We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +08000201623 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
With the immense technological developments we have had in the past decade, we have been gifted with the power to remain connected with people worldwide. Even in remote locations, with the help of cellular network technology, people can access any information and stay connected with anybody from any corner of the world. Recently, we have been introduced to another cellular network technology – 5G. But do you know What is 5G?
It is the fifth-generation cellular network technology, representing a significant leap over its predecessor, 4G. It promises dramatically faster data download and upload speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity, enabling more simultaneous connections.
But this cellular technology is not just about high-speed internet, to know more about it, read this blog. In this blog, you will learn more about What is 5G, its importance, the types of 5G wireless services and how it benefits society.
Table of Contents
1) What is 5G?
2) Why is 5G Important?
3) How Does 5G Technology Work?
4) What is the Difference Between 5G and 4G/3G?
5) 5G Use Cases
6) Benefits of 5G on Society
7) Is 5G Faster Than Wi-Fi?
8) Who Invented 5G?
9) Conclusion
What is 5G?
5G, the 5th generation mobile network, is the latest global wireless standard following 1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G. It’s designed to connect virtually everyone and everything, including machines, objects, and devices.
5G technology promises higher multi-Gbps peak data speeds, ultra-low latency, greater reliability, massive network capacity, increased availability, and a more uniform user experience (UX), as detailed in the 5G Technology Guide. These enhancements enable new user experiences (UX) and connect various industries, offering higher performance and improved efficiency.
Why is 5G Important?
Now that you have a little idea of What is 5G technology, let’s see how it is transforming the way we live. This technology is considered a cornerstone in the evolution of digital connectivity, heralding significant changes across various sectors. Its importance stems from several key factors which are as follows:
a) Enhanced Speed and Capacity: 5G offers exponentially faster data transfer speeds than 4G, potentially reaching up to 10 Gbps. This speed improves the user experience for mobile internet. It also enables rapid downloading and uploading of large files, high-quality video streaming, and seamless cloud-based services.
b) Reduced Latency: It significantly reduces latency – the time a signal takes to travel from origin to receiver and back – to as low as one millisecond. This is vital for applications that require real-time responses, such as telemedicine, autonomous vehicles, and advanced gaming.
c) Increased Connectivity: It can support a much higher density of devices – up to 1 million per square kilometre. This aspect is vital for the growing Internet of Things (IoT), enabling more smart devices and sensors to connect reliably.
d) Industrial and Urban Transformation: It is set to revolutionise industries by enabling smart factories with connected sensors and machines, improving efficiency and safety. It also underpins the development of smart cities, facilitating better traffic management, energy distribution, and public services.
e) Innovation Enabler: The high speed and low latency of 5G unlock the potential for new technological innovations in virtual and augmented reality, AI, and next-generation emergency services.
How Does 5G Technology Work?
To help you understand the 5G network, we have explained how this cellular technology works:
1) Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) is a critical method in 5G technology that efficiently manages data transmission. It splits the radio spectrum into several narrowband channels at different frequencies.
This approach is advantageous because it reduces interference and can simultaneously carry a high amount of data. OFDM in 5G is an enhanced version known as OFDM-A, or Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access. It allows several users to access the network simultaneously by assigning them different subcarriers.
The key benefit of OFDM is its ability to handle the high-speed data transmission required by 5G Applications while coping with issues like signal interference and reflection, common in densely built-up areas.
Moreover, OFDM supports both high-bandwidth applications, such as video streaming, and low-bandwidth applications, like IoT devices, making it versatile. This technology's efficient spectrum use makes it fundamental to the functionality and performance of 5G networks.
2) Reduced Tower Size in 5G
In 5G networks, the size of cell towers and antennas is notably reduced compared to previous generations. This reduction is possible because of the higher frequency bands (millimetre waves) that 5G uses, which require smaller antennas.
These smaller cell sites, often called small cells, can be easily installed in various settings, like light poles and rooftops. The advantage of smaller towers is their ability to be densely deployed in urban areas. This provides more extensive coverage and better signal quality.
However, the higher frequency signals have a shorter range and are more susceptible to interference from physical obstacles like buildings and trees. To combat this, 5G networks rely on a more extensive network of these small cells to ensure consistent coverage. If you're preparing for a technical discussion or 5G Interview Questions, understanding these challenges and solutions is crucial.
This approach leads to a more distributed network infrastructure, enabling the massive bandwidth and low latency features of 5G. The deployment of small cells is a crucial aspect of the 5G network. It facilitates its capacity to support many high-bandwidth connections in densely populated urban areas.
3) Breakdown of Network Slicing
Network slicing enables the creation of tailor-made networks that meet specific requirements of diverse applications, such as the following:
a) Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB)
b) Ultra-reliable Low-latency Communications (URLLC)
c) Massive Machine Type Communications (mMTC)
Each network slice can be customised with bandwidth, speed, capacity, connectivity, and security settings. For instance, a slice designed for IoT devices can prioritise power efficiency and comprehensive coverage, while a slice for autonomous vehicles might focus on ultra-low latency and high reliability.
Learn everything about the concept of Digital Twin and how it is deployed – join our Digital Twin Training!
What is the Difference Between 5G and 4G/3G?
While 5G operates on the same radio frequencies as its predecessors, there are several key differences between 5G and 4G, 4G LTE, and 3G:
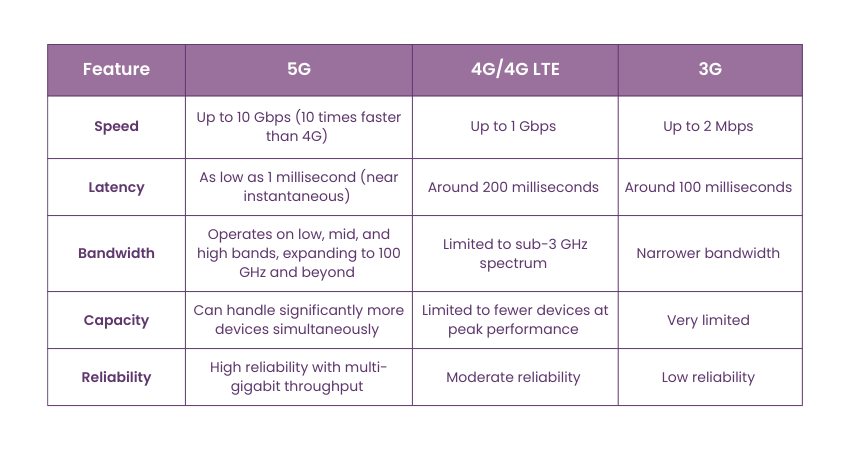
1) Faster Speeds
5G networks can hit speeds of up to 10 gigabits per second, making them 10 times faster than 4G networks. Tasks that used to take significant time, such as downloading a movie or backing up a database, can now be done much faster.
2) Low Latency
A key factor behind the speed improvement is reduced latency, which refers to the time delay between sending and receiving data. While 4G networks have a latency of around 200 milliseconds, 5G reduces this to just one millisecond, allowing for near-instantaneous communication.
3) Higher Bandwidth
5G can operate across a wider range of bandwidths, from low band to mid band to high band, by expanding radio spectrum resources from sub-3 GHz used in 4G to 100 GHz and beyond. This broader bandwidth means 5G can handle more devices simultaneously, providing higher capacity, multi-gigabit throughput, and low latency.
These advancements make 5G a significant upgrade over previous generations, offering faster, more reliable, and more efficient connectivity.
5G Use Cases
As 5G technology continues to expand, its potential to drive economic growth and enhance connectivity is boundless. Here are some ambitious ways 5G could transform our world:
1) Smarter Communities
5G's capability to collect data from IoT devices is poised to improve daily life, whether in busy urban centers or isolated rural regions. City planners, emergency responders, and others are looking to 5G to help reduce traffic, improve planning, lower air pollution, and generally enhance the quality of life for their communities.
2) Better Healthcare
In healthcare, 5G networks enable advancements in remote surgery, data analytics, and patient care. The low latency of 5G allows real-time information sharing over HD video, making remote surgeries more feasible. Additionally, IoT-connected devices using 5G can provide real-time patient monitoring, helping doctors care for patients outside of direct supervision.
3) Greater Sustainability
5G will significantly enhance the ability of enterprises to monitor their Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) goals, such as reducing carbon emissions, ensuring worker safety, and managing supply chains. One of 5G's key benefits is its energy efficiency compared to previous generations. It will also support the development of electric vehicles, smart buildings, and remote work, all of which contribute to lower carbon emissions.
These use cases illustrate how 5G technology can revolutionise various aspects of our lives, making our communities smarter, healthcare better, and our world more sustainable.
Do you want to learn more about 5G Wireless services? Register now for our 5G Wireless Training!
Benefits of 5G on Society
The following are some benefits of 5G on society:
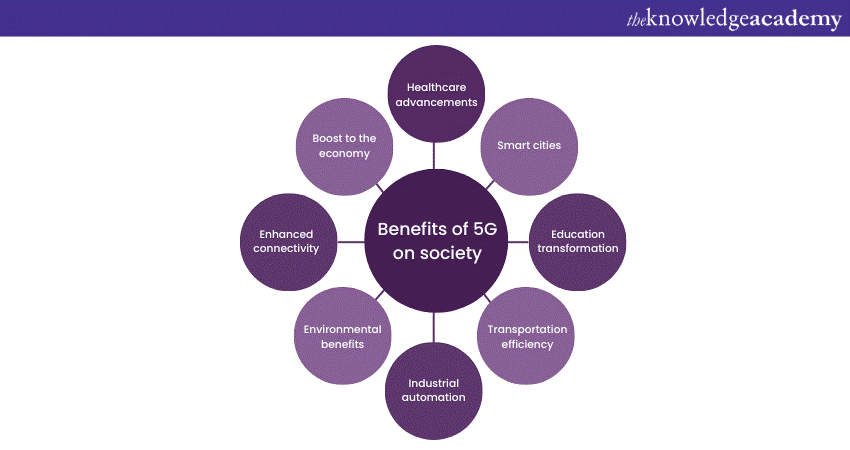
a) 5G provides ultra-fast internet speeds, improving Effective communication and access to information
b) Creates new job opportunities and fosters innovation, contributing to economic growth.
c) Telemedicine and remote surgeries benefit greatly from the Benefits of 5G Technology, improving healthcare accessibility and efficiency.
d) Facilitates smart infrastructure development, leading to efficient resource management and improved urban living.
e) Allows high-quality online learning experiences, making education more accessible.
f) Supports the development of autonomous vehicles and smart traffic systems, reducing congestion and improving safety.
g) Enhances manufacturing with IoT and AI integration, increasing productivity and safety.
h) Enables efficient energy management and supports sustainable practices through smart technology integration.
Is 5G Faster Than Wi-Fi?
5G can be faster than Wi-Fi depending on the conditions and technology. With speeds reaching up to 10 Gbps, 5G often outperforms older Wi-Fi standards. However, Wi-Fi 6 and newer routers can match 5G speeds in ideal settings, making both highly competitive for fast connectivity.
Who Invented 5G?
5G wasn’t invented by one person but was developed through global collaboration. Telecom companies, industry leaders, and organisations like the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) played key roles in creating 5G standards, ensuring it works worldwide.
Learn more about some of the best advanced technologies – join now for our Advanced Technologies Courses!
Conclusion
We hope you learnt What is 5G and its importance and benefits on society. This technology stands as a transformative force, ushering in a new era of connectivity. It promises to revolutionise various sectors, from healthcare to transportation, by offering unprecedented speed, reduced latency, and increased capacity. The widespread adoption of 5G will significantly enhance societal and economic growth, shaping a more connected and efficient future.
Enhance your knowledge more on Internet of Things IoT Systems and Applications– sign up now for our Internet of Things IoT Systems and Applications Training!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is 5G?

5G is the fifth-generation cellular network technology. It provides faster data speeds, reduced latency, and the capability to connect many more devices at once. 5G is designed to support a growing range of applications and devices, including the Internet of Things (IoT), advanced mobile broadband, and emerging technologies.
How Fast is 5G Compared to 4G?

5G is significantly faster than 4G. It has the potential to offer speeds up to 20 Gbps, which is about 100 times faster than 4G. The actual speed users experience will depend on various factors, including the network provider, the device used, and the number of devices connected to the network.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is the Knowledge Pass, and how does it work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are related Advanced Technology courses and blogs provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Advanced Technology Courses, including 5G Wireless courses, Digital Twin, and Internet of Things IoT Systems and Applications. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Advanced Technology Trends of 2024.
Our Advanced Technologies blogs covers a range of topics related to 5G Wireless, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Project Management skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Advanced Technology Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 5G Wireless Training
5G Wireless Training
Thu 29th May 2025
Thu 24th Jul 2025
Thu 4th Sep 2025
Thu 6th Nov 2025
Thu 29th Jan 2026
Thu 16th Apr 2026
Thu 3rd Sep 2026
Thu 10th Dec 2026






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


