We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +33 805638382 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Step into the fascinating world of Supply Chain vs Logistics—two sides of the same coin that keep our daily lives running smoothly. Though they may seem similar, they each have a distinct part to play. The Supply Chain is the all-covering journey of a product, from creation to customer. Logistics is the critical link that ensures this journey is smooth, overseeing the transport and storage of goods. Together, they form a seamless network that powers businesses and satisfies consumers.
This blog simplifies these complex concepts, making them accessible to everyone. So come along, let’s explore the exciting career prospects in the Supply Chain vs Logistics landscape.
Table of Contents
1) What is a Supply Chain?
2) What is Logistics?
3) Difference between Supply Chain and Logistics
4) Types of jobs in Supply Chain and Logistics
5) Conclusion
What is a Supply Chain?
Supply Chain Management (SCM) is essentially the orchestration of the movement, data, and financial aspects of a product or service. This process begins with the acquisition of raw materials and continues through to the delivery of the final product to the consumer.
While logistics is often thought to be synonymous with the supply chain, it is, in fact, just one segment of it. Modern SCM systems are digital and encompass the physical handling of materials as well as the software required for the collaboration of all entities involved in the creation and fulfilment of a product or service. This includes suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, transporters, and retailers.
The scope of supply chain activities includes the sourcing of materials, managing the lifecycle of a product, strategising supply chain operations (which covers inventory control and the upkeep of assets and production lines), overseeing logistics (like transportation and fleet management), and managing orders. Furthermore, SCM involves overseeing international trade activities, which include managing overseas suppliers and complex global production strategies.
What is Logistics?
Logistics encompasses the various procedures required to move goods, whether within an organisation or from the seller to the buyer. Logistics managers are tasked with navigating the complexities of these processes, and there are specialised certifications available for these experts. Effective logistics hinges on meticulous attention to detail: selecting the most efficient routes while considering legal regulations and circumventing potential disruptions such as infrastructure work, geopolitical conflicts, or inclement weather.
Decisions regarding shipping providers and packaging need to be made judiciously, balancing cost considerations against factors like weight and environmental impact. The total cost of logistics may also encompass elements beyond mere transportation, including those that contribute to customer satisfaction and the provision of appropriate storage facilities.
For instance, if a consignment of dairy products is ruined due to a breakdown in refrigeration, the responsibility falls on the logistics team.
Logistics management software is available to assist businesses in optimising routing and shipping choices, managing expenses, safeguarding assets, and monitoring the flow of goods. This software often includes features that automate various tasks, such as selecting carriers based on changing rates or contractual agreements, printing shipping labels, integrating transactions into financial records, scheduling carrier pickups, documenting deliveries and signatures, and supporting inventory management, among other capabilities.
Difference between Supply Chain and Logistics
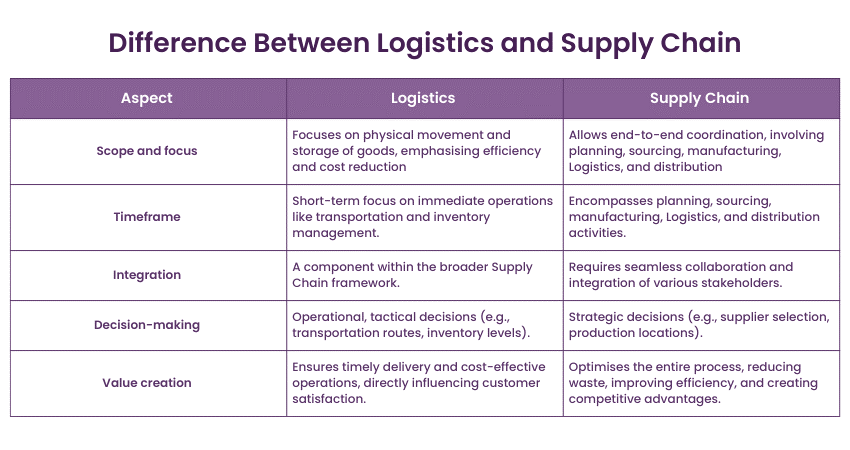
There are various differences that separate Logistics and Supply Chain from each other. Some of the major differences are discussed below:
Responsibility
Supply Chain manages the entire journey of a product from raw materials to the final product, including production and distribution. It makes sure all stages are well-coordinated. On the other hand, Logistics handles the transportation, storage, and warehousing of goods. It focuses on moving products efficiently and managing inventory.
Goal
Supply Chain works to make the whole production process smooth, efficient, and cost-effective, meeting customer needs. Good Supply Chain management improves overall operations. In contrast, Logistics ensures goods are moved and stored efficiently, reducing transportation costs and managing inventory well. Effective Logistics ensures the timely and safe delivery of products.
Relationship
Supply Chain includes Logistics as part of its larger process. It connects various steps to ensure products move smoothly from start to finish. On the other hand, Logistics is a key part of the Supply Chain, dealing with transportation and storage. It helps the Supply Chain by managing the physical movement of goods.
Timeframe
Supply Chain involves long-term planning and strategy to ensure efficient production and delivery over extended periods. It aims for continuous improvement and optimisation. On the other hand, Logistics often deals with short-term, day-to-day operations like managing shipments, inventory, and transportation schedules. It ensures timely delivery and efficient handling of goods.
Integration
Supply Chain integrates various functions such as procurement, production, and distribution to create a seamless Supply Chain Management Process. It requires coordination across different departments and external partners. In contrast, Logistics integrates transportation and storage activities within the Supply Chain. It works closely with other Supply Chain functions to ensure smooth movement of goods.
Decision Making
Supply Chain covers strategic decisions related to sourcing, production, and distribution networks. It focuses on long-term efficiency and cost-effectiveness. On the other hand, Logistics includes operational decisions such as routing, warehousing, and inventory management. It focuses on optimising day-to-day activities for timely and efficient delivery.
Value creation
Supply Chain creates value by optimising the entire production and delivery process, reducing costs, and improving customer satisfaction. It enhances overall business performance. In contrast, Logistics adds value by ensuring goods are delivered on time and in good condition, reducing transportation costs, and managing inventory effectively. It contributes to the efficiency of the Supply Chain.
Learn the types of products for importation with our Import Export Course – join today!
Types of jobs in Supply Chain and Logistics
There are many career opportunities in Supply Chain and logistics, each crucial for the smooth and efficient movement of goods and services. Let's explore these roles:

Supply Chain Management
Supply Chain Management (SCM) involves the strategic coordination of a complex network that includes various stakeholders, such as distributors and transportation providers, all working together to deliver a finished product to the consumer.
Supply Chain Managers specialise in:
a) Demand planning: Aligning the supply chain with consumer demand.
b) Strategy development: Enhancing production and delivery efficiency while maintaining quality.
c) Relationship building: Forming and sustaining partnerships that benefit the company’s financial health.
Logistics Management
Logistics Management is focused on managing the movement of goods within the supply chain, which encompasses:
a) Developing business partnerships.
b) Contract negotiation.
c) Scheduling for transport logistics.
d) Keeping a robust network that includes suppliers, storage, and transport services.
Procurement Management
Procurement Management is the initial stage of the supply chain, ensuring that companies have consistent sources for their products. Responsibilities include:
a) Vendor selection based on cost-effectiveness, availability, and material quality.
b) Scheduling purchases to align with market demand and supply chain trends.
c) Cost analysis and optimisation.
Operations Management
Operations Management sits at the core of the supply chain, involving internal business management and, often, supply chain responsibilities. Key tasks involve:
a) Managing production, sales, and distribution.
b) Overseeing budget, cost, and profitability.
c) Balancing supply and demand.
d) Forecasting and staff management.
e) Operations managers may have varying degrees of supply chain involvement based on company size.
Warehouse Management
Warehouse Management is crucial for logistics and supply chain efficiency, ensuring timely and quality delivery without increasing costs. Warehouse Managers are responsible for:
a) Inventory and staff management.
b) Enhancing operational efficiency.
c) Coordinating workflows.
d) Collaborating with logistics teams.
Transportation Management
Transportation Management plays a vital role in logistics by coordinating the transportation of goods, especially in manufacturing sectors. Transportation Managers are tasked with:
a) Selecting optimal transportation methods.
b) Setting cost and delivery expectations.
c) Working with transportation service providers.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between Supply Chain vs Logistics is important for anyone interested in these fields. Supply Chain Management covers the whole journey of a product, from raw materials to the customer. Logistics focuses on moving, storing, and delivering goods. By learning about Supply Chain vs Logistics, you can find which career suits your interests and skills.
Understand the Supply Chain structure and its planning process with our Supply Chain Management Training – join today!
Frequently Asked Questions

No, Supply Chain Management is a broader concept that covers Logistics. Supply Chain includes all processes involved in the production and distribution of goods, while Logistics focuses on the transportation and storage aspects.

A degree in Logistics, Supply Chain, or a related field is often required. Additional certifications and practical experience through internships can also enhance your qualifications.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Industry Training, including Logistics Management Training, Supply Chain Management Training, and Import-Export Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Types of Supply Chain Management.
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to Logistics, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Supply Chain Management skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Supply Chain Management Training
Supply Chain Management Training
Fri 3rd Jan 2025
Fri 7th Mar 2025
Fri 2nd May 2025
Fri 4th Jul 2025
Fri 5th Sep 2025
Fri 7th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


