We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +08000201623 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Accounting is a fundamental concept in the financial world, yet most people do not know, What is Accounting? Well, it involves the systematic accounting cycle of recording, classifying, summarising, and interpreting financial transactions and events. These transactions can range from sales and purchases to investments and expenditures.
According to Sussap, the global Accounting industry accounts worth £530 billion in 2023. The exponential growth of the industry is proof of its importance in organisation and personal finance. In this blog, we will learn What is Accounting, the fundamentals of Accounting. Also, we will explore its purpose, types, principles, and standards.
Table of Contents
1) Introduction to Accounting
2) Purpose and importance of Accounting
3) Principles and standards
4) Key concepts in Accounting
5) Types of Accounting
6) Conclusion
Introduction to Accounting
Accounting provides a structured framework for businesses, organisations, and individuals to keep track of their financial activities, a key focus in Accounting Interview Questions. Organisations can also assess their financial health and make informed decisions. The two main parts of Accounting are as follows:
a) Income statements: The income statement showcases the financial performance over a specific period – revenue and expenses as a key point.
b) Balance sheets: The balance sheet displays the financial position, showcasing the business assets and liabilities.
Purpose and importance of Accounting
At its core, Accounting serves two primary purposes: recording financial transactions and providing relevant financial information for decision-making. The ability to accurately record and report financial activities ensures transparency and accountability within an organisation. These records enable stakeholders, such as business owners, investors, creditors, and regulators, to examine the financial health of an entity and make informed judgments.
Accounting also facilitates effective decision-making by providing timely and reliable financial information. Business decisions, such as investing in new equipment, expanding operations, or allocating resources, rely heavily on accurate financial data.

By analysing financial reports, decision-makers can evaluate the profitability, liquidity, and solvency of a business, ultimately leading to well-informed choices. Some of the benefits of Accounting are as follows:
a) Financial reporting: Financial reporting helps organisations create accurate and transparent financial statements that communicate an organisation's financial performance to stakeholders.
b) Decision making: Accounting helps in providing data-driven insights that guide strategic decisions, resource allocation, and future planning.
c) Compliance: Ensuring adherence to financial regulations and standards in Accounting helps in facilitating transparent business practices.
d) Performance evaluation:
Assessing an organisation's efficiency, profitability, and growth trajectory is the key role of Accounting.
Prepare Like a Pro! – Explore the top Financial Modelling Interview Questions and boost your confidence for your next job interview.
Principles and standards
Accounting definitions and concepts cannot be learned without understanding its principle and standards. These principles and standards can help you develop Basic Accounting Skills, which is helpful for both individual and organisations levels.
Principles and standards provide a framework for maintaining consistency, accuracy, and comparability in financial reporting across different entities and industries. Some of the key principles and standards include the following:
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
IFRS is a globally accepted set of Accounting standards introduced by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). It is widely adopted in many countries, promoting consistency and transparency in financial reporting on a global scale.
IFRS allows businesses to convey their financial stories in a recognised and comprehensible format globally. One of the key benefits of IFRS is the enhancement of comparability. Investors and stakeholders can easily compare the financial performance and position of companies from different countries.
Industry specific standards
Industry-specific standards are guidelines designed to cater to the unique characteristics of different sectors, ensuring that financial information accurately reflects the objectives of each industry.
Industry-specific standards go beyond addressing operational complexities. They also play a vital role in regulatory compliance. Regulatory bodies often collaborate with industry experts to develop Accounting guidelines that reflect the sector's realities and adhere to legal and regulatory requirements
Conservatism principle
The conservatism principle of Accounting, which is also known as the Prudence principle, suggests that Accountants should exercise caution when recording financial transactions. It is better to underestimate assets and revenues and overestimate liabilities and expenses to avoid overstating financial position and performance.
It prevents the temptation to manipulate numbers to present an unclear financial picture than reality warrants. Financial decisions and outcomes are often uncertain, and this principle urges Accountants to take caution, especially to assess the financial health of a business.
Accrual principle
Unlike cash Accounting, which records transactions only when cash changes hands, the Accrual Principle emphasises recording transactions when they occur, irrespective of the timing of cash flows.
This principle is rooted in the notion of matching revenue with expenses. It recognises that transactions often involve a chain of events that extend beyond the moment of cash exchange. It ensures that revenue is recognised when its earned. At the same time, expenses are recorded when they're incurred, even if there's a delay in the actual cash movement.
Boost Your Accounting Knowledge! Understand the Difference Between Cost Accounting and Financial Accounting.
Key concepts in Accounting
After understanding What is Accounting and its principles, it’s time to understand its concepts. The key concept of Accounting provides a structured way to record, analyse, and communicate the financial health of an organisation. These concepts are the foundation on which the whole system relies. Some of the crucial concepts in Accounting are as follows:
Revenue and expenses
These are the core components of Accounting’s income statement. Revenue is the income generated by selling goods and services, while expenses are the costs incurred to generate that revenue. The difference between revenue and expenses determines the net income or net loss.
If revenue surpasses expenses, the result is a positive net income—a profit. This is the ideal scenario where a business is making money. But if expenses outweigh revenue, it leads to a negative net income—a loss.
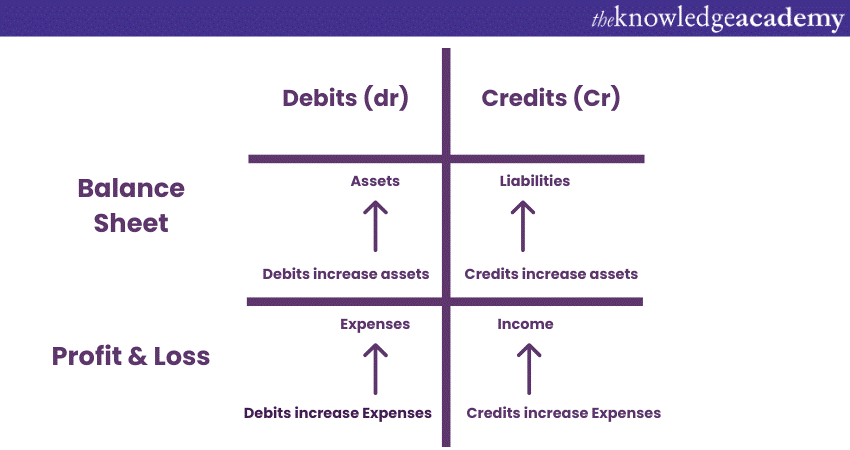
Double-entry bookkeeping
This foundational concept forms the basis of Accounting. Each financial transaction has a dual effect on the financial statements, with at least two accounts being impacted—one account is debited, and another is credited. This ensures that the Accounting equation (assets = liabilities + equity) remains in balance.
This concept works like a safety net that prevents financial errors from slipping through the cracks. With every financial transaction, there are at least two entries: a debit and a credit. Debits and credits are the balancing forces in Accounting, maintaining equilibrium in the financial world. When you spend money (debit), it needs to come from somewhere (credit). Therefore, Double-Entry Accounting ensures the financial equation remains balanced and accurate.
Register to our Book Keeping Training and master bookkeeping essential skills!
Financial statements
Financial statements in Accounting clearly show the company's financial health, performance, and overall well-being. These statements are a collection of essential documents that summarise the financial activities and position of a business within a specific period. They act as a guide that helps business owners, investors, and stakeholders in navigating the often-intricate landscape of finance.
Assets, liabilities, and equity
These are the fundamental components of an Accounting balance sheet. Assets represent what an organisation owns, liabilities represent what it owes, and equity represents the residual interest of the owners. The balance between these components is crucial for financial stability.
Types of Accounting
There are different Types of Accounting used by various organizations and stakeholders. These types offer distinct perspectives, shedding light on specific financial aspects and aiding decision-makers in navigating the complex world of numbers. Mentioned below are some of the most important types of Accounting:
Financial Accounting
This branch of Accounting primarily caters to external stakeholders. Financial statements are made up of the following components:
a) Income statements
b) Balance sheets
c) Cash flow statements
These statements provide an overview of a company's financial performance and position. Investors use financial statements to evaluate the profitability and solvency of a business before investing.
Managerial Accounting
Also known as Cost Accounting, Activity-Based Costing focuses on providing internal stakeholders, like managers and executives, with valuable financial insights. Managerial Accountants analyze costs, budgets, and performance metrics to aid in decision-making. For instance, managers may use cost reports and Activity-Based Costing methods to determine the profitability of different product lines, helping them allocate resources more effectively.

Tax Accounting
Tax Accounting is centred around ensuring compliance with tax laws and regulations. Tax Accountants calculate taxes owed, prepare tax returns, and advise on tax strategies to minimise tax liability while remaining within legal bounds. Businesses rely on tax accountants to navigate the complex tax landscape and avoid penalties.
Auditing
Auditing involves the independent examination of an entity's financial records and statements to verify their accuracy and adherence to Accounting standards. External Auditors provide an unbiased assessment of financial reports, enhancing their credibility and reassuring stakeholders. Therefore, Auditing is crucial for maintaining transparency and building trust.
Conclusion
Accounting is the language of business that allows them to communicate their financial activities and performance to various stakeholders. Its significance lies in its ability to provide transparency, accountability, and informed decision-making. In this context, understanding Bookkeeping vs Accounting is crucial, as both play distinct yet complementary roles in managing finances. We hope that this blog has helped you understand What is Accounting and its most important types and concepts.
Want to empower your financial expertise? Register for our comprehensive Accounting and Finance Training!
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Accounting Course
Accounting Course
Fri 11th Apr 2025
Fri 13th Jun 2025
Fri 8th Aug 2025
Fri 26th Sep 2025
Fri 21st Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


