensors constantly update the user's viewpoint based on head movements for a dynamic experience.
Immersive environment
An immersive environment is a result of the following components:
a) 3D audio: Surround sound or spatial audio enhances realism, reacting to the user's position.
b) Haptic feedback: Some systems incorporate tactile sensations, allowing users to feel virtual objects.
User interaction
User interaction is achieved through the features given below:
a) Hand tracking: Advanced systems enable users to manipulate virtual objects with hand gestures.
b) Real-time feedback: Immediate response to user actions ensures a seamless and immersive VR encounter.
Explore the future of technology with our Introduction to Virtualisation Technologies Course. Join now for advanced skills and hands-on expertise!
Key features of Virtual Reality systems
Discussed below are some of the key features of Virtual Reality systems:
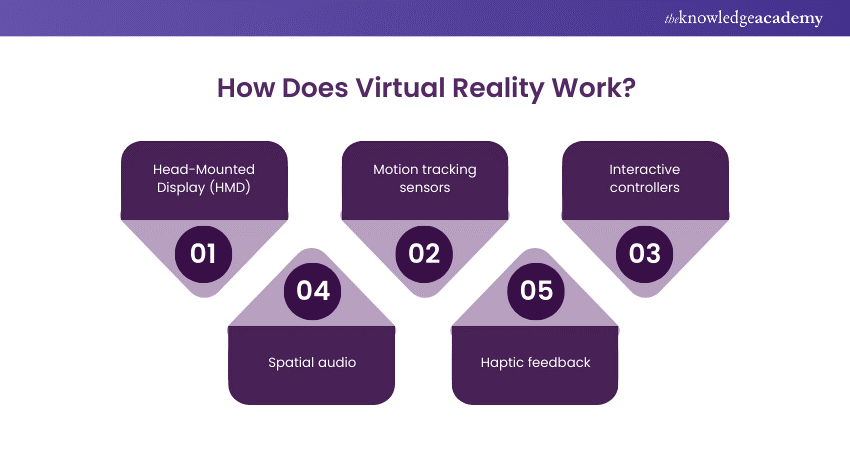
a) Head-Mounted Displays (HMDs): Central to VR systems, HMDs are wearable devices that include screens and lenses, providing users with immersive visual experiences. These displays often track head movements, adjusting the view in real time.
b) Motion tracking sensors: Essential for user interaction, motion tracking sensors monitor the movements of the user's head and sometimes the entire body. This technology enables accurate rendering of virtual environments based on the user's position and orientation.
c) Interactive controllers: Controllers, such as handheld devices or gloves, facilitate user input in the virtual space. They enable actions like grabbing, pointing, and manipulating objects, enhancing the sense of presence.
d)Spatial audio: VR systems incorporate spatial audio to simulate 3D soundscapes. This creates a more immersive experience by allowing users to perceive audio from specific directions, contributing to a realistic and dynamic environment.
e) Realistic graphics and rendering: High-quality graphics and rendering are crucial for creating lifelike virtual environments. Advanced systems focus on delivering realistic textures, lighting, and shading, enhancing the overall visual fidelity.
f) Haptic feedback: Some VR systems integrate haptic feedback mechanisms, providing users with tactile sensations. This can include vibrations, resistance, or other feedback, enhancing the sense of touch and making virtual interactions more convincing.
Conclusion
As we have learned, Virtual Reality uses special gadgets like headsets and sensors to make you feel like you're in a different world. These gadgets show you things that look real and move as you move, fooling your senses. We hope this blog answered your question on How Does Virtual Reality Works.
Transform your expertise in Virtual Reality with our comprehensive Virtual Reality (VR) Training. Sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions

Virtual Reality (VR) is a computer-generated simulation that immerses users in lifelike environments. Achieved through specialised hardware like VR headsets, VR replicates sensory experiences, enabling users to interact with and walk around the digital surroundings.

Virtual Reality works by using special devices like headsets that immerse users in computer-generated environments. These headsets have screens and sensors that track your movements, adjusting what you see in real-time. Combined with realistic graphics and spatial audio, VR creates an illusion of being in a different world.

For a basic VR setup, you need a compatible VR headset, a computer or gaming console with adequate processing power and graphics capabilities, and motion-tracking controllers for interaction. Some VR systems may require external sensors for precise tracking. Ensure your hardware meets the specifications of the VR content you intend to explore and consider a comfortable space for immersive experiences.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, blogs, videos, webinars, and Interview Questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Advanced Technologies Courses, including Introduction to Virtualisation Technologies, Internet of Things IoT Systems and Applications Training etc. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into “What is the Metaverse?”
Our Advanced Technology blogs cover a range of topics related to Virtual Reality, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Advanced Technology skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.

The Knowledge Academy’s FlexiPass is a pre-paid training voucher that is built specifically for clients and their dynamic needs. It provides access to a wide range of courses at a pre-determined price, with robust safety measures. FlexiPass gives clients the added benefit of upskilling on a budget that best fits them.
Upcoming Advanced Technology Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Virtual Reality (VR) Training
Virtual Reality (VR) Training
Fri 10th Jan 2025
Fri 14th Mar 2025
Fri 9th May 2025
Fri 11th Jul 2025
Fri 12th Sep 2025
Fri 14th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


