We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 0800 446148 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Getting bullied, feeling unsafe, and being a victim of a crime are no longer confined only to the physical world. Because of the Internet, we are living in a global village and are prone to encounter such issues more than ever. Who would have imagined 30 years ago that we could be tormented in a place that doesn’t even exist?
In a world where Digital Crime is rising, how can we try to make the internet a safer and better place? Computer Forensics has proven to be a critical discipline for such scenarios. This field combines Technology and Law Enforcement to trace illegal activities, making it an essential part of modern Cyber Security. Let’s explore the intricate world of Computer
Table of Contents
1) What is Computer Forensics?
2) Why is Computer Forensics Important?
3) How Does Computer Forensics Work?
4) Types of Computer Forensics
5) Computer Forensics Skills
6) Computer Forensics Techniques
7) Computer Forensics Careers
8) Computer Forensics Use Cases
9) Computer Forensics vs Cyber Security
10) Computer Forensics Challenges
11) Conclusion
What is Computer Forensics?
Computer Forensics is the science of investigating digital devices to unveil, gather, and protect important evidence related to any unlawful activities. It involves analysing Computers, Mobile Phones, and networks to trace dubious activities, recover hidden or deleted data, and make a detailed digital trail. This evidence is often vital in legal cases, helping to prosecute Cybercriminals, resolve corporate disputes, or track down hackers.
By carefully recovering information from various digital sources, Computer Forensics is a boon in solving Cybercrimes like data breaches, corporate fraud, and identity theft. Its findings are not just data; they are evidence that ensures justice is served in a world increasingly reliant on Digital Technology.
Why is Computer Forensics Important?
Computer Forensics has become important for ensuring our safety in the digital space as we have completely surrendered ourselves to the hands of Technology. As Cybercrimes like hacking, data breaches, and identity theft become more sophisticated, the role of Forensic Experts in investigating these crimes is extremely necessary. They have the skills to:
a) Recover hidden or deleted data
b) Trace Cybercriminal activities, and
c) Ensure that the evidence collected is reliable for legal cases.
Computer Forensics could recover or tamper with critical Digital Evidence, undermining justice. This field is the guardian of truth in a virtual world, ensuring that Cybercriminals are held accountable and legal processes are upheld with integrity. It’s an essential defence in today’s battle against Cybercrime.
How Does Computer Forensics Work?
Computer Forensics operates through a well-defined process to ensure that Digital Evidence is handled precisely and can stand up in court.
The first step is:
Data Acquisition: Where Forensic Experts create an exact digital copy of the device in question to prevent tampering with the original data.
This is followed by:
A Thorough Analysis: Where specialists dig into the digital landscape, searching for files, logs, or suspicious activities that could point to illegal actions.
Every piece of data, no matter how hidden, is scrutinised. Once the investigation is complete, a comprehensive report detailing the findings is compiled. This report becomes critical in legal or corporate settings, helping resolve cases with clear, digital evidence that ensures justice is served to the victim.
Safeguard the future of Digital Security with our Certified Cyber Security Professional Training. Join now!
Types of Computer Forensics
There are several types of Computer Forensics. Some of these include:
1) Disk Forensics: Investigates storage devices like Hard Drives and SSDs to recover deleted or hidden files.
2) Network Forensics: Analyses Data Traffic over a network to detect unauthorised access or suspicious activity.
3) Mobile Forensics: Recovers data from Smartphones and Tablets, including Call Logs, Messages, and App Data.
4) Email Forensics: Focuses on analysing emails to track Phishing Attacks or Corporate Fraud.
5) Memory Forensics: Examines a computer’s RAM to recover volatile data that may have been lost after a shutdown.
Computer Forensics Skills
To excel in Computer Forensics, professionals need a blend of Technical and Analytical Skills. Here are some of the essential skills for this field of work:
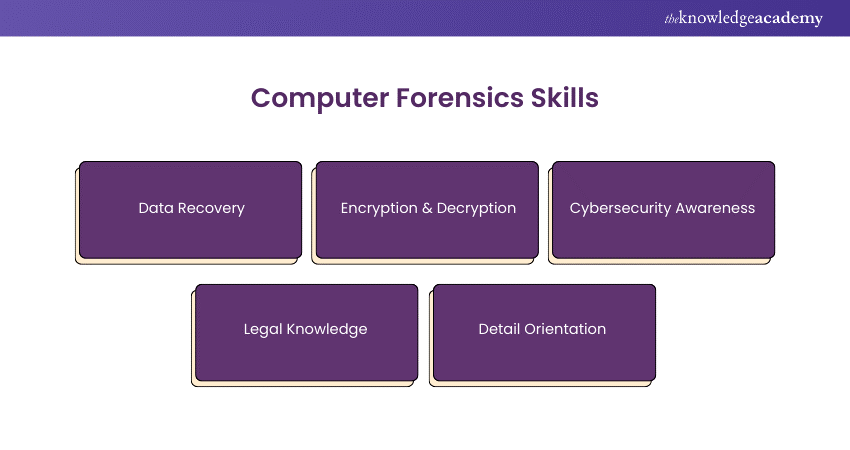
a) Data Recovery: The ability to retrieve lost or deleted files without damaging the original data.
b) Encryption & Decryption: Understanding of encryption methods to access secured information.
c) Cyber Security Awareness: Knowing how Cybercriminals operate helps Forensic Experts anticipate and counter their tactics.
d) Legal Knowledge: Forensic Analysts must ensure their findings meet legal standards to be admissible in court.
e) Detail Orientation: High attention to detail is essential when analysing vast amounts of data to pinpoint evidence.
Stay one step ahead—build your defence with our Cyber Security Awareness Training. Join now!
Computer Forensics Techniques
Computer Forensics Techniques are essential tools used to uncover digital evidence hidden within devices. Here, we have listed some of the Computer Forensics Techniques:
a) File Carving: A method to recover deleted files from unallocated disk space without relying on file system metadata.
b) Keyword Searches: Analysts use specific keywords to quickly locate files, emails, or messages related to the investigation.
c) Log Analysis: Forensic professionals examine system logs to trace user activities, network connections, or program executions.
d) Steganography Detection: Techniques to uncover data that may have been hidden in images or other files.
e) Metadata Analysis: Investigate the metadata of digital files (such as creation dates and modification records) to build activity timelines.
Computer Forensics Careers
A career in Computer Forensics offers multiple paths, from working in Law Enforcement to Private Companies:
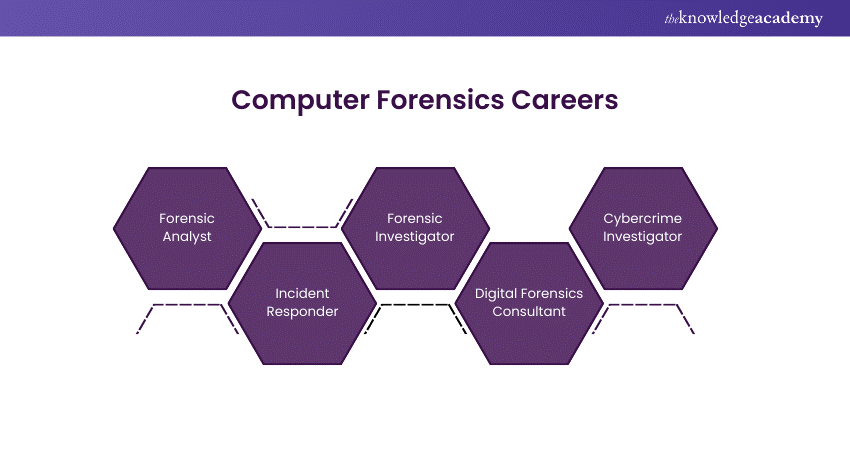
a) Forensic Analyst: Specialises in examining digital evidence for criminal or civil cases.
b) Incident Responder: Quickly reacts to Cyberattacks, securing systems and analysing Data Breaches.
c) Forensic Investigator: Works closely with legal teams to present digital evidence in court.
d) Digital Forensics Consultant: Provides guidance to businesses on Digital Forensics Tools, Data Security, and Forensic Readiness.
e) Cybercrime Investigator: Focuses on identifying and stopping Cybercriminals through detailed Forensic Analysis.
Computer Forensics Use Cases
Computer Forensics plays a significant role in solving Cybercrimes and Corporate Offenses. From exposing frauds to resolving legal issues, its use cases highlight the necessity of Forensic Analysis in securing businesses and serving justice. Here are some of its real-world use cases:
a) Corporate Fraud: Forensic Investigators uncover hidden transactions, Document Manipulation, and unauthorised Data Access within companies.
b) Cyber Espionage: Governments and corporations use Computer Forensics to detect and respond to Cyberattacks aimed at stealing sensitive data.
c) Data Breaches: Forensics helps determine how hackers gained access to systems and what data was compromised, guiding future Cyber Security measures.
d) Legal Disputes: Digital evidence such as emails, contracts, or metadata can be pivotal in resolving legal disputes.
e) Ransomware Investigations: By analysing affected systems, forensic experts can trace the origins of Ransomware Attacks and recover Encrypted Data.
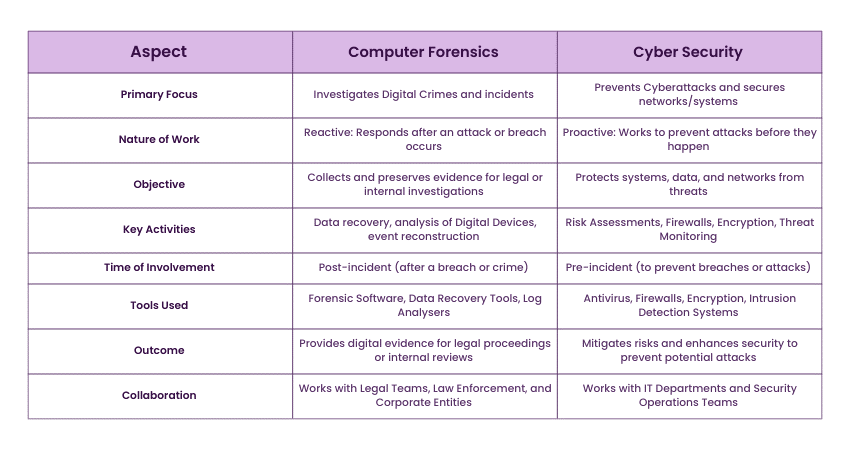
Computer Forensics vs Cyber Security
Here is an outline on how Computer Forensics and Cyber Security differ in their goals, approaches, and methods, yet complement each other in protecting the Digital Landscape:
Computer Forensics Challenges
Despite its benefits, Computer Forensics faces several challenges. These challanges include:
a) Encryption: Strong encryption can make data inaccessible to Forensic Investigators.
b) Data Volume: Daily data can overwhelm investigators, making it challenging to sift through everything efficiently.
c) Cloud Storage: Evidence stored in the cloud presents legal challenges, especially when dealing with Cross-border Investigations.
d) Legal Hurdles: Forensic Professionals must ensure that their methods comply with legal standards, or the evidence they collect could be deemed inadmissible.
Conclusion
As Cybercrime continues to evolve, Computer Forensics acts like a Guardian of the (Digital) Galaxy. It is an indispensable tool in today’s Legal and Corporate Investigations, from recovering hidden files to presenting evidence in court. With specialised skills and advanced techniques, Computer Forensics experts are on the front lines of fighting Cybercrime, ensuring Data Integrity and Security in our increasingly Digital World.
Master the art of defence against manipulation with our Social Engineering Training!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Role of a Computer Forensic Analyst?

A Computer Forensic Analyst investigates Digital Devices to recover data and gather evidence related to Cybercrimes. Their work involves analysing files, emails, and network activities, ensuring the integrity of the evidence for legal proceedings.
How is Computer Forensics Used in Corporate Investigations?

Computer Forensics is used in corporate investigations to uncover Corrupt Activities, Unauthorised Access, or Data Breaches. Investigators examine emails, documents, and transaction records to identify suspicious actions and ensure evidence holds up in legal or regulatory contexts.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Cyber Security Training, including the Computer Forensics Foundation Training, Social Engineering Training and Cyber Security Awareness Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Types of Computer Viruses.
Our IT Security & Data Protection Blogs cover a range of topics related to Cyber Security, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Cyber Security Skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Computer Forensics Foundation Training
Computer Forensics Foundation Training
Thu 22nd May 2025
Thu 24th Jul 2025
Thu 25th Sep 2025
Thu 11th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


