We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +358 942454206 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

In the modern era, efficient communication stands as a cornerstone for successful business operations. With this emphasis on seamless interaction, the role of reliable email servers has become paramount. Enter Microsoft Exchange Server: a stalwart in the domain of enterprise-level email, calendaring, and communication solutions. But like any advanced software, it has its unique set of requirements. In this blog, we will guide you through the several intricate prerequisites and requirements to use Microsoft Exchange Server to your advantage.
Table of Contents
1) Microsoft Exchange Server Requirements
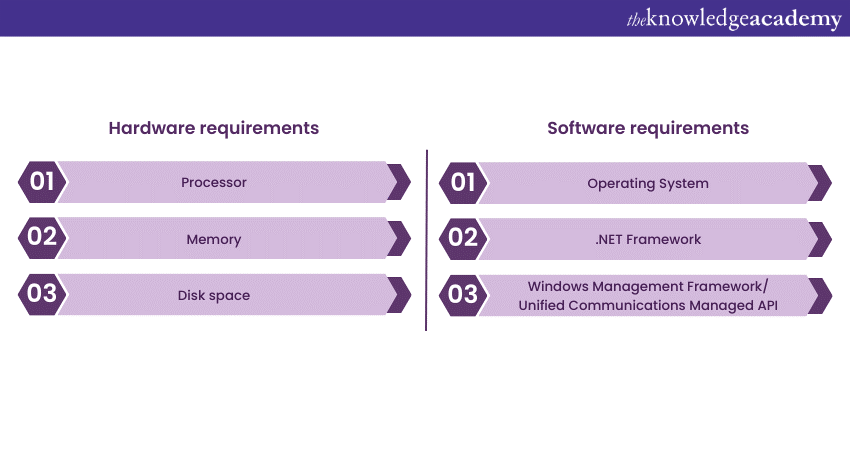
a) Hardware requirements
b) Software requirements
c) Database requirements
d) Client access requirements
e) Network and security considerations
f) Architectural recommendations
2) Conclusion
Microsoft Exchange Server Requirements
This section of the blog will dive into the different Microsoft Exchange Server Requirements.
Hardware requirements
Every piece of software has its unique hardware needs, and the Microsoft Exchange Server is no exception. Ensuring your hardware meets or exceeds these specifications will greatly enhance performance and reliability.
a) Processor
The Microsoft Exchange Server operates optimally on a 64-bit processor. However, the specifics, such as the number of cores and speed, often depend on the precise version of Exchange you're using, as well as your anticipated workload. For businesses expecting high email traffic, investing in a faster, multi-core processor is a wise choice.
b) Memory
RAM serves as a foundation for any software's operational efficiency. Different roles within the Exchange Server have varying memory needs. For instance, if you designate your server to be primarily responsible for the mailbox role, you'd require considerably more memory compared to if it was just taking on an edge transport role. It’s also essential to note that as your user base grows, so too might your memory requirements.
c) Disk space
Apart from the initial space required for the software installation, one must factor in the space for logs, databases, updates, and user mailbox growth. Over time, the amount of email data can grow exponentially, especially in larger organisations. Planning for this growth is crucial to avoid potential disruptions or the need for unplanned hardware changes.
Unlock the full potential of Exchange Server by joining our comprehensive Administering Microsoft Exchange Server 2016/2019 M20345-1 Course today!
Software requirements
The stability and efficiency of the Exchange Server are as much about the software environment as they are about the hardware.
a) Operating System (OS)
Historically, Microsoft Exchange Server has been designed to run optimally on certain editions of Windows Server. As both products evolve, ensuring you're running a version of Windows Server that's fully supported by your chosen Exchange Server edition is paramount.
b) .NET Framework
.NET Framework serves as a backbone for many Microsoft applications, including Exchange Server. Depending on which version of Exchange you’re implementing, there will be a specific version of the .NET Framework that it's compatible with. Ensuring alignment between these two can prevent many potential issues.
c) Other essential software requirements
Several other software prerequisites might be necessary depending on your Exchange Server version. These can include the Windows Management Framework (WMF), which provides task automation and configuration management, and the Unified Communications Managed API, which is necessary for voice messaging and other communication features.
Unlock the full potential of Microsoft Exchange with our expert-led Microsoft Exchange Server Training!
Database requirements
The very foundation of the Microsoft Exchange Server is its database – a repository where emails, contacts, calendars, and other essential data reside. It's paramount to select storage that delivers high availability and rapid access. Often, larger organisations employ Database Availability Groups (DAGs) to ensure continuous mailbox access, even amidst failures.
Proper configuration is vital to prevent data loss and ensure smooth data retrieval. Moreover, considering the growth trajectory of the organisation can help in forecasting storage needs, thus avoiding potential disruptions or the need for abrupt scaling.
Deploy Microsoft Exchange Server in Linux – Get Started with Compatibility and Installation!
Client access requirements
The Microsoft Exchange Server’s efficacy is also gauged by how seamlessly clients can access it. The server must support various protocols, including POP, IMAP, and MAPI, to ensure uninterrupted access. The configuration should align with the kind of devices clients use, be it desktop computers, laptops, tablets, or smartphones.
Furthermore, the experience should be optimised for both internal networks and external access, especially for remote workers. This not only implies technical compatibility but also encompasses the user experience, ensuring that accessing emails and other features is intuitive and straightforward.
Network and security considerations
Deploying Microsoft Exchange Server goes beyond just the software; it’s about safeguarding one of an organisation's primary communication channels. On the network front, ensuring optimal configurations for Exchange traffic, such as proper port settings, can prevent lags and disruptions. Security, however, is paramount.
Implementing Secure Socket Layer (SSL) certificates can encrypt communications between the client and the server. Additionally, configuring firewalls to protect against external threats while not hindering Exchange Server traffic is a delicate but crucial balance. Regular security audits and updates are indispensable to ensure protection against evolving cyber threats.
Prepare for Success with Microsoft Exchange Server Interview Questions – Start Learning!
Architectural recommendations
The architectural foundation of your Exchange Server setup can have long-term implications on its performance, scalability, and maintenance.
1) On-premises: Traditionalists might prefer this method, where the entire setup is housed within the organisation. This provides direct control over the hardware and software but comes with the responsibility of regular maintenance and manual upgrades.
2) Cloud-based: As the tech world increasingly embraces the cloud, many are opting for Exchange Online, Microsoft’s cloud-based solution. This offers scalability and eliminates the need for manual updates. However, control is somewhat reduced as servers are managed by Microsoft.
3) Hybrid setup: For those unwilling to commit entirely to either end of the spectrum, there's the hybrid option. This combines on-premises and cloud, offering a balance between control and scalability.
Conclusion
To sum it up, deploying and optimising Microsoft Exchange Server demands one to adhere to several Microsoft Exchange Server Requirements. By understanding its database, client access, and network security intricacies, businesses can ensure robust, secure, and seamless communication channels. As with all technological endeavours, staying updated and proactive is the key to maximising value and efficiency.
Unlock expert skills in Exchange Server by joining our Designing And Deploying Microsoft Exchange Server 2016/2019 M20345-2 Course today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Microsoft Technical Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Retired : Administering Microsoft Exchange Server 2016/2019 M20345-1
Retired : Administering Microsoft Exchange Server 2016/2019 M20345-1
Mon 13th Jan 2025
Mon 17th Feb 2025
Mon 18th Aug 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


