We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +358 942454206 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Imagine putting on a headset and being instantly transported to magical lands, futuristic cities, or the ocean's depths. This is where Virtual Reality (VR) takes the reins, blending reality and imagination into a vivid experience. VR isn't just cutting-edge technology; it's a gateway to experiences we once only dreamed of.
The term "Virtual Reality" dates back to 1938, when a French dramatist described the illusory nature of theatre characters as "la réalité virtuelle." While science fiction writers have long envisioned VR, only recently has technology advanced enough to make it a reality!
VR experiences are now mainstream in entertainment, healthcare, the military, business, and more, emerging as a positive force in various ways. As VR technology continues to grow, it promises to transform entertainment, education, and more, turning every moment into an adventure. Join us as we explain What is Virtual Reality and why is it important.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding What is Virtual Reality
2) How does the VR technology work?
3) Different types of Virtual Realities
4) Components of VR technology
5) Key features of Virtual Reality
6) Applications of Virtual Reality
7) Benefits of Virtual Reality
8) Limitations of Virtual Reality
9) What is an Example of Virtual Reality?
10) What is VR Mostly Used For?
11) Conclusion
Understanding What is Virtual Reality
Virtual Reality (VR) is an advanced technology that creates a simulated environment, offering a digital experience drastically different from the real world. Using sophisticated computer graphics, VR replicates real or imagined environments and simulates a user's physical presence in these spaces.
This interaction with an unusual world in a seemingly tangible way is achieved through devices like VR headsets or rooms equipped with projectors, which immerse the user in a 360-degree environment.
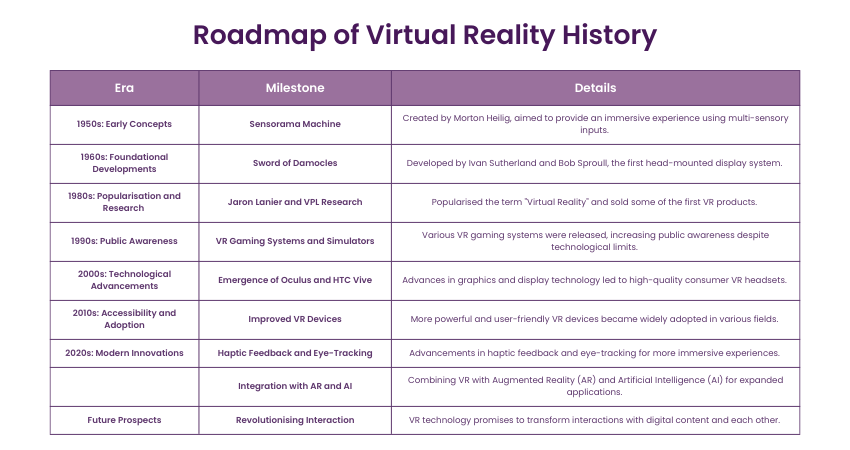
Roadmap of Virtual Reality History
Here's a table summarising the roadmap of Virtual Reality history:
How Does the VR Technology Work?
VR technology operates through a combination of hardware, software, and sensory synchronicity, creating a fully immersive experience. Here's how VR works:
1) Head-Mounted Display (HMD)
a) Utilises a headset or goggles to present the virtual environment.
b) Contains screens and lenses to project images to each eye, creating a stereoscopic 3D effect.
2) Motion Tracking
a) Includes sensors that track the user's head, hand, and body movements.
b) Allows the virtual environment to respond dynamically as the user looks around, moves, or interacts.
3) Input Devices
a) Uses controllers, gloves, or other tools to enable interaction with the virtual world.
b) These devices are tracked for position and orientation, allowing for natural and intuitive interaction.
4) Audio Output
a) Incorporates headphones or is compatible with external audio systems to provide spatial sound.
b) Enhances the realism of the virtual environment with immersive audio.
5) Software
a) Relies on specialised software to generate realistic images, sounds, and other sensations.
b) This software responds to the user's movements, updating the virtual scene accordingly.
6) Processing Power
a) Requires powerful processors and graphics capabilities to render complex virtual environments in real-time.
b) Essential for maintaining immersion and preventing motion sickness by avoiding latency or lag.
Learn more about Advanced Technologies – sign up now for our Advanced Technologies Courses!
Different types of Virtual Realities
Now that you are aware of What is Virtual Reality and how it operates, let’s have a look at its various types. VR has evolved into various forms, each offering unique experiences and catering to different uses. Some of these forms include:
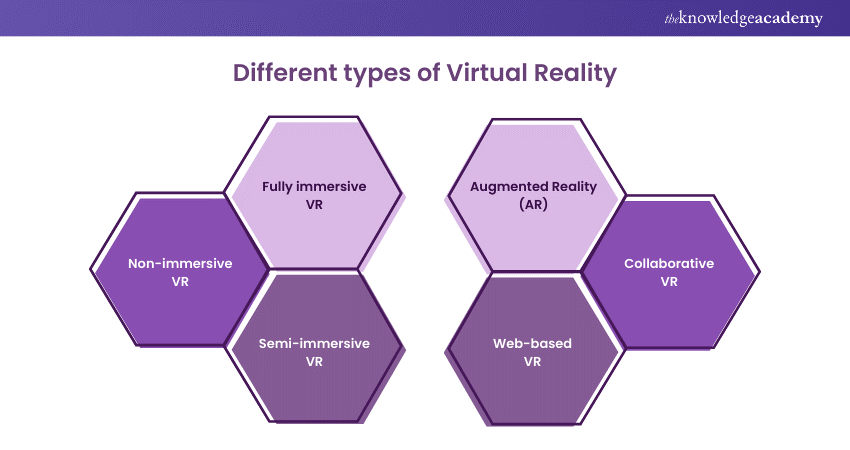
1) Non-immersive VR
a) Experienced on a PC or video game console.
b) Users interact with a virtual environment using a keyboard, mouse, or controller.
c) The 3D world is viewed through a screen.
d) Users remain aware of the real world and are not fully enclosed in the virtual environment.
2) Fully immersive VR
a) Uses Head-Mounted Displays (HMDs) with high-resolution screens.
b) Includes advanced motion tracking and stereo sound.
c) Requires a powerful computer or gaming console.
d) Sensors track movement, and specialised gloves or hand controllers allow interaction within the virtual environment.
3) Semi-immersive VR
a) A hybrid between non-immersive and fully immersive VR.
b) Typically involves large projection systems or multiple screens.
c) Partially immerses the user in a virtual environment.
d) Commonly used for educational and training purposes, such as flight simulators.
4) Augmented Reality (AR)
a) Overlays digital information onto the real world (AR).
b) Users can see and interact with virtual objects in their real environment.
c) Utilises smartphones or AR glasses.
5) Collaborative VR
a) Involves multiple users inhabiting and interacting within the same virtual space.
b) Gaining traction in fields like education and business.
c) Used for virtual classrooms and virtual meeting spaces.
6) Web-based VR
a) Allows users to experience VR through a web browser.
b) Does not require specialised software or powerful hardware.
c) Makes VR more accessible.
d) Ideal for educational content and simple gaming.
Are you interested in learning more about Virtual Reality? Register now for our Virtual Reality (VR) Training!
Components of VR technology
Virtual Reality is an intricate blend of hardware and software components working in unison to create immersive, interactive digital environments. Let’s have a detailed look at its composition:
Hardware Components Utilised in Virtual Reality
The hardware components of Virtual Reality are critical in creating a believable and immersive VR experience. Key hardware elements include:
1) Non-immersive VR
a) Experienced on a PC or video game console.
b) Users interact with a virtual environment using a keyboard, mouse, or controller.
c) The 3D world is viewed through a screen.
d) Users remain aware of the real world and are not fully enclosed in the virtual environment.
2) Fully immersive VR
a) Uses Head-Mounted Displays (HMDs) with high-resolution screens.
b) Includes advanced motion tracking and stereo sound.
c) Requires a powerful computer or gaming console.
d) Sensors track movement, and specialised gloves or hand controllers allow interaction within the virtual environment.
3) Semi-immersive VR
a) A hybrid between non-immersive and fully immersive VR.
b) Typically involves large projection systems or multiple screens.
c) Partially immerses the user in a virtual environment.
d) Commonly used for educational and training purposes, such as flight simulators.
4) Augmented Reality (AR)
a) Overlays digital information onto the real world.
b) Users can see and interact with virtual objects in their real environment.
c) Utilises smartphones or AR glasses.
5) Collaborative VR
a) Involves multiple users inhabiting and interacting within the same virtual space.
b) Gaining traction in fields like education and business.
c) Used for virtual classrooms and virtual meeting spaces.
6) Web-based VR
a) Allows users to experience VR through a web browser.
b) Does not require specialised software or powerful hardware.
c) Makes VR more accessible.
d) Ideal for educational content and simple gaming.
Software employed in Virtual Reality
1) VR Platforms and Development Engines
a) Tools like Unity and Unreal Engine.
b) Used to develop VR content.
c) Provides the framework for creating and rendering 3D environments, incorporating physics, and managing user interactions.
2) Application Software
a) Encompasses specific VR applications and games.
b) Developed for various purposes, from entertainment and gaming to educational and training programs.
3) Simulation Software
a) Vital for professional and educational VR applications.
b) Accurately replicates real-world scenarios and environments for training and learning purposes.
4) User Interface Software
a) Manages the VR system's User Interface.
b) Makes it intuitive and accessible.
c) Allows users to navigate, select, and interact within the VR environment efficiently.
5) Integration Tools
a) Integrates VR systems with other software and hardware.
b) Includes motion capture systems, external sensors, and haptic devices.
c) Enhances the overall VR experience by adding more layers of interactivity and realism.
Enhance your knowledge of Quantum Computing with our Quantum Computing Training!
Key Features of Virtual Reality
Virtual Reality technology is defined by several key features that set it apart from traditional media and gaming experiences. These features are interactivity, immersion, and sensory input, each crucial in making VR a unique and engaging technology. Let’s have a look:
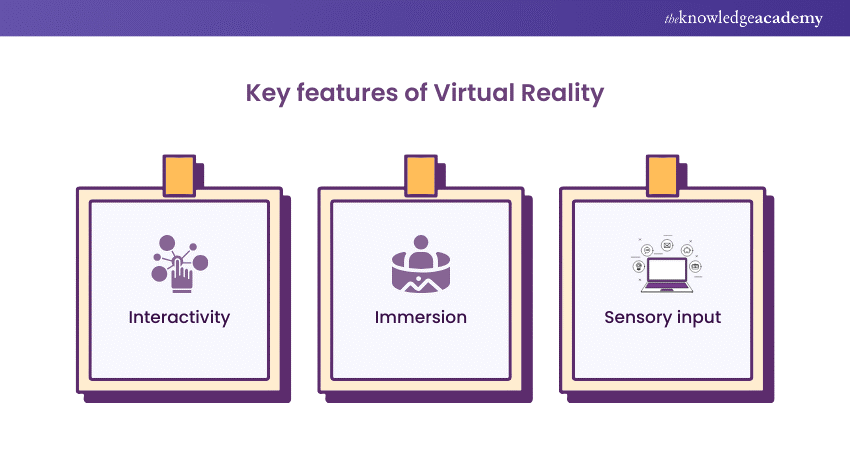
Interactivity
Interactivity in Virtual Reality (VR) allows users to engage meaningfully with the virtual environment through two-way communication. This is facilitated by input devices like motion controllers, gloves, and full-body suits, enabling actions such as grabbing and manipulating virtual objects. The level of interactivity varies, from simple 360-degree viewing to complex interactions, enhancing user engagement and creating a sense of presence.
Example: Surgical Training Simulations
a) Description: Medical professionals use VR to practice surgical procedures. Using motion controllers and haptic feedback devices, they can perform virtual surgeries, allowing them to practice techniques and improve their skills in a risk-free environment.
b) Impact: This interactive training helps surgeons gain confidence and experience, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Immersion
Immersion is the sensation of being physically present in a virtual world. VR achieves this through convincing, interactive environments that surround the user. Immersion can be psychological (emotional investment) or physical (mirroring user movements). High-quality graphics, realistic 3D audio, and responsive interactions contribute to a more immersive experience, maintaining user attention and enhancing realism.
Example: Virtual Tourism
a) Description: Companies like Google Earth VR allow users to explore famous landmarks and cities around the world from the comfort of their homes. Users can "walk" through the streets of Paris, visit the Grand Canyon, or stand on the Great Wall of China.
b) Impact: This immersive experience provides a sense of presence and adventure, making users feel as if they are actually visiting these places.
Sensory input
Sensory input is crucial for creating a believable VR experience. VR primarily uses visual and auditory inputs, with head-mounted displays for 3D views and headphones for 3D sound. Haptic feedback, provided through controllers or suits, simulates touch, enhancing realism. Advanced systems may also incorporate smell and taste. Engaging multiple senses helps create a more convincing and immersive virtual world.
Example: Virtual Reality Therapy
a) Description: VR is used in therapy to treat conditions like PTSD, anxiety, and phobias. For instance, a VR system might simulate a public speaking scenario for someone with social anxiety, complete with realistic visuals and sounds. Haptic feedback can simulate physical sensations, like the feeling of holding a microphone.
b) Impact: Engaging multiple senses helps create a realistic and controlled environment for exposure therapy, aiding in the treatment process.
Do you want to learn more about Nanotechnology? Join us now for our Nanotechnology Training!
Applications of Virtual Reality
Virtual Reality has transcended its initial entertainment applications to become a versatile tool in various fields. Its ability to create immersive, interactive 3D environments has opened innovative possibilities across many sectors, ranging from education and healthcare to industry and beyond.
Let’s see some of these applications in detail:
Education and Training
VR offers immersive learning experiences, such as virtual field trips and biology explorations, enhancing understanding and retention. It also provides safe training environments for high-risk fields like aviation and medicine.
Examples:
a) Google Expeditions: Offers virtual field trips to places like the Pyramids of Giza and the Great Wall of China.
b) 3D Human Anatomy: Allows students to explore the human body in detail.
c) Virtual Space Exploration: Enables students to travel through space and visit planets and stars.
Healthcare and Therapy
VR is used for therapeutic purposes, including exposure therapy for PTSD and phobias, and physical rehabilitation to improve motor skills and coordination.
Examples:
a) Osso VR: Provides realistic surgical training simulations for medical students and surgeons.
b) MindMotion: Used in neurorehabilitation to assist stroke patients in regaining motor skills.
c) Exposure Therapy: Treats PTSD and phobias by gradually exposing patients to their fears in a controlled virtual environment.
Architecture and Real Estate
VR allows virtual tours of buildings before construction, aiding in design understanding and modifications. It also enables remote property exploration for potential buyers.
Examples:
a) Matterport: Creates 3D virtual tours for real estate agents to showcase properties.
b) Virtual Design Reviews: Architects present and modify building designs in a virtual environment before construction.
Retail and Fashion
VR reshapes shopping with virtual stores and allows designers to showcase their creations through virtual runways and fittings.
Examples:
a) IKEA VR Experience: Allows customers to explore and customise kitchen designs.
b) Tommy Hilfiger Virtual Fashion Shows: Offers virtual runways for customers to experience fashion from home.
Gaming and Entertainment
Virtual Reality Gaming provides immersive experiences and is used for virtual concerts, museums, and theme park rides.
Examples:
a) Beat Saber: A popular VR game that provides an immersive gameplay experience.
Louvre Museum's VR Experience: "Mona Lisa: Beyond the Glass" allows visitors to explore the famous painting in a new way.
Automotive Industry
VR aids in car design and manufacturing by allowing virtual model creation and simulating assembly lines to identify issues before physical implementation.
Examples:
a) Ford: Uses VR to design and test new vehicle models.
b) Audi: Employs VR to train employees on assembly line tasks, improving efficiency and reducing errors.
Learn how to evaluate networks and understand architecture and design with our Internet of Things IoT Systems and Applications Training – register now!
Benefits of Virtual Reality
There are some benefits of using Virtual Reality. Let's have a look at these points:
a) Immersive learning and training: It provides a realistic environment for practising skills and experiencing scenarios, enhancing education and professional training.
b) Healthcare applications: Offers new methods for therapy and rehabilitation, aiding in treating psychological disorders and physical recovery.
c) Enhanced entertainment: Transforms User Experience in gaming and media with interactive and engaging content.
d) Design and prototyping: Assists in efficient design and development processes in various industries, such as architecture and automotive, through virtual prototyping and testing.
e) Safe simulation environment: Enables risk-free simulation of dangerous or complex scenarios, instrumental in aviation and medical training.
f) Accessibility to experiences: Allows exploration of places and experiences that might be physically inaccessible, broadening educational and cultural opportunities.
Enhance your knowledge of Satellite Communication – sign up now for our Satellite Communication Training!
Limitations of Virtual Reality
Even though Virtual Reality is being used in almost every industry, there are some limitations. These are:
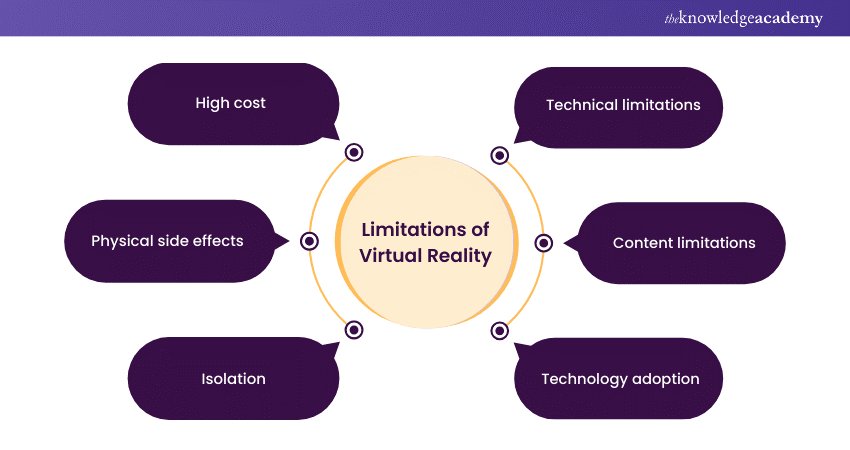
a) High cost: The expense of VR technology, including headsets and necessary hardware, can be prohibitive.
b) Physical side effects: Some users experience motion sickness, eye strain, and disorientation while using VR.
c) Isolation: Virtual Reality experiences can be socially isolating, distracting users from real-world interactions.
d) Technical limitations: Issues like limited resolution and field of view can affect the realism and immersion of Virtual Reality.
e) Content limitations: There is a need for more diverse and high-quality VR content to utilise its capabilities fully.
f) Technology adoption: Widespread adoption is still limited, partly due to the required technological infrastructure and user familiarity.
Get familiarised with Reverse Engineering – register now for our Reverse Engineering Training!
What is an Example of Virtual Reality?
An example of Virtual Reality is the Oculus Rift headset, which immerses users in 3D gaming environments, allowing them to interact with the virtual world through motion tracking and hand controllers.
What is VR Mostly Used For?
VR is mostly used for immersive gaming, training simulations in fields like healthcare and military, virtual tours, and educational experiences, providing users with interactive and engaging environments.
Conclusion
We hope you now have a clear understanding of What is Virtual Reality, its features, benefits, limitations, and applications. VR has evolved significantly from its early conceptual stages in the 1950s to the advanced systems we see today. This journey, marked by technological advancements and increased accessibility, has made VR a powerful tool across various fields. From immersive gaming to revolutionary applications in healthcare and education, VR continues to transform our interaction with digital content and the world around us.
Do you want to learn about Digital Twin? – register now for our Digital Twin Training!
Frequently Asked Questions

a) VR Headsets: Devices like the Oculus Rift or HTC Vive that provide immersive visual and auditory experiences.
b) Motion Controllers: Handheld devices that track hand movements, allowing users to interact with the virtual environment.
c) Haptic Gloves: Wearable gloves that provide tactile feedback, enhancing the sense of touch in VR.

VR can solve problems such as:
a) Training and Simulation: Providing safe, realistic training environments for fields like healthcare, aviation, and the military.
b) Therapy and Rehabilitation: Assisting in mental health treatments and physical rehabilitation through controlled, immersive environments.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Virtual Reality courses, including Introduction to Virtualisation Technologies, Quantum Computing Training, and Nanotechnology Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Advanced Technology Trends.
Our Advanced Technology blogs covers a range of topics related to Virtual Reality, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Virtual Reality Skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Advanced Technology Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Virtual Reality (VR) Training
Virtual Reality (VR) Training
Fri 10th Jan 2025
Fri 14th Mar 2025
Fri 9th May 2025
Fri 11th Jul 2025
Fri 12th Sep 2025
Fri 14th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


