We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +33 805638382 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

The Sarbanes Oxley Act, a legislative response to alarming corporate scandals, represents a watershed moment in modern financial governance. his Act was enacted in 2002 as a direct response to the widespread accounting fraud and unethical practices that eroded public trust in financial markets.
Furthermore, named after its sponsors, Senator Paul Sarbanes and Representative Michael Oxley, the Sarbanes Oxley Act aimed to restore investor confidence by introducing comprehensive reforms that transformed corporate accountability, financial reporting, and auditing practices.
Uncover the layers of the Sarbanes Oxley Act. Gain valuable knowledge about regulatory compliance, internal controls, and corporate transparency below.
Table of Contents
1) What is the Sarbanes Oxley Act?
2) Sarbanes Oxley Act History
3) The Main Purpose of the Sarbanes Oxley Act
4) Criticism of the Sarbanes Oxley Act
5) The Key Provisions Under the Sarbanes Oxley Act
6) Benefits of the Sarbanes Oxley Act
7) Conclusion
What is the Sarbanes Oxley Act?
The Sarbanes Oxley Act (SOX), enacted in 2002 by the U.S. Congress, emerged in response to high-profile corporate scandals that eroded public trust in the financial markets. Named after the two sponsors, Senator Paul Sarbanes and Representative Michael Oxley, the act aimed to restore integrity and accountability within the corporate sector. SOX introduced a series of comprehensive reforms that revolutionised corporate governance, financial reporting, and auditing practices.
Additionally, the key provisions of the Sarbanes Oxley Act include the establishment of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (PCAOB), an independent regulatory body responsible for overseeing auditing firms and enforcing auditing standards. Now the CEOs and CFOs of public companies need to personally certify the accuracy of financial statements, enhancing executive accountability.
More importantly, the act mandates that audit committees be composed of independent directors to ensure impartial oversight of financial reporting and internal controls. Additionally, SOX emphasises the evaluation and reporting of internal controls over financial reporting for preventing fraud and inaccuracies. Whistleblower protections encourage employees to report misconduct, safeguarding them from retaliation.
History of Sarbanes Oxley Act
The Sarbanes Oxley Act is a crucial piece of legislation that has reshaped the corporate governance and financial practices constantly in the United States. Here is the brief History about Sarbanes Oxley you must need to know to proceed forward with the topic:
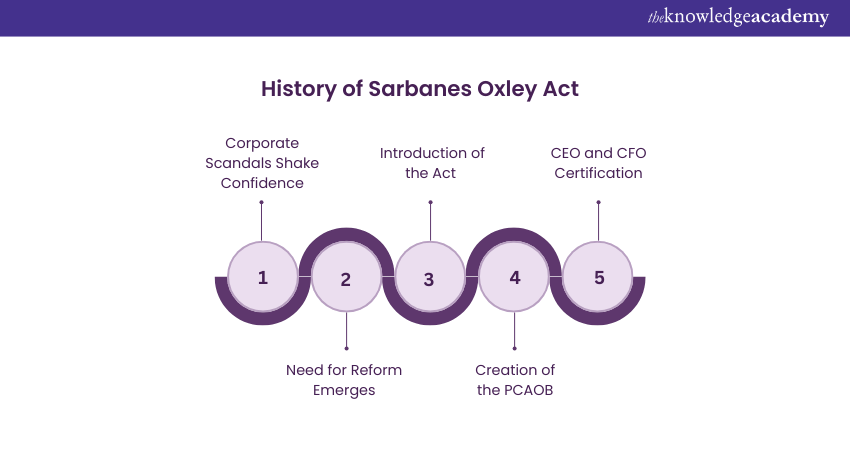
1) Corporate Scandals Shake Confidence: The enactment journey began in the early 2000s when the infamous scandals, Enron and WorldCom were exposed worldwide because of their allegations of accounting fraud and unethical practices. These practices have caused widespread investor losses and also hindered public interest severely.
2) Need for Reform Emerges: The intense cry of public outrage and a comprehensive demand for greater accountability forced the US Congress to address these weaknesses in corporate governance and financial reporting.
3) Introduction of the Act: In 2002, Senator Paul Sarbanes and Representative Michael Oxley gave their sponsorship for the newly-designed Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX). It was created to restore the confidence of the investors and improve their corporate accountability.
4) Creation of the PCAOB: Over the course of time, the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (PCAOB), a central aspect of SOX, was established to particularly take care of the auditing firms and establishing auditing standards and compliance.
5) CEO and CFO Certification: The Act further mandates that CEOs and CFOs will be required to personally certify the accuracy of financial statements, by holding top executives accountable for the veracity of company financials.
Kickstart your Audit career here with ISO 37301 Compliance Management Systems Lead Auditor Training - join today!
The Main Purpose of the Sarbanes Oxley Act
The Sarbanes Oxley Act of 2002 introduced numerous wide scale reforms to improve corporate accountability and transparency. Here are the key purposes of the Sarbanes Oxley Act of 2002 described below:
1) Corporate Governance: It improves corporate governance and financial transparency against the major accounting scandals.
2) Financial Reporting: It demands stricter regulations for financial reporting by ordering companies to put robust internal controls into action and ensure the accuracy of their financial statements.
3) Investor Protection: Sarbanes Oxley Act of 2002 aims to protect investors by improving their accountability among corporate executives and board members while also increasing the penalties charges for fraudulent financial activity.
4) Market Trust: It also helps in building greater trust in the financial markets by bringing together investor confidence and improving the overall integrity of the corporate financial system.
5) Auditing Standards: It ensures that external auditors comply with established guidelines to boost the reliability of financial reports.
6) Disclosure Requirements: The law mandates that companies disclose more information about their financial conditions and requires executives to personally certify the financial statements' accuracy.
Gain specialty in Compliance Management Techniques with ISO 19600 Compliance Management Systems Training- sign up now!
Criticism of the Sarbanes Oxley Act
Despite bringing corporate governance together, the Sarbanes Oxley Act has also faced with numerous criticisms from a different stakeholder. Here are the criticisms of the Sarbanes Oxley Act described as follows:
1) Compliance Costs: Critics argue that the Sarbanes Oxley Act imposes excessive compliance costs on businesses, especially the smaller companies that struggle to meet the stringent requirements.
2) Financial Burden: Numerous globally organisations have faced severe financial burdens due to the need for enhancing internal controls and detailed financial reporting processes.
3) Resource Diversion: The elevated scrutiny required by the Act can divert resources from core business activities and stifle innovation.
4) Unintended Consequences: Detractors contend that the Act may discourage companies from going public or prompt them to seek foreign markets with less regulatory oversight.
5) Root Causes: Some critics believe that the Sarbanes Oxley Act does not effectively address the root causes of corporate fraud.
The Key Provisions Under the Sarbanes Oxley Act
With time, the Sarbanes Oxley Act (SOX) gave rise to several pivotal provisions to improve corporate accountability and transparency, notably through Sections 302, 404, and 802. Here is a list of the provisions under the Sarbanes described in detail described below:
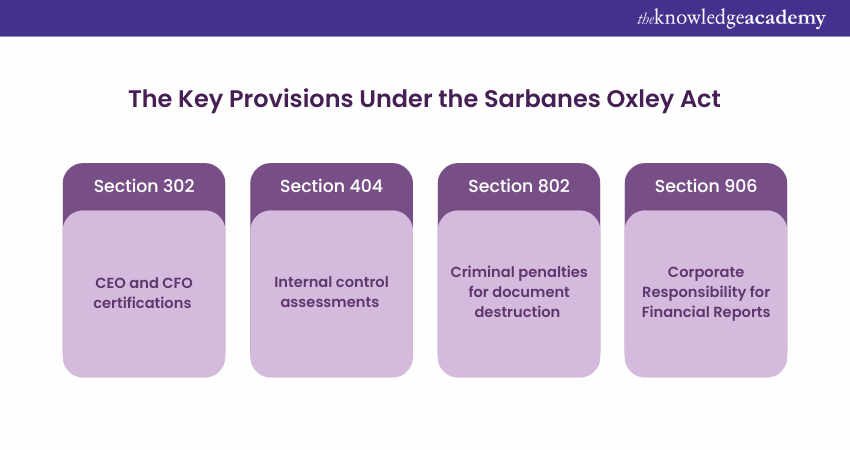
1) Section 302 - CEO and CFO Certifications
SOX Section 302 made it compulsory for all CEOs and CFOs of public companies to personally attest the accuracy of their company's financial statements and disclosures. This provision primarily holds top executives accountable for the reliability of financial information. Therefore, it necessitates a statement asserting their understanding of internal controls and their effectiveness.
2) Section 404 - Internal Control Assessments
Section 404 has remained one of the most impactful provisions, which mandated that companies would assess and report on how effective their internal controls are over financial reporting. This involves identifying potential risks, evaluating control procedures, and ensuring that financial data is accurately captured and presented to the relevant stakeholders. The provision also demands external auditors to attest to the effectiveness of these controls.
3) Section 802 - Criminal Penalties for Document Destruction
Section 802 primarily addresses the investigations and introduction of criminal penalties for the destruction, alteration, or falsification of records, documents, or tangible objects. This is with the intent to impede, block, or influence any legal investigation or proceeding. This provision seeks to prevent tampering with evidence and ensure the integrity of investigations.
4) Section 906: Corporate Responsibility for Financial Reports
Section 906 of the Sarbanes Oxley Act was started in response to the much-needed corporate accountability by imposing strict criminal penalties on executives whose actions knowingly lead to fraudulent financial reports. This section requires that CEOs and CFOs of all companies submit a statement with their company's periodic reports.
Benefits of the Sarbanes Oxley Act
The Sarbanes Oxley Act (SOX) provides significant benefits to the corporate ecosystem by adapting transparency, accountability, and investor confidence. Below listed are some of its key benefits you need to know:
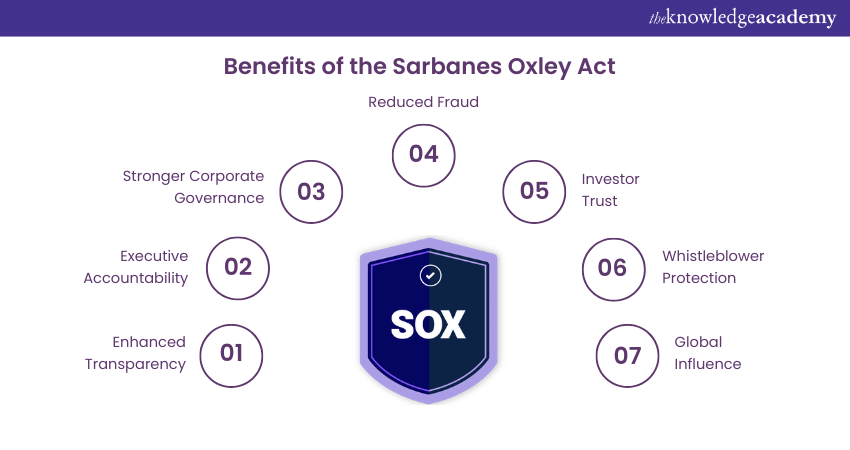
1) Enhanced Transparency: The rigorous reporting requirements of the Sarbanes Oxley Act ensure optimum accuracy and timely financial disclosures, which allow investors to make informed and empowering decisions.
2) Executive Accountability: The Act also mandates certifications, ranging from the CEO and CFO to analyse the accuracy of financial statements and internal controls.
3) Stronger Corporate Governance: The independent audit committees improve oversight, and further reduces the conflicts of interest and enhancing checks and balances.
4) Reduced fraud: The internal control assessments under Section 404 minimise the risk of financial fraud, further enhancing the integrity of financial reporting.
5) Investor trust: Its critical reforms have restored investor trust, attracted capital and contributed to stable financial markets.
Master internal Auditing best practices with our Certified Internal Auditor Training- register today!
Conclusion
We hope you understand in depth about the Sarbanes-Oxley Act. The Sarbanes-Oxley Act is a testament for optimal reshaping corporate practices. Through its stringent provisions, the Act has fortified accountability, heightened transparency, and fostered enduring investor confidence. Its legacy will continue to resonate as time passes, setting a precedent for ethical governance in modern business.
Transform your Quality Management approach- sign up for our ISO 10001 Quality Management System Training today!
Frequently Asked Questions

The four critical SOX controls are: Segregation of Duties (to prevent one person from controlling multiple transaction phases), Access Controls (to restrict financial data to authorized personnel), Regular Reconciliation (to align internal and external records), and Monitoring and Auditing (to ensure compliance with controls).

The Sarbanes Oxley Act (SOX) rule is a guideline set by the US Congress that states the necessary regulations to optimise corporate governance and financial disclosures for public companies in the United States.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Sarbanes-Oxley Training, including Sarbanes-Oxley Certified Professional Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Top 15+ Sarbanes-Oxley Compliance Software.
Our ISO & Compliance Blogs cover a range of topics related to ISO standards and compliance frameworks, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your auditing and quality management skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming ISO & Compliance Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Sarbanes-Oxley Certified Professional
Sarbanes-Oxley Certified Professional
Mon 10th Mar 2025
Mon 2nd Jun 2025
Mon 8th Sep 2025
Mon 3rd Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


