We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +33 805638382 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Big Data Storage is necessary to manage the enormous amount of data being produced every second since traditional methods are insufficient. It allows businesses to keep, handle, and analyse extensive datasets, promoting data-informed choices and creativity. Platforms such as Hadoop, Amazon S3, and Apache Cassandra provide strong options for handling the challenges of data complexity and scalability.
Having a good grasp of these tools enables companies to discover hidden insights and remain competitive. This blog delves into Big Data Storage and its tools, showcasing how these technologies transform Data Management, improving efficiency and effectiveness.
Table of Contents
1) What is Big Data Storage?
2) Types of Big Data Storage
3) Popular Tools for Big Data Storage
4) Best Practices for Efficient Big Data Storage
5) How Does Big Data Storage Work?
6) Pros and Cons of Using Big Data Storage
7) Conclusion
What is Big Data Storage?
Big Data Storage encompasses the Storage of diverse data types, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data, which can originate from various sources such as social media, sensors, transactional systems, IoT devices and more.
Big Data Storage is versatile in handling data variety. This includes structured data like databases, semi-structured data like JSON or XML, and unstructured data such as images, videos, and text documents. These diverse data types often coexist within the same Storage environment.
Unlock the power of Big Data for your organisation with our Big Data and Analytics Training today!
Types of Big Data Storage
There are various types of Big Data Storage solutions For example, Distributed File Systems (DFSs) which is capable of handling massive datasets to NoSQL databases designed for flexible, unstructured data. Some crucial types can be listed down as follows:
1) Distributed File Systems
Distributed File Systems play a pivotal role in managing and storing Big Data across clusters of computers. One of the most prominent examples is the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS). HDFS is designed to handle large files by breaking them into smaller blocks and distributing them across multiple nodes in a cluster. This approach ensures that data can be processed in parallel, significantly enhancing the efficiency of Data Storage and retrieval.
By leveraging Distributed File Systems, organisations can achieve both high scalability and fault tolerance. In the event of a node failure, data is automatically replicated to other nodes, ensuring data integrity and availability. This redundancy feature is critical in Big Data environments where large datasets must be reliably stored and processed.
2) NoSQL Databases
NoSQL Databases represents a groundbreaking shift in Database Management, especially concerning Big Data applications. Unlike traditional Relational Databases, which are optimised for structured data, NoSQL Databases excel at handling unstructured or semi-structured data types commonly found in Big Data scenarios.
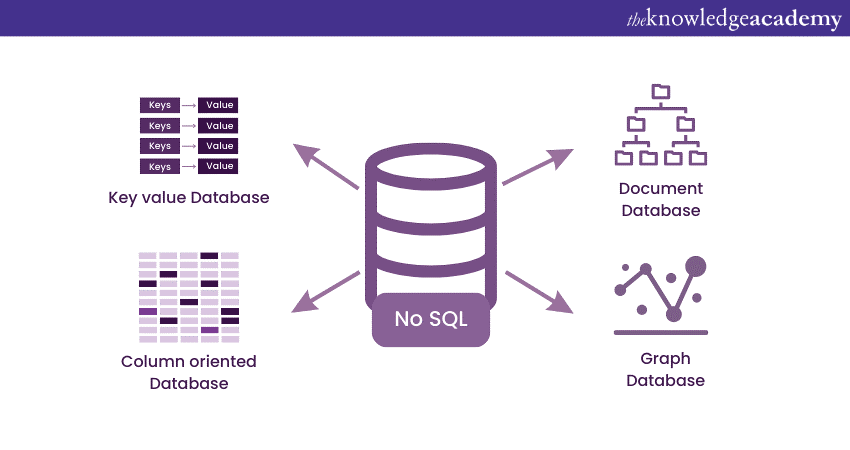
NoSQL Databases employ various data models, including document-oriented, key-value, column-family, and Graph Databases. Each model caters to specific types of data and use cases. This versatility makes NoSQL Databases a powerful tool for organisations dealing with diverse data types and requirements.
3) Data Warehouses
Data Warehouses are specialised repositories designed for the Storage and analysis of structured data. They offer a structured approach to Data Storage, making them indispensable for Business Intelligence (BI) and Analytics. Data Warehouses consolidate data from various sources, including Operational Databases, into a unified, organised format optimised for querying and reporting.
Data Warehousing solutions often employ techniques like indexing, partitioning, and materialised views to optimise query performance. This enables organisations to extract insights from their data efficiently and in near-real-time. Additionally, Data Warehouses support complex analytics operations, including Data Mining, Trend Analysis, and Predictive Modelling, which are fundamental for informed decision-making.
4) Object Storage
Object Storage is a scalable and cost-effective solution tailored for storing vast amounts of unstructured data, such as images, videos, and backups. Unlike Traditional File Systems or Block Storage, which organise data hierarchically in folders, Object Storage uses a flat address space, associating each Data Object with a unique identifier.
This approach simplifies Data Retrieval and access, as Objects can be accessed directly without the need for a hierarchical file structure. Additionally, Object Storage platforms like Amason S3 and Google Cloud Storage offer features such as Versioning, Metadata tagging, and Data Lifecycle Management, enhancing Data Governance and accessibility.

Popular Tools for Big Data Storage
From Distributed File Systems to scalable NoSQL Databases and versatile Object Storage platforms, these tools are fundamental for successfully implementing Big Data Storage solutions.
1) Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS)
HDFS serves as the cornerstone of the Hadoop ecosystem, playing a pivotal role in the Storage and processing of Big Data. It is designed to handle large files by distributing them across a cluster of commodity hardware. This distribution enables parallel processing, which is essential for dealing with massive datasets.
Master Hadoop and advance your career with our Hadoop Big Data Certification Course – Register now!
2) Cassandra
Cassandra is a NoSQL Database renowned for its high availability and scalability, making it an excellent choice for real-time applications where uninterrupted performance is critical. It employs a distributed architecture that allows it to operate across multiple nodes, ensuring that even in the event of node failures, data remains accessible.
3) Amazon S3
Amazon S3 is a widely adopted Object Storage solution provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS). It offers secure, durable, and highly scalable Storage capabilities, making it a go-to choice for a wide range of applications, from data backups to content distribution. One of S3's strengths lies in its versatility. It accommodates various types of data, including images, videos, logs, and backups.
4) Google Cloud Storage
Google Cloud Storage is a highly reliable and scalable Object Storage solution integrated into the Google Cloud Platform (GCP). It provides a secure and cost-effective means of storing and retrieving data, making it an attractive option for organisations leveraging the GCP ecosystem. One of the standout features of Google Cloud Storage is its seamless integration with other GCP services.
5) Apache Hive
Apache Hive simplifies the process of querying and analysing large datasets by providing a SQL-like interface on top of Hadoop. It allows users familiar with SQL to leverage their existing skills to work with Big Data. Hive's strength lies in its ability to translate SQL queries into MapReduce jobs, enabling efficient processing of data stored in Hadoop's Distributed File System.
Harness Big Data Insights to drive data-driven success with our Big Data Analysis Course – Join now!
Best Practices for Efficient Big Data Storage
Effectively harnessing the potential of vast datasets requires careful consideration of best practices that optimise Storage resources, ensure data accessibility, and enhance overall system performance. Some of these best practices have been discussed below:
1) Data Partitioning and Sharding
Data Partitioning, also known as Sharding, is a crucial technique in Big Data Storage that involves dividing large datasets into smaller, more manageable pieces. Each Partition, or Shard, contains a subset of the data and is stored separately. This practice distributes the Storage and processing load across multiple nodes or servers, enhancing both performance and scalability.
By strategically Partitioning data, organisations can achieve several benefits. First, it enables parallel processing, allowing multiple nodes to work on different Partitions simultaneously. This accelerates query response times and improves overall system performance. Second, it reduces the risk of data bottlenecks, as the workload is distributed across multiple storage units.
2) Compression techniques
Efficient storage of Big Data often involves the application of Compression techniques. Compression reduces the physical Storage footprint of data, leading to cost savings and improved performance. It works by encoding data in a way that reduces redundancy and removes unnecessary information, resulting in smaller file sizes.
Various Compression algorithms exist, each suited for specific data types and use cases. For example, Gzip and zlib are commonly used for general-purpose Compression, while specialised algorithms like Snappy and LZO are favoured for high-speed Compression of specific data formats.
3) Data Lifecycle Management
Data Lifecycle Management involves the systematic management of data from its creation to its eventual deletion or archival. This practice is essential in Big Data environments, where the volume of data can be overwhelming. By implementing effective Data Lifecycle policies, organisations can optimise Storage resources and ensure that valuable data is retained while unnecessary or obsolete data is appropriately managed.

The Data Lifecycle typically consists of several stages: Creation, Storage, Usage, Archiving, and Deletion. Each stage requires distinct Storage considerations and policies. For example, frequently accessed data may be stored on high-performance Storage systems, while Archival data may be moved to cost-effective, long-term Storage solutions like cold Storage or tape archives.
4) Disaster Recovery Planning
In the world of Big Data, Disaster Recovery Planning is paramount to safeguarding valuable datasets in the event of a catastrophic event or system failure. This practice involves the creation of robust strategies, processes, and infrastructure to quickly recover and restore data in the event of an unforeseen incident.
A comprehensive Disaster Recovery Plan should encompass data backups, Offsite Storage, redundancy, and failover mechanisms. Regular backups, performed at appropriate intervals, ensure that critical data is preserved and can be restored to a known state. Offsite Storage, in geographically diverse locations, provides an additional layer of protection against localised disasters.
How Does Big Data Storage Work?
Big Data Storage efficiently manages and analyses large data sets by using networks of affordable servers and high-capacity disks. These extensive datasets are stored on remote servers in Cloud storage. They are accessed through the internet. Virtual machines offer a secure environment for data storage. This setup enables the swift creation of more virtual machines when the data exceeds the current server's capacity.
This method provides the ability to grow storage capacity for organisations without needing large hardware investments. It remains cost-effective. It ensures data is easily accessible, safe, and efficiently controlled, even as quantities keep increasing. The decentralised structure of the Cloud also improves duplication. This reduces the possibility of losing data and experiencing downtime.
Big Data Storage systems are created to manage both organised and unorganised data, making them perfect for a variety of industries. These systems aid in the continual advancement of data-driven strategies, improving business performance and innovation. They are useful, whether applied in real-time analytics, Machine Learning, or large-scale data archiving.
Pros and Cons of Using Big Data Storage
The advantages and disadvantages of Big Data Storage typically hinge on the quantity of data being handled. Here are a few advantages:
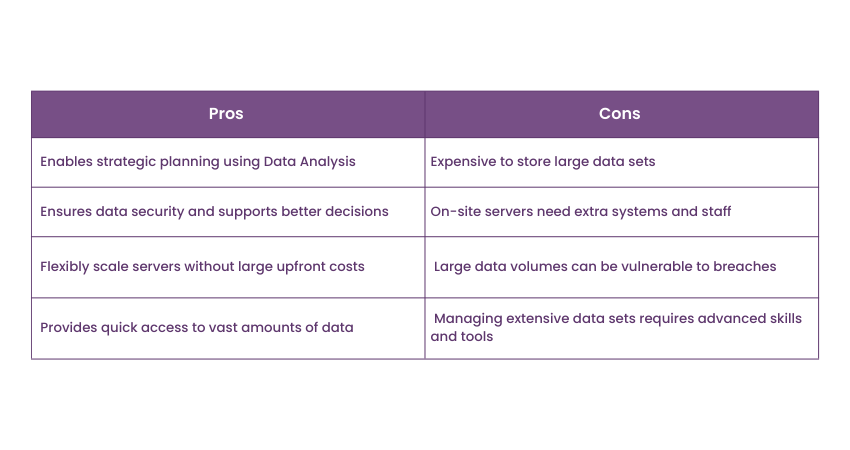
Pros
a) Data-driven Decisions: Businesses can make data-driven decisions by using large-scale Data Analysis for strategic planning and decision-making.
b) Informed Choices: Informed decisions are possible with Big Data Storage, which ensures data security for professionals to utilise analytical tools. This results in well-informed choices, enhanced customer service, and increased efficiency.
c) Scalability: Cloud storage provides flexibility for businesses to increase or decrease servers without the need for a large initial cost.
d) Efficiency: It provides instant access to vast amounts of data.
Cons
Nevertheless, there are some elements one must take into account when utilising Big Data Storage.
a) High Costs: Keeping extensive data sets can be pricey, with costs increasing as data volume grows. Managing servers located in the office may necessitate extra resources and personnel, leading to higher expenses.
b) Resource Demands: The need for extra hardware and infrastructure for on-site servers can result in high expenses. Skilled personnel are also required to efficiently manage, maintain, and monitor the systems.
c) Data Security Risks: Cyberattacks and breaches are drawn to significant amounts of data. It is crucial to have strong security measures in place to prevent unauthorised access to sensitive information.
d) Complexity: The complex processes and tools involved in managing and analysing large data sets. Advanced skills and specialised knowledge are needed to effectively manage data and extract valuable insights.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Big Data Storage is a game-changer for modern businesses, enabling them to efficiently manage and analyse vast amounts of data. By leveraging advanced tools like Hadoop, Amazon S3, and Apache Cassandra, companies can unlock valuable insights, drive innovation, and maintain a competitive edge. Embracing these technologies not only enhances Data Management but also empowers organisations to make informed, impactful decisions. Dive into the world of Big Data Storage and transform your data into a strategic asset.
Unlock the Secrets of Big Data with our Big Data Analytics & Data Science Integration Course today!
Frequently Asked Questions

Exabyte-scale storage is the maximum Data Storage capacity available now, with petabytes being more frequently used. Hyper-scale data centres and innovative Cloud storage options can manage huge amounts of data, increasing to zettabyte levels as technology advances.

Many data are stored in distributed storage systems such as cloud platforms, data lakes, and on-premises servers. These systems consist of tools such as Hadoop, Amazon S3, and Google Cloud Storage, created to efficiently manage large and varied data sets.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Big Data and Analytics Training, including the Big Data Analysis Training, Hadoop Big Data Certification, and Advanced Data Analytics Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Types of Data in Statistics.
Our Data, Analytics & AI Blogs cover a range of topics related to Big Data, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Data Analytics skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Data, Analytics & AI Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Hadoop Big Data Certification
Hadoop Big Data Certification
Thu 23rd Jan 2025
Thu 20th Mar 2025
Thu 22nd May 2025
Thu 17th Jul 2025
Thu 18th Sep 2025
Thu 20th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


