We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +358 942454206 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Managing multiple IT service providers can be a complex puzzle. To ensure seamless service delivery and optimal business outcomes, a robust framework is essential. Enter the SIAM Operating Model. This strategic blueprint outlines the governance, roles, responsibilities, and processes for managing an intricate IT ecosystem.
By understanding the intricacies of the SIAM Operating Model, organisations can unlock its potential for cost reduction, improved service quality, and enhanced Risk Management. Let's delve into the details of this transformative approach.
Table of Contents
1) What is a SIAM Model?
2) SIAM Operating Model's key Factors
3) How to Make a SIAM Operating Model?
4) Advantages of a SIAM Operating Model
5) SIAM Operating Model Challenges
6) Conclusion
What is a SIAM Model?
Service Integration and Management (SIAM) is a management methodology that coordinates and governs multiple service providers to deliver a cohesive service experience to an organisation. Unlike traditional models where a single vendor provides all services, SIAM integrates multiple service providers—both internal and external—into a unified framework.
This approach ensures that all services are aligned with the organisation's objectives and are managed cohesively to deliver consistent quality. The SIAM Model helps in mitigating complexities associated with multi-sourcing, optimising service delivery, and improving governance and accountability.
SIAM Operating Model's key Factors
Here are the key factors of SIAM Operating Model:
1) Change is Hard!
Implementing a SIAM Model involves significant organisational change, which can be challenging. The transition from a single service provider or a less structured multi-provider environment to a SIAM Model requires careful planning and management. Resistance to change is a common hurdle, as stakeholders may be accustomed to existing processes and reluctant to adopt new methodologies.
Therefore, effective change management strategies are crucial. This includes clear communication of the benefits of SIAM, training and support for staff, and involving key stakeholders in the transition process. A well-managed change process helps in minimising disruptions and ensures a smoother transition to the SIAM Model.
2) A SIAM Operating Model isn't just ITSM
While IT Service Management (ITSM) focuses on optimising and managing IT services, a SIAM operating model extends beyond IT. It integrates various service domains, including IT, HR, finance, facilities, and more. This holistic approach ensures that all service areas work together seamlessly, providing a unified service experience.
SIAM requires a broader set of skills and knowledge beyond traditional ITSM, as it involves managing relationships, governance, and integration across different service domains. The key is to view SIAM as a comprehensive management approach rather than just an extension of ITSM, ensuring that all service areas align with the organisation's strategic objectives.
3) Changing Existing Contracts is Hard
One of the major challenges in implementing a SIAM Model is the modification of existing contracts with service providers. These contracts may not initially support the collaborative and integrated nature of a SIAM Model. Changes might be needed to include new performance metrics, reporting requirements, and collaboration clauses that facilitate integration among different providers.
Navigating these changes can be intricate and time-consuming, frequently necessitating legal consultation and meticulous negotiation to secure agreement from all parties on the revised terms. This highlights the critical need for flexible and adaptable contracts that can accommodate the ever-evolving nature of a SIAM environment.
4) A SIAM Operating Model Requires a Strategy
A successful SIAM implementation requires a well-defined strategy. This strategy should outline the objectives of adopting SIAM, the expected benefits, and the steps involved in the transition. It should also address governance structures, roles and responsibilities, performance metrics, and Risk Management strategies.
A well-defined SIAM strategy ensures that all stakeholders comprehend the goals and work in harmony towards them. It aids in setting realistic expectations and timelines, enabling the organisation to track progress and make necessary adjustments. This strategy should be regularly updated to reflect any changes in organisational objectives or the external environment.
5) Don't Presume that Everyone is Knowledgeable Enough
A common pitfall in implementing SIAM is assuming that all stakeholders have a sufficient understanding of the model and its implications. The complexities of SIAM, involving coordination between multiple service providers and the integration of diverse services, require a deep understanding of the model's principles and practices.
Therefore, it is crucial to invest in education and training for all involved parties, including internal staff and external service providers. Workshops, training sessions, and regular updates can help ensure that everyone possesses the essential knowledge and skills to operate effectively within a SIAM framework. This educational component is vital for the successful adoption and ongoing management of the SIAM Model.
Master Service Integration with SIAM™ Certification! Enroll now to lead multi-vendor IT environments effectively.
How to Make a SIAM Operating Model?
To create a SIAM Operating Model, start by defining clear objectives that align with the organisation's goals, focusing on improving service delivery and coordination. Identify and categorise all internal and external service providers, understanding their roles and contributions. Develop a governance structure with well-defined roles and responsibilities, including a Service Integration Manager or team to oversee the process.
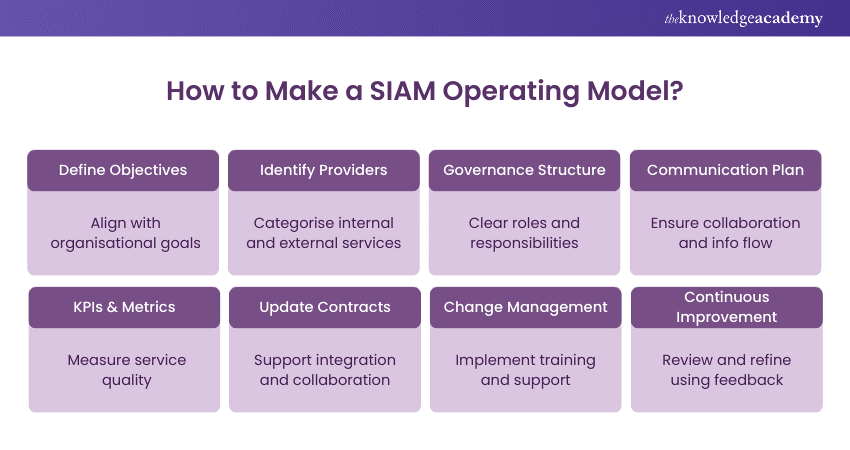
Create a communication plan to ensure effective collaboration and information flow among stakeholders. Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to measure service quality and efficiency. Review and update existing contracts to include clauses that support integration and collaboration among providers.
Implement change management strategies, providing necessary training and support to all involved parties. Finally, continuously review and refine the SIAM Model using performance data and feedback to ensure it remains effective and aligned with the organisation's objectives. This approach helps build a cohesive, efficient, and scalable SIAM framework.
Enhance your skills to lead seamless Service Integration with our SIAM™ Foundation Training- Join now!
Advantages of a SIAM Operating Model
SIAM can be applied globally across various organisations, extending beyond IT services to any environment, sourcing services from multiple providers. One of the significant advantages of SIAM is its adaptability, allowing organisations to draw from other best practices, frameworks, methodologies, and standards used in IT and ITSM.
The benefits of adopting a SIAM Model include:

a) Reduced Operational Risk: Spreads operational risks across multiple service providers rather than relying on a single provider.
b) Greater Access to Expertise: Provides access to top-tier skills across a broad range of suppliers and technologies.
c) Agility in Meeting Demands: Enables organisations to respond swiftly to increasingly complex business demands.
d) Increased Accountability: SIAM contracts and scopes provide transparency, holding service providers accountable for their part of the end-to-end service chain.
e) Increased Flexibility and Nimbleness: Allows easy onboarding and offboarding of service providers, adapting to organisational needs.
Kickstart your IT Management journey with our VeriSM™ Foundation Training -Register now!
SIAM Operating Model Challenges
A SIAM Model must clearly define policies and principles, establishing ownership of roles and responsibilities across its three layers. While SIAM encompasses a process, it goes beyond mere end-to-end process management. Instead, it deepens process management by involving multiple stakeholders in process execution. Due to this complexity, it's crucial to focus on clearly defining roles and responsibilities, adhering to these key principles:
a) Ensure all role definitions are relevant to the SIAM Model.
b) Include necessary knowledge, skills, competencies, and capabilities in each role definition.
c) Incorporate integration and collaboration capabilities where applicable.
d) Separate role definitions for the customer organisation, service integrator, and service providers to prevent duplication or overlap.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the SIAM Operating Model offers a comprehensive framework for managing multiple service providers, enhancing service delivery, and achieving organisational goals. By understanding its key components and implementing best practices, organisations can navigate the complexities of multi-sourcing and foster a collaborative, efficient service environment.
Become a Service Integrator professional with our SIAM™ Professional Training- Sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions

The Service Integrator in SIAM coordinates and manages multiple service providers, ensuring they work together to deliver cohesive and efficient services. They oversee integration, governance, and performance, aligning all services with organisational goals.

Common pitfalls in SIAM implementation include inadequate stakeholder engagement, lack of clear governance structures, insufficient training, and underestimating the complexity of integrating multiple providers. Effective planning and communication are key to avoiding these issues.

Organisations can transition to a SIAM Model by defining clear objectives, establishing a governance structure, identifying and categorising service providers, updating contracts, implementing change management strategies, and continuously refining the model based on feedback and data.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various SIAM™ Training, including the SIAM™ Professional Training, and SIAM™ Foundation Training. These courses cater to different skill levels and provide comprehensive insights into VeriSM.
Our IT Service Management Blogs cover a range of topics related to IT Service Management, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Service Integration Skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course




 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


