We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 0800 446148 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Safeguarding personal data is more critical than ever, and understanding the key GDPR Requirements is your first line of defence in the digital world. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) imposes meticulous standards that can significantly impact your business operations. But, how can mastering these requirements revolutionise your Data Management practices?
This blog will highlight the essential GDPR Requirements that can ensure that your organisation complies and excels in this regulatory landscape. By embracing these essential requirements, you can fortify your organisation against breaches and cultivate unwavering trust with your clients.
Table of Contents
1) Comprehending GDPR Obligations
2) What are GDPR Requirements?
a) Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency
b) Limitation of Purpose
c) Data Minimisation
d) 72-hour Breach Notification
e) Accuracy
f) Storage Limitation
g) Consent
h) Personal Data Breaches
i) Privacy by Design
j) Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIA’s)
3) GDPR Requirements: Individual Rights
4) Conclusion
Comprehending GDPR Obligations
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is implemented by the European Union (EU), sets forth comprehensive guidelines and obligations for data privacy. The Benefits of GDPR include safeguarding privacy rights, that include access, correction, and erasure of personal data. GDPR principles mandate organisational and technical safeguards to ensure data security and require prompt notification of impacted individuals and authorities in the event of data breaches.
To ensure compliance, businesses frequently perform GDPR Audits to evaluate and improve their Data Protection measures. Overall, GDPR requirements aim to strengthen personal Data Protection, increase transparency in data processing, and hold businesses accountable for managing customer information.
What are GDPR Requirements?
The GDPR Requirements are structured to ensure Data Privacy and Security, making businesses more transparent and accountable. Let’s take a look at some of those crucial requirements:
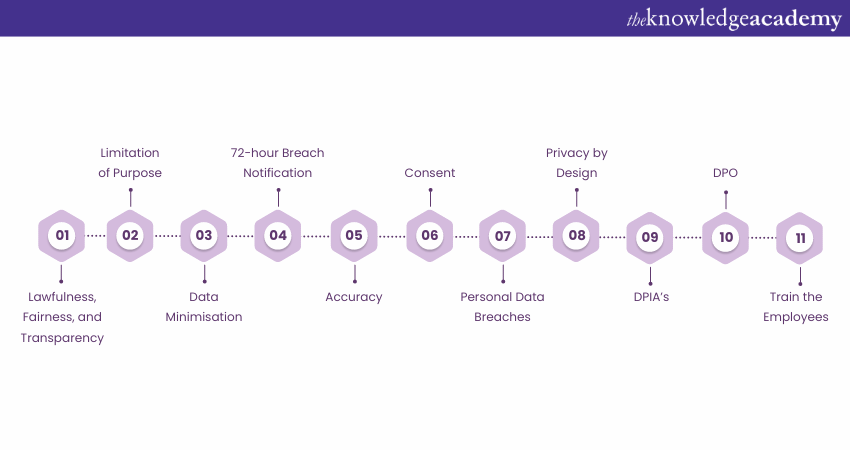
1) Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency
Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency are core GDPR Requirements. Lawfulness requires a valid legal basis for processing personal data. Fairness ensures data is processed in a non-discriminatory and honest manner. Transparency mandates that organisations be open about data usage. These principles ensure legal, fair, and transparent data processing, building trust and demonstrating a commitment to privacy rights.
2) Limitation of Purpose
The second key GDPR requirement is purpose limitation, which mandates that personal data be collected and processed only for specific legal objectives. Organisations must clearly state their reasons for data collection and limit it to what is necessary for those purposes. This principle protects individuals’ privacy by ensuring their data isn’t used in unexpected ways.
3) Data Minimisation
Data minimisation requires businesses to collect, process, and store only the minimum personal data necessary for a specific purpose. Organisations must gather data for explicit, lawful reasons and ensure it is sufficient, relevant, and limited to what is needed. This principle protects individuals’ privacy by reducing the amount of data collected and processed.
Sign up for our Data Privacy Awareness Course and receive the expertise to navigate the complexities of Data Protection.
4) 72-hour Breach Notification
GDPR mandates that organisations notify relevant authorities and affected individuals within 72 hours of a personal data breach that highlights a risk to individuals’ rights and freedoms. This requirement promotes prompt and efficient responses, responsibility, and transparency in data processing. Notifications must detail the breach, affected individuals, potential impacts, and corrective actions. Non-compliance can turn into hefty fines, reputational damage, and legal consequences. Therefore, businesses must have robust data breach response strategies to quickly identify, investigate, and report breaches.
5) Accuracy
According to the GDPR's accuracy requirement, Personal data must be accurate and, when needed, kept current. Organisations must take reasonable measures to guarantee that the Personal data they process is accurate, comprehensive, and not misleading. They must also make sure that any errors are quickly fixed or removed.
6) Storage Limitation
Storage Limitation is a fundamental principle of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) that governs how organisations in the United Kingdom and the European Union should handle Personal data. This principle states that Personal data should be kept in a form that allows the identification of individuals for no longer than is necessary for the purposes for which it is processed.
7) Consent
Under General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), consent means that a person has given permission for their personal information to be collected, processed, and shared. This permission must be freely given, specific, and informed, and the person must have taken action, such as clicking buttons or checking boxes, to indicate their agreement. Consent is considered to be one of the six lawful bases and should be used only in certain circumstances.
8) Personal Data Breaches
This is an essential requirement of GDPR as data breaches are the most important element of GDPR. The most important aspect of understanding about GDPR Breach Under Article 4, a Personal data breach is defined as any such event that causes an accident or any unlawful destruction, loss, or unauthorised access to Personal data, private data transmission or storage or illegal data processing.
Remain vigilant and safeguard your business from potential breaches – join our GDPR Training now!
9) Privacy by Ddesign
Privacy by design is a crucial requirement to know Why is GDPR Important why gdpr is importantwhy gdpr is important is that requires and why organisations to should incorporate privacy and Data Protection into their products, services, and systems from the beginning. This means that privacy and Data Protection should be considered as the primary factor rather than being added as an afterthought.
This requirement includes data minimisation, purpose limitation, transparency, security, and user control. By implementing privacy by design, organisations can ensure GDPR Compliance GDPR complianceGDPR compliance while also protecting the privacy and Data Protection rights of individuals.
10) Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIAs)
DPIAs under Article 35 assist organisations in assessing the potential risks and impacts of their data processing activities on individuals' privacy and Data Protection rights. A DPIA is required during the following situationswhen:
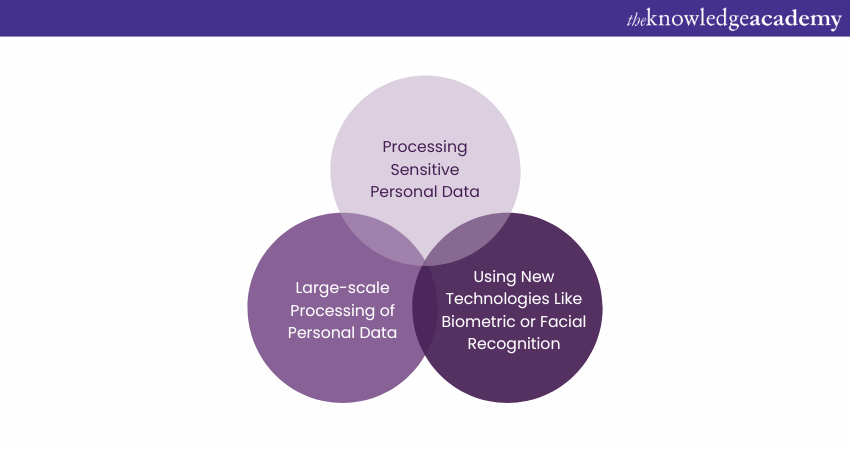
Join our Certified EU GDPR Foundation Course and gain a solid understanding of data privacy regulations
11) Data Transfers
Data transfers refer to the movement of Personal data across borders, particularly outside the European Union (EU) and the United Kingdom (UK). GDPR requires that when such transfers occur, organisations must ensure that the Personal data is adequately protected.
This can be achieved by using mechanisms like Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs), Binding Corporate Rules (BCRs), or obtaining explicit consent from Data Subjects. Additionally, organisations should assess the Data Protection laws and practices of the recipient country to ensure an adequate level of protection.
12) Accountability for Processors
Under GDPR, Data Processors are entities or individuals that process Personal data on behalf of Data Controllers. Accountability for Processors means that processors share in the responsibility for ensuring GDPR compliance. They must only process data in accordance with the controller's instructions, implement appropriate security measures, and assist the controller in meeting its obligations, such as responding to Data Subject requests and cooperating with supervisory authorities. Processors also have their own compliance requirements and should maintain records of their processing activities.
13) Records of Processing Activities
Records of processing activities are detailed documentation maintained by Data Controllers and processors to resubject categories, data retention periods, security measures, and any international data transfers.
Maintaining these records is a fundamental aspect of GDPR accountability and transparency. They provide a clear overview of an organisation's data processing activities, helping supervisory authorities and Data Subjects understand how Personal data is handled.
14) Cooperation with Supervisory Authorities
Cooperation with supervisory authorities is a key requirement of GDPR, emphasising the importance of working with Data Protection regulators. Organisations should be ready to provide information and assistance to supervisory authorities when requested.
This cooperation includes responding to inquiries, providing access to relevant documents, and notifying authorities of data breaches within 72 hours. Cooperation ensures that regulators can effectively oversee compliance and enforce GDPR Requirements. Timely and transparent communication with supervisory authorities is crucial in demonstrating commitment to Data Protection and resolving potential issues.
15) Data Protection Officer (DPO)
The GDPR mandates that certain organisations hire a DPO. The DPO is in charge of managing a company's Data Protection plan and making sure that it complies with GDPR regulations.
Article 39 lists the prerequisites for a DPO, which include the following:
a) Spreading awareness regarding Data Protection to inform the staff regarding the same
b) Observing the organisation's Data Protection policies and practices
c) Advising management as to the necessity of Data Protection Impact Assessments
d) Acting as the organisation's point of contact with its supervisory authority
e) Working as a point of contact for people regarding privacy issues
16) Train the Employees
An essential element in ensuring GDPR compliance is training staff on the regulation's requirements and duties. Employees who handle Personal data need to be aware of their GDPR responsibilities and how to incorporate Data Protection practices into their regular work.
Follow the steps below to train the employees on specific requirements of GDPR:
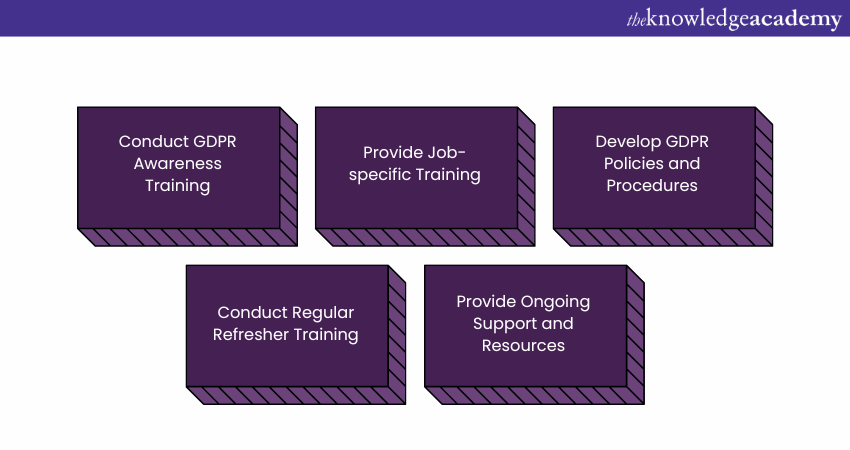
Organisations can reduce the risk of data breaches and non-compliance, preserve individual privacy rights, and help ensure that Personal data is processed in accordance with the rule by training staff about its GDPR Requirements and their obligations.
Master the skills needed to protect sensitive information and navigate complex privacy laws – join our Certified Data Protection Officer (CDPO) Training now!
GDPR Requirements: Individual Rights
Individual rights are a fundamental aspect of GDPR, designed to empower individuals in the UK and the EU with control over their Personal data. Below are the GDPR Requirements pertaining to Individual rights:
1) Right to be Informed
Individuals have the right to be informed about how their Personal data is collected, processed, and for what purposes. Organisations must provide clear and concise privacy notices that explain these details.
2) Right to Access
Individuals can request access to their Personal data that an organisation holds. Upon request, organisations must provide a copy of the data and information about its processing within a month.
3) Right to Rectification
Data subjects have the right to possess inaccurate or incomplete Personal data corrected by the Data Controller. This ensures that their data is up-to-date and accurate.
4) Right to Erasure
Individuals can request the deletion of their Personal data in certain circumstances, such as when it is no longer necessary for the original purpose of processing.
5) Right to Restrict Processing
In specific situations, individuals can request that the processing of their Personal data be restricted. During this period, data may only be stored and not processed further.
6) Right to Data Portability
Individuals have the right to receive their data in a structured and machine-readable format, allowing them to transfer it to another organisation when applicable.
7) Right to Object
Individuals are allowed to object to the processing of their data, particularly for direct marketing purposes. Upon receiving an objection, the organisation must cease processing the data.
8) Rights Related to Automated Decision-making, Including Profiling
GDPR provides protection against solely automated decisions, including profiling, that have significant legal or similarly significant effects on individuals. In such cases, individuals have the right to challenge these decisions and seek human intervention.
Conclusion
Mastering these top 15+ GDPR Requirements is crucial for any organisation handling EU citizens’ data. By following these guidelines, you can build trust with your customers, safeguard their privacy and enhance your reputation. Make GDPR your ally in fostering a secure digital environment.
Enhance your organisation’s compliance with our GDPR Awareness Training – join us and safeguard sensitive information today!
Frequently Asked Questions

A GDPR Questionnaire is a tool used by organisations to assess their compliance with the General Data Protection Regulation. It typically includes questions on data processing activities, security measures, and data subject rights to identify areas needing improvement.

A GDPR Checklist is a comprehensive list of tasks and requirements that organisations must follow to seek compliance with the General Data Protection Regulation. It covers Data Protection principles, individual rights, data breaches, and documentation to help maintain GDPR adherence.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various GDPR Trainings, including the GDPR Awareness Training, Data Privacy Awareness Course, and Personal Data Protection Bill Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into GDPR Changes.
Our IT Security & Data Protection Blogs cover a range of topics related to GDPR, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your IT Security and Data Protection skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Certified Data Protection Officer (CDPO)
Certified Data Protection Officer (CDPO)
Thu 1st Jan 1970







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


