We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +33 805638382 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Imagine stepping into a room filled with dynamic energy, where creativity flows like a river, and innovation is the common language. This is the essence of a Design Thinking Workshop, a transformative space where ideas are born, shaped, and refined to solve real-world problems. It’s not just about thinking outside the box; it’s about redefining the box itself.
In a Design Thinking Workshop, participants don’t just learn; they experience. They dive deep into understanding user needs, collaborate across disciplines, and prototype solutions that are both practical and visionary. Let’s dive in to learn more!
Table of Contents
1) What is a Design Thinking Workshop?
2) How to Run a Design Thinking Workshop?
3) What Kinds of Challenges are Addressed With a Design Thinking Workshop?
4) Remote Design Thinking Workshop Best Practices
5) Conclusion
What is a Design Thinking Workshop?
Design Thinking emerges as a powrful approach that provides industries with a framework for innovative solutions. The Design Thinking Workshop is at the core of Design Thinking, which is a collaborative and dynamic space where participants embark on a journey of empathy, creativity, and iterative problem-solving.
In a Design Thinking Workshop, diverse teams come together to tackle complex challenges using a user-centric approach. The workshop is structured into phases that guide participants through understanding user needs, brainstorming creative ideas, prototyping solutions, and testing them for feedback. It’s not just a meeting or brainstorming session; it’s a curated process designed to fuel creativity, build empathy, and foster collaborative innovation.
The magic of a Design Thinking Workshop lies in its ability to break down silos and foster a shared understanding among participants. Whether it’s a cross-functional team from different departments or a group of individuals with varying expertise, the workshop serves as a melting pot where diverse perspectives blend to create meaningful solutions. By focusing on the user experience, Participants align their goals, ensuring every idea and decision is grounded in solving real-world problems.
The workshop environment is intentionally designed to be open, flexible, and conducive to creative thinking. Commonly used visual tools like sticky notes, whiteboards, and design templates help capture ideas and insights as they emerge. Participants are encouraged to challenge assumptions, think creatively, and build on each other’s ideas in a rapid, iterative cycle. This approach fosters a mindset of continuous improvement, emphasising learning and adapting quickly rather than rigidly following preconceived plans.
What sets a Design Thinking Workshop apart is its focus on empathy. Before diving into solutions, participants spend significant time understanding the users they’re designing for—their needs, pain points, and desires. This human-centric approach ensures that the solutions generated are not only innovative but also truly relevant and impactful.
Overall, a Design Thinking Workshop is more than just a problem-solving session; it’s a transformative experience that empowers teams to approach challenges with a fresh perspective. By fostering collaboration, creativity, and empathy, these workshops equip participants with the tools and mindset needed to drive meaningful innovation in their organisations.
How to Run a Design Thinking Workshop?
These steps will help you to understand how to run a Design Thinking Workshop.
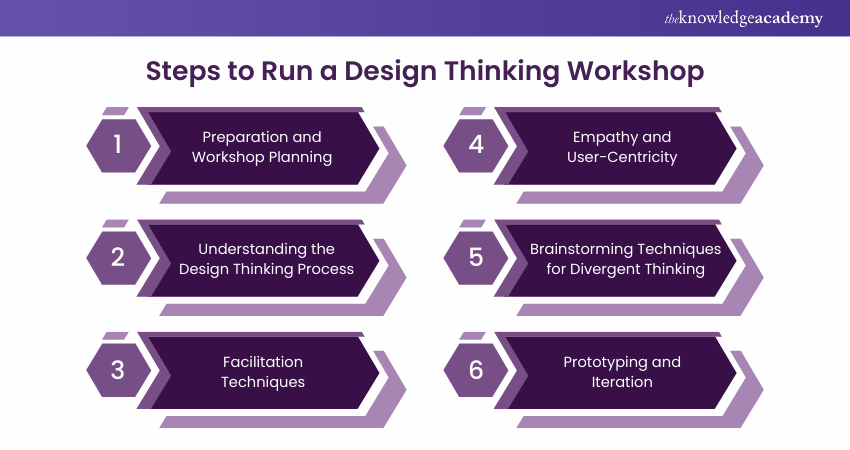
Step 1: Preparation and Workshop Planning
The success of a Design Thinking Workshop hinges on meticulous preparation. This phase lays the groundwork for a productive, engaging workshop experience that drives innovation and problem-solving. From defining objectives to selecting the right facilitators, each element plays an essential role in shaping the workshop's outcome.
a) Defining Workshop Objectives
Before embarking on any workshop, having clear and well-defined objectives is essential. What specific challenge or opportunity does the workshop address? Are you aiming to ideate new product features, enhance customer experiences, or streamline internal processes? You set a clear direction that guides the workshop process by pinpointing the desired outcomes.
b) Choosing the Ideal Venue and Resources
The workshop's physical environment significantly impacts the participants' experience. An open, comfortable, and conducive space fosters creativity and active engagement. Additionally, consider the resources required for hands-on activities and prototyping. Access to tools, materials, and technology is essential for turning ideas into tangible solutions.
c) Crafting the Workshop Agenda
A well-structured agenda is the backbone of a productive Design Thinking Workshop. Divide the workshop into distinct phases (empathise, define, ideate, prototype, test) and allocate sufficient time for each. Within each phase, outline specific activities, discussions, and exercises facilitating the creative process. Keep the agenda flexible enough to adapt to the group's pace and needs.
d) Designing Materials and Visual Aids
Visual aids and materials convey information and guide participants through activities—design worksheets, templates, and other materials that align with the workshop's objectives. Clear visuals enhance understanding and contribute to a visually appealing and engaging workshop atmosphere.
Effective workshop planning is the backbone of a successful Design Thinking Workshop. This phase involves structuring the workshop agenda, setting a realistic timeline, curating the participant mix, and ensuring all necessary resources are in place.
e) Setting a Realistic Timeline:
Time management is a crucial aspect of workshop planning. Balance the need for in-depth exploration to make progress within the allocated time. Allocate time strategically, ensuring participants have ample opportunity for brainstorming, prototyping, and testing. While adhering to the workshop timeline, also build flexibility to adjust the pace based on the group's dynamics and progress.
f) Eating a Diverse Participant Mix:
Diversity among participants enriches the workshop experience by bringing together various perspectives and expertise. Curate a mix of individuals from different departments, roles, and backgrounds. This diversity encourages fresh viewpoints and stimulates creative thinking, leading to innovative solutions that may not emerge in a homogenous group.
g) Preparing Facilitators and Resources:
Facilitators play a pivotal role in guiding participants through the workshop. Ensure they are well-versed in Design Thinking techniques, capable of managing group dynamics and fostering inclusivity. Also, gather and prepare all necessary resources, from post-it notes and markers for brainstorming to prototyping materials like paper, tape, and modelling clay.
Understand employee engagement, sign up for our Leadership Training now!
Step 2: Understanding the Design Thinking Process
The Design Thinking process guides problem-solving and innovation through interrelated phases. This iterative framework is centred around empathy, creativity, and collaboration, allowing teams to unravel complex challenges and create user-centred solutions.
a) Empathise: Stepping Into the User’s Shoes:
The journey begins with empathy—the foundation of Design Thinking. In this phase, participants immerse themselves in the users' world, seeking to understand their needs, emotions, and pain points. Techniques like conducting interviews, observations, and creating empathy maps enable a deep connection with the users' perspectives. This understanding fuels meaningful insights that shape the subsequent phases.
b) Define: Framing the Problem Statement:
The define phase involves synthesising the insights gained to define the core problem. It's about reframing the challenge from the user's perspective, ensuring that the problem statement aligns with their real needs. This phase narrows down the focus and sets a clear direction for ideation.
c) Ideate: Generating Creative Solutions:
Ideation is a brainstorming powerhouse where participants use creativity to explore various solutions. Quantity matters here, as divergent thinking leads to unexpected and innovative ideas. Techniques such as brainstorming, mind mapping, and "crazy 8s" fuel the generation of ideas without limitations.
The prototyping phase brings ideas to life in tangible forms. Prototypes can range from sketches and storyboards to physical mock-ups and digital models. These prototypes serve as tangible artefacts that facilitate communication and experimentation. They allow teams to visualise solutions and gather feedback before investing significant resources.
Testing is about putting prototypes in the hands of users to gather feedback. This phase is essential for validating assumptions, identifying potential flaws, and refining solutions iteratively. By observing how users interact with prototypes, teams gain insights that lead to improvements and iterations, ensuring that the final solution resonates deeply with user needs.
d) Embracing Iteration:
What sets the Design Thinking process apart is its iterative nature. The phases are not linear; they loop back and meet with each other again. Insights gained during testing may prompt revisiting the ideation phase, leading to refined solutions. This iterative approach allows teams to learn from failures, continuously improve, and adapt solutions based on evolving insights.
e) Applying Design Thinking Beyond Products:
While the Design Thinking process is often associated with product innovation, its principles extend to various domains. The iterative and user-centric approach can be applied to diverse challenges, from designing better services and experiences to improving internal processes and systems.
Understand how Design Thinking solves business problems, sign up for our Design Thinking For R&D Engineers Training now!
Step 3: Facilitation Techniques
Effective facilitation is the cornerstone of a successful Design Thinking Workshop, ensuring that participants engage fully, collaborate effectively, and navigate the various phases of the process seamlessly. Here are some key facilitation techniques to create an environment conducive to innovation and problem-solving:

a) Encouraging Active Participation:
Facilitators should actively engage participants and encourage everyone to contribute. Use techniques like "round-robin" to ensure that every voice is heard, preventing dominant individuals from monopolising discussions. Encourage quieter participants to share their insights as well.
b) Managing Group Dynamics and Conflicts:
Diverse groups can bring conflicting viewpoints. Facilitators should mediate conflicts constructively, encouraging respectful dialogue. Techniques like "agree to disagree" can help manage differences without derailing the workshop's progress.
c) Navigating Through the Design Thinking Phases:
Guide participants through each Design Thinking phase, ensuring they understand the objectives and activities. Facilitate smooth transitions between phases, helping participants carry insights and ideas from one phase to the next.
d) Time Management and Pace:
Maintain a steady pace throughout the workshop, ensuring each phase gets attention. Monitor the clock and adjust if activities take longer than expected. Encourage participants to stay on track without rushing.
e) Maintaining Enthusiasm:
Facilitators set the tone for the workshop, maintaining enthusiasm, energy, and positivity throughout. Your excitement can inspire participants to engage and invest in the activities fully and invest in the activities, fostering a collaborative environment where creativity and problem-solving thrive. Effective facilitation not only drives active participation but also ensures smooth transitions between workshop phases, keeping everyone aligned and focused on the goals.
Learn the role of an instructional designer in an organisation, sign up for our Instructional Design Training now!
Step 4: Empathy and User-Centricity
The idea of empathy lies at the core of Design Thinking, guiding the development of user-centric solutions that truly resonate. This phase is pivotal in understanding users' needs, experiences, and emotions, ensuring that the final solutions align closely with their realities.
Empathy sets the tone for a human-centred approach permeating the Design Thinking process. By emphasising the human aspect of problem-solving, teams are more likely to develop solutions prioritising user needs over technical constraints. This focus on deeply understanding users' emotions, behaviours, and pain points ensures that the final solutions resonate meaningfully with their real-world experiences. Building this empathy-driven mindset encourages teams to view challenges from the user’s perspective, resulting in more relevant and impactful innovations.
Step 5: Brainstorming Techniques for Divergent Thinking
Divergent thinking techniques are vital for generating a broad range of creative ideas during a Design Thinking Workshop. Methods like “crazy 8s,” mind mapping, and SCAMPER push participants to explore unconventional solutions.
By initially focusing on quantity over quality, teams can uncover bold, innovative ideas. Facilitators create a safe environment where all ideas are welcomed, encouraging creative risk-taking. Once ideas are generated, techniques like clustering and dot voting help prioritise and refine concepts for further development.
Traditional brainstorming sessions encourage participants to generate many ideas, often without evaluation. Techniques like "crazy 8s," "SCAMPER," and "mind mapping" help break conventional thinking patterns and promote the exploration of new and unexpected ideas.
a) Organising and Clustering Ideas:
After a productive brainstorming session, ideas can be overwhelming. Facilitators guide participants in organising and categorising ideas into clusters that share common themes. This process provides clarity and sets the stage for deeper exploration.
b) Collaborative Idea Selection Methods:
Selecting ideas for further development involves collaboration. Methods like "dot voting" or "idea prioritisation matrix" enable participants to evaluate and prioritise concepts collectively. This democratic approach ensures that various perspectives contribute to the selection process.
c) Fostering Open and Inclusive Discussions:
Encourage participants to share theirideas openly, regardless of their feasibility. A culture of inclusivity ensures that diverse viewpoints are heard, and participants feel empowered to contribute even unconventional or bold suggestions.
d) Embracing Playful and Risk-taking Mindsets:
Creativity flourishes when participants feel free to take risks and embrace playful thinking. Facilitators encourage a culture where no idea is too outrageous, fostering an environment where novel and groundbreaking concepts can emerge.
Step 6: Prototyping and Iteration
The prototyping and iteration phase turns abstract ideas into tangible solutions through hands-on experimentation and continuous refinement. Rapid prototyping allows quick validation, using both low-fidelity sketches and high-fidelity models, depending on the stage and feedback needed.
Prototypes balance complexity with available resources and involve collaboration from diverse participants. User testing then provides insights to refine and improve prototypes, leading to solutions that are user-friendly and aligned with the defined problem. This iterative approach ensures solutions evolve into effective, user-centered outcomes.
What Kinds of Challenges are Addressed With a Design Thinking Workshop?
Design Thinking Workshops are tailored to address a wide range of complex challenges that require creative problem-solving and user-centric solutions. Some common challenges include improving product design, enhancing customer experiences, and streamlining internal processes. These workshops are particularly effective in tackling issues where traditional problem-solving approaches may fall short, such as when dealing with unclear problem definitions, misaligned team objectives, or a lack of innovative ideas.
Additionally, Design Thinking Workshops can be used to address larger societal or business challenges, including adapting to social changes, creating more inclusive services, or developing sustainable solutions.
By focusing on empathy, collaboration, and iterative testing, these workshops help teams navigate uncertainties and design solutions that are not only innovative but also aligned with user needs and long-term goals.
For businesses, challenges like launching new products, refining existing services, or exploring new market opportunities can also be effectively tackled using this approach. Whether the goal is to create a breakthrough product or improve team dynamics, a Design Thinking Workshop provides a structured yet flexible framework to explore and address these challenges creatively.
Remote Design Thinking Workshop Best Practices
To ensure the smooth execution of your remote Design Thinking Workshop, consider the following best practices:
Thorough Preparation
Develop a comprehensive agenda that outlines the workshop's flow and objectives. Prior to the workshop day, conduct a practice run-through to ensure seamless coordination and fine-tune timings. Given the unique challenges of virtual settings, allocate extra time to address any unforeseen issues.
Avoid Extended Sessions
Acknowledging the natural distinctions between in-person and remote workshops, especially in participant engagement, it's a good idea to steer clear of lengthy sessions. This helps maintain ongoing engagement and ensures everyone participates optimally.
Unlike in-person workshops that naturally incorporate breaks, It can be challenging to maintain energy levels throughout an entire day. Opt for shorter digital workshops, and if needed, spread the session over two days. This approach ensures sustained engagement, effectiveness, and optimal participation from all involved.
Use the Right Digital Tools
Choosing the right digital tools is crucial for a smooth remote workshop. Platforms that offer features like breakout rooms, real-time collaboration on whiteboards, and easy file sharing are essential. Ensure participants are familiar with these tools ahead of time and provide clear instructions for using them during the workshop. Reliable technology and well-chosen tools can greatly enhance collaboration and the overall workshop experience.
Foster Interactive Communication
Remote settings can sometimes lead to reduced engagement, so it's important to foster interactive communication. Encourage active participation using methods like polls, chat discussions, and quick ice-breaker activities. Additionally, keep the communication channels open throughout the workshop, allowing participants to freely share ideas and ask questions, ensuring everyone feels included and heard.
Conclusion
Design Thinking Workshops empower teams to approach challenges with empathy, creativity, and collaboration. Understanding users, generating ideas, and iterating solutions offer a transformative way to innovate across industries. Embrace these principles to embark on a journey of impactful problem-solving and continuous improvement.
Unleash your creativity with our Design Thinking Training – Sign up today!
Frequently Asked Questions

Participants enhance skills like creative problem-solving, empathy, collaboration, and adaptability while developing a user-centric mindset. They also cultivate a proactive approach to innovation, learning how to quickly iterate and refine ideas based on real-world feedback.

Yes, tools like brainstorming, mind mapping, sticky notes, and empathy maps are key for fostering collaboration and creative thinking. Digital platforms like virtual whiteboards also enhance team interaction in both remote and in-person workshops.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. By tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Leadership Courses, including Leadership Skills Training, Certified Artificial Intelligence for Leaders Training, and Design Thinking Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Design Thinking Skills.
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to Design Thinking, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Design Thinking skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Successful People Management and Team Leadership
Successful People Management and Team Leadership
Fri 6th Dec 2024
Fri 14th Feb 2025
Fri 16th May 2025
Fri 25th Jul 2025
Fri 29th Aug 2025
Fri 10th Oct 2025
Fri 28th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


