We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +33 805638382 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

In the face of an accident, knowing what to do can make all the difference. First Aid is your first line of defence, a crucial skill that can mean the difference between life and death. But What is First Aid? And how do you practice it? It truly is a risky business if you don't know what you are doing. The right moves can help save a life or prevent tragic adversities. At the same time, the wrong ones can cost a life or limb.
Join us as we explore What is First Aid. Discover why it’s essential, how to master it, and the DRSABCD action plan that could one day save a life. This blog is your guide to becoming one of the many everyday heroes who step up in critical moments. Let’s learn together how to be prepared for emergencies and make a real impact.Table of Contents
1) What Exactly is First Aid?
2) Why is First Aid Necessary?
3) The Role of First Responders (First Aiders)
4) Three Key Actions for Dealing with Emergencies
5) First Aid for Different Conditions
6) Conclusion
What Exactly is First Aid?
If you've seen the movie, ‘Fight Club’, you'd know the first thing to do if someone has a lye burn is pour vinegar instead of water. As the water would react with lye and only worsen the burn.
That is a great example of First Aid! In emergencies, people who need a doctor might not be able to wait to be taken to a hospital! Anyone who knows First Aid can help save the day! First Aid is an attempt to give the sick or injured person momentary relief or prevent further damage. This first step during an emergency is called First Aid.
Some common first-aid techniques
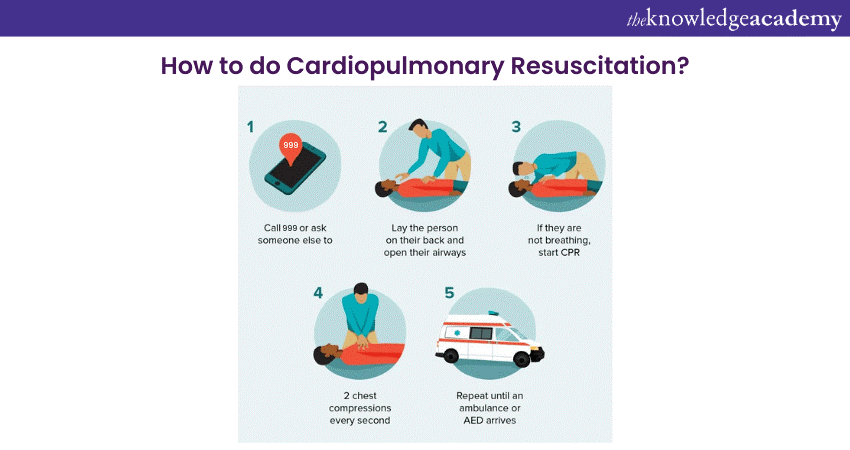
a) Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR): In a situation where a person has stopped breathing, or the heart has indeed stopped with such standard possibilities of death, a person can save their life by giving chest compressions alongside rescue breaths to the individual.
b) Automated External Defibrillator (AED): A device that applies shock of an electric current to the heart of the patient who would most likely be in a condition of probable cardiac arrest at that time.
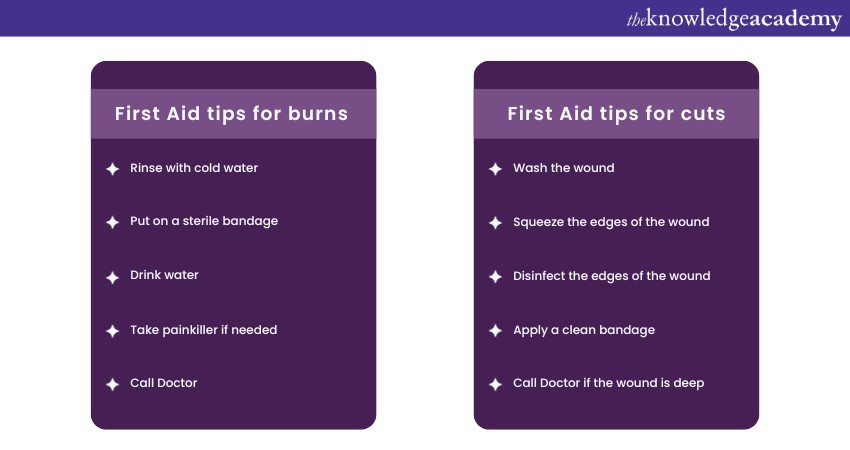
c) Bleeding control: When there are indications of any form of cut, piercing, or wound and the blood is profusely oozing, care needs to be taken to staunch the blood by applying pressure at the site in a bid to forestall extensive damage or even the loss of more blood. One may avoid going into shock in case of blood loss or infection.
d) Burn: The burn area should be cooled directly with water or a wet cloth to reduce pain and inflammation. In both mild and severe burns, this will reduce damage to the skin and the underlying tissues.
e) Choking: An individual who is choking can be relieved at first Aid through blows and marches that are done on the abdomen. This process can ensure the object that has blocked the passage goes out successfully. Clearing the passage and the victim breathing again.
Why is First Aid Necessary?
Now that you know What is First Aid, let’s understand its importance in detail. First Aid is necessary for several important reasons:
1) Saving lives: The primary goal of First Aid is to save lives. Your immediate help can make a difference in case of an injury or unexpected illness, which are serious conditions. First Aid is basic care that involves simple actions such as Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation , controlling bleeding or opening up an airway, just to mention a few which have the effect of saving a life.
2) Preventing further injury: First Aid training is not merely about saving lives; it is also about saving any aggravations that may increase the complexity of an accident. The main role you have at this point is to stabilise the injured individual's condition and supply immediate care; by doing so, you help decrease the probability of getting hurt further.
3) Promoting recovery: First Aid reduces injury complications, hence allowing those in need to heal quickly. When a person gets immediate and effective care, the possibilities of treatments succeeding and the patient having a full recovery can be highly improved.
4) Minimising pain and suffering: The First Aid services relieve a hurt or sick person of the sufferings they have been going through. What it gives is empathy and understanding. This can bring the sea of sorrow nearer to the shoreline.5) Buying time for professional help:Medical aid is not possible every scenario. First Aid is like a bridge that provides immediately needed first aid until para-medical or medical assistance comes.
6) Empowering individuals: Having sufficient First Aid skills enables people to act well on different emergencies that may take place directly around them. So, it provides people with the capacity and tools to achieve goals and to support individuals who can’t do it by themselves.
Elevate your team's safety standards – join our Health and Safety Training for Managers and Supervisors today!
The Role of First Respondents (First Aiders)
When things go sideways at a local gathering or a public place, and someone gets hurt, the First Responder jumps into the fray. With their swift and assured actions, this person becomes the anchor in a storm of worry and confusion.
First Respondersare more than just the First Aid providers on the scene; they're a source of immediate relief, making quick decisions which can differentiate between a close call and a crisis.
They keep the situation from spiralling by stepping up and providing essential care and a sense of security until the cavalry arrives. It's this blend of readiness, skill, and compassion that makes First Responders invaluable in First Aidscenarios, acting as the community's safety net, ready to catch us at our most vulnerable.
Three Key Actions for Dealing with Emergencies
In those heart-stopping moments when someone's out cold or not answering, speed's your best friend, and the Danger, Response, Send for Help, Airway, Breathing, CPR, and Defibrillation, which is also known as DRSABCD, is your roadmap to help.
Think of it as your First Aid ABCs with a little extra. DRSABCD is a lifesaver hack you can adapt. Here are the first three steps while to taking action:

Assess the Environment for Hazards
Hazards come in many forms, from fires and smoke to electrical dangers and traffic. To keep everyone safe, it’s important to either remove the hazard or move people to a safer location, always with the priority of saving lives.
Stay vigilant for signs of danger: look out for flames, sparks, exposed wires, broken glass, and listen for sirens or alarms. If you smell gas or smoke, it’s time to evacuate.
Remember, being a hero is about being smart. Don’t put yourself at risk; if you’re not sure it’s safe, stay back and wait for the experts to arrive. Your safety is just as important as helping others.
Request Medical Assistance If Required
The second step is to check for a response from the person in danger by asking their name or gently squeezing their shoulders. If there’s no response, call 999 for help and do not leave the person alone.
When contacting emergency services, provide:
a) Your name and location
b) The number of people involved and their condition
c) The type of emergency and what happened
d) Any relevant details, like allergies or medications
Stay on the call and follow the operator’s instructions until they tell you to hang up.
Provide Care
The third step is to provide care based on the person's condition and the DRSABCD action plan:
a) Airway: Check for blockages in the mouth. If found, roll the person onto their side and clear the airway. If clear, leave them as found and open the airway by tilting their head back with a chin lift.
b) Breathing: Check for breathing by looking, feeling, and listening. If they aren’t breathing or breathe irregularly, give two breaths at 30-second intervals.
c) Circulation: Check for a pulse on the person's neck or wrist. If absent, check for tight clothing around the neck. If still absent, start chest compressions at a rate of 100-120 per minute.
d) Defibrillation: If available, use a defibrillator and follow its prompts.
Continue care until help arrives or the person shows signs of life. Following these steps can potentially save a life.
First Aid for Different Conditions
In accordance with the seriousness of the injury/illness, you might call for First aid, which is specific. Some common possibilities that may require First Aid are:
Allergic Reactions and Anaphylaxis
If the person with an allergic reaction is severely symptomatic with breathing problems, swoleness, and hives, give them the epinephrine injection if it is available and call the emergency service.
Asthma Attacks
In case someone is having an asthma attack they are facing breathing dysfunction. Let them sit up and give them their inhaler or nebuliser. Invite them to lift their shoulders, take a deep breath, and then release it slowly. If they are not getting better, tell them to call a doctor for help.
Bleeding
If somebody is bleeding, put something clean on it and press on the hurt, so the blood won't flow. See if you can place the wound somewhere above their heart and sink it downward, making it less noticeable. Call a doctor if bleeding is from the wrong spot or keep going.
Burns
In these instances, give someone at least 10 minutes in cold water. Usage of ice, butter or creams should be avoided. The wound should be covered with a clean layer of gauze. Seek medical care in case the burn is large, deep, or sustains high-risk areas such as the face or hands.
Choking
This is when something gets stuck in the throat and blocks the airway. If someone is choking, ask them to cough if they can. If they cannot cough, speak, or breathe, perform the Heimlich manoeuvre by standing behind them and giving five quick abdominal thrusts. Repeat until the object comes out or they become unconscious. If they become unconscious, call 999 and start CPR.
Fractures (Broken bones)
These are breaks or cracks in the bones caused by trauma or stress. If someone has a fracture, do not move them unless necessary. Immobilise the injured part with a splint or sling. Apply ice to reduce swelling and pain. Call local emergency hotlines if the fracture is open, severe, or involves the head, neck, back, chest, or abdomen.
Head injuries
If someone suffers from injuries to the head, check if the person is awake and can respond. Contact the local helpline for emergency help if they're unconscious, seem confused, or start vomiting, having seizures, or bleeding from the nose or ears. Keep them still and watch their breathing and heartbeat.
Poisoning
If someone has swallowed, inhaled, or touched something poisonous, its best to contact emergency services immediately and follow their advice. Please don't make them throw up unless you're told to. Try to figure out what they were poisoned with.
Seizures
If someone is having a seizure, move away all sharp objects and put something soft under their head. Do not hold them down or constrain them. Avoid putting anything in their mouth. Call for help if the seizure lasts more than 5 minutes or if they have another one.
Shock
When not enough blood reaches the organs, they might go into a state of shock. If someone looks like they're in shock, call for help, lay them down, and lift their legs. Keep them warm and calm. Watch their breathing and pulse until help gets there.
Equip your team with life-saving skills – Invest in First Aid At Work Training today!
Conclusion
First Aid is the most basic knowledge that must be mastered to help people and support emergency situations until professional help arrives. Learning what to do is important because it can make a big difference in someone's life and give their loved more time with them. First Aid can help ensure that no further damage is done. Having provided you with the required knowledge about What is First Aid, we hope that you are now able to apply it in emergency situations to save the lives of those in need.
Start promoting Health and Safety in your workplace with our Helath and Safety Courses today!
Frequently Asked Questions

Common myths include misconceptions that you should always induce vomiting for poisoning, apply butter to burns, or that only professionals can perform CPR. These myths can hinder effective First Aid and cause further harm.

Quick and appropriate First Aid can help save lives by stabilising victims, preventing conditions from worsening, and minimising the severity of injuries until professional medical help arrives.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Health & Safety Courses, including Advance First-Aid training, Active and healthy lifestyle training and Counselling Masterclass. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into The Difference Between a Panic Attack vs Anxiety Attack.
Our Health & Safety blogs cover a range of topics related to First Aid, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your First Aidskills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Health & Safety Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 First Aid at Work
First Aid at Work
Thu 20th Feb 2025
Thu 26th Jun 2025
Thu 25th Sep 2025
Thu 20th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


