We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +08000201623 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

In today’s digital age, the Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) is crucial for organisations to standardise their service selection, planning, delivery, maintenance, and the entire IT lifecycle. Despite its importance, many organisations do not know What is ITIL.
ITIL is the cornerstone for many organisations, regardless of their size or scale. In the current era, the thought of operating a business without IT services is inconceivable. Hence, it is vital for newcomers to the IT industry to understand this indispensable framework. Peruse this blog to learn more about "What is ITIL" and its critical role in ensuring the delivery of robust services.
Table of Contents
1) What is ITIL?
2) History of ITIL
3) ITIL vs ITSM: Key Differences Explained
4) What are the Guiding Principles of ITIL?
5) What is the ITIL Framework?
6) ITIL V3 to V4: What’s New in Certifications?
7) Benefits of ITIL
8) Drawbacks of ITIL
9) How can you put ITIL Into Practice?
10) How to Avoid Common ITIL Adoption Mistakes?
11) Conclusion
What is ITIL?
ITIL, or the Information Technology Infrastructure Library, is an all-encompassing framework that aids organisations in effectively managing their IT services. It delineates a structured approach to IT Service Management, with guidelines, best practices, and processes that ensure IT services harmonise with the business’s objectives and requirements. Originating in the United Kingdom, ITIL was initially implemented by the British government to bring uniformity to IT practices. Over time, ITIL has garnered global recognition and is widely adopted.
The core objective of ITIL is to synchronise IT services with business necessities. It supports organisations in providing value to their clientele by offering direction on designing, transitioning, operating, and enhancing IT services.
History of ITIL
The ITIL has evolved significantly since its inception in the 1980s. Each version of ITIL has built upon its predecessor, introducing new concepts and practices to improve IT Service Management. Let's explore each in detail:
ITIL V1: The Origin
ITIL Version 1 was created in the 1980s by the UK government. It provided the first set of guidelines for managing IT services. These guidelines helped organisations improve their IT service quality. ITIL V1 focused on standardising IT practices across different industries. This version laid the foundation for future improvements in IT Service Management.
ITIL V2: The First Major Evolution
ITIL Version 2 was introduced in the year 2000. It built upon the original guidelines and added new processes for better IT management. This version was more user-friendly and practical for businesses. ITIL V2 became very popular and widely adopted. It helped organisations streamline their IT services and improve efficiency.
ITIL V3: Introducing the IT Service Lifecycle
ITIL Version 3 was released in 2007. This version introduced the concept of the IT Service Lifecycle. It covered the entire lifecycle of IT services, from planning to retirement. ITIL V3 aimed to align IT services more closely with business needs. It helped organisations manage their IT services in a more holistic and integrated way.
ITIL 4: Embracing the Service Value System
ITIL 4 was launched in 2019. This version introduced the Service Value System, which is a more flexible approach to IT Service Management. It focuses on delivering value to customers and adapting to changing business environments. ITIL 4 incorporates modern practices like Agile and DevOps. It helps organisations stay relevant and effective in the digital age.
ITIL vs ITSM: Key Differences Explained
ITIL and ITSM are terms often used in the world of IT, but they mean different things.
Understanding ITIL vs ITSM is crucial for IT professionals.
a) Paradigm vs Framework: ITSM is the overarching paradigm or philosophy that focuses on managing IT services to meet business needs. ITIL is a specific framework within that paradigm, offering a set of best practices and processes for implementing ITSM effectively.
b) Scope: ITSM can be implemented using various frameworks (ITIL, COBIT, ISO/IEC 20000, etc.), but ITIL is one of the most widely adopted frameworks for ITSM.
What are the Guiding Principles of ITIL?
The seven guiding principles of ITIL are designed to help organisations adopt and adapt ITIL practices. These principles are:
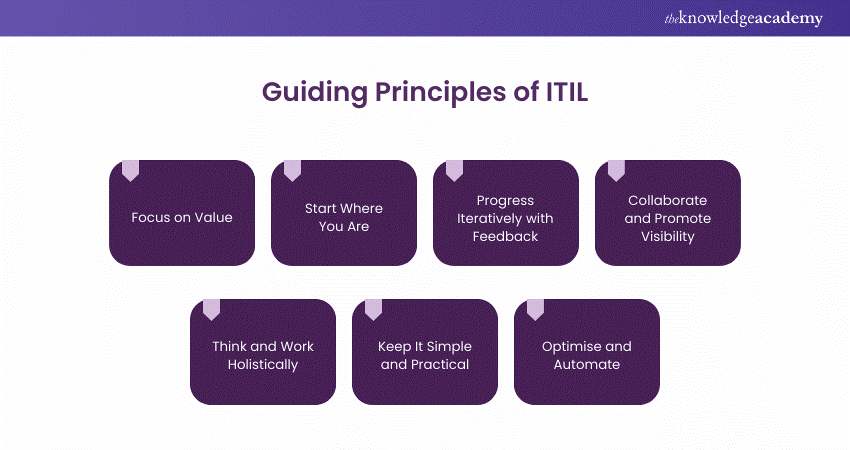
a) Focus on Value: Always keep the customer’s perspective in mind and ensure that everything you do adds value for them.
b) Start Where You Are: Assess your current situation and use existing resources and capabilities before creating something new.
c) Progress Iteratively with Feedback: Take small steps and build on feedback to continually improve and avoid overwhelming changes.
d) Collaborate and Promote Visibility: Work together across teams and make sure everyone understands the processes and goals.
e) Think and Work Holistically: Consider the entire organisation and how different parts work together rather than focusing on individual components.
f) Keep It Simple and Practical: Avoid complexity and unnecessary work. Focus on what is essential and what will deliver value.
g) Optimise and Automate: Streamline processes to make them as efficient as possible, and use automation to reduce manual work and increase consistency.
What is the ITIL Framework?
The ITIL Framework is divided into key stages that guide the lifecycle of IT services. Each stage has specific goals and activities to ensure services are effective and aligned with business objectives.
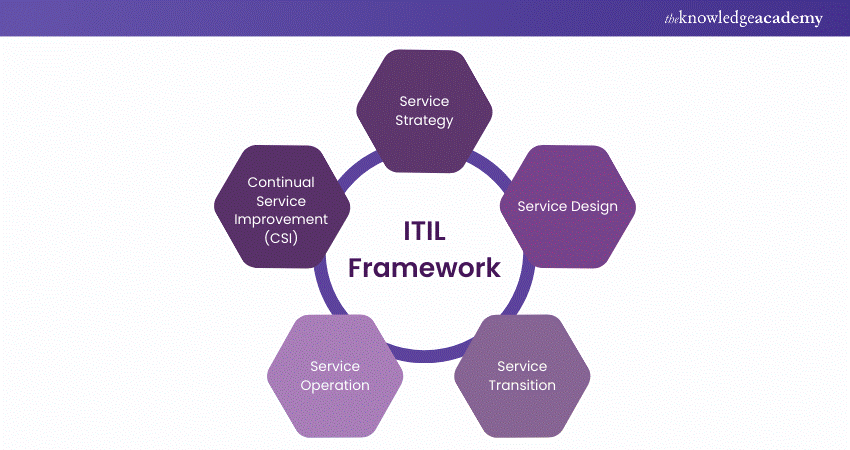
a) Service Strategy: This is the first stage where the overall vision and goals for IT services are set, aligning with the organisation’s strategic objectives. It involves understanding market needs, spotting growth opportunities, and creating a clear plan for service implementation.
b) Service Design: Building on the service strategy, this stage focuses on creating actual IT services. It includes designing the processes, policies, and procedures that will ensure services are reliable, scalable, and efficient.
c) Service Transition: This stage acts as a bridge between design and operation. Here, the designed services are moved into the live environment. This involves thorough testing, training, and documentation to ensure a smooth transition.
d) Service Operation: This is where services are delivered to customers. It involves managing incidents, problems, changes, and service requests, while ensuring services are available, perform well, and are secure.
e) Continual Service Improvement (CSI): This stage is about ongoing improvement. It involves measuring service performance, finding areas for enhancement, and making changes to improve service quality, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
Learn best practices for creating IT service with our ITIL® 4 Specialist: Create Deliver and Support Certification – Join today!
ITIL V3 to V4: What’s New in Certifications?
The transition from ITIL V3 to V4 brings significant updates to the certification process. Here are the changes:
a) New Specialist Modules: ITIL V4 now includes two optional extension modules: ITIL 4 Specialist: Sustainability in Digital and IT and ITIL 4 Specialist: Acquiring and Managing Cloud Services.
b) Modernised Practices: ITIL V4 updates the certification process to include the latest best practices and technologies. This ensures that IT professionals stay current with industry standards.
c) Holistic Approach: The new certifications focus on a comprehensive view of IT Service Management. This helps professionals understand the entire lifecycle of IT services.
d) Integration with Modern Methodologies: ITIL V4 incorporates elements of Agile, DevOps, and other contemporary practices. This integration helps streamline processes and improve efficiency.
e) Business Alignment: The changes ensure that IT services are better aligned with current business needs and objectives. This alignment helps organisations achieve their goals more effectively.
Benefits of ITIL
There are several benefits of ITIL. Let’s discuss these benefits:
Providing Better Services
ITIL helps businesses deliver higher-quality IT services. It sets clear guidelines for managing IT processes, ensuring consistency and reliability. By following ITIL practices, companies can meet customer needs more effectively. This leads to increased customer satisfaction.
Delivering Superior Support
ITIL improves how IT support teams handle issues and requests. It provides an approach for managing incidents and problems. This helps resolve issues quickly and reduce downtime. As a result, users experience better and more efficient support.
Enabling Business Change
ITIL helps organisations adapt to change more smoothly. It offers frameworks for managing and implementing new IT services or updates. This ensures changes are well-planned and executed with minimal disruption. Ultimately, it supports business growth and innovation by making transitions easier.
Drawbacks of ITIL
The following are some drawbacks of implementing ITIL:
1) ITIL's comprehensive nature can lead to complexity in implementation, particularly for smaller organisations
2) The structure of ITIL may limit adaptability and hinder organisational agility
3) ITIL adoption requires significant resources when it comes to training, documentation, and tools
4) Emerging technologies are not extensively covered in ITIL, potentially leaving organisations unprepared.
5) Updates to ITIL can be slow, causing it to fall behind current IT industry trends.
6) ITIL's focus on processes might overshadow essential cultural and organisational aspects.
7) Excessive documentation encouraged by ITIL can result in bureaucratic inefficiencies.
8) Customising ITIL processes for an organisation's needs might prove to be challenging to achieve.
9) Resistance to the cultural shift required by ITIL can hinder successful implementation.
10) Critics often argue that ITIL's origins in IT operations might not sufficiently address broader strategic IT alignment.
Understanding the ITIL Advantages and Disadvantages is crucial for organisations considering its implementation.
How can you put ITIL Into Practice?
ITIL can be tricky to understand and even harder to put into practice. However, there are some best practices to make adoption easier, including the following:
a) Understand the Purpose: Start by clearly understanding why you want to adopt ITIL. Business leaders should have strong reasons for this decision and know how ITIL will benefit their organisation.
b) Gain Expertise: Implementing ITIL requires specialised knowledge. It’s not something you can just pick up from a manual. Ensure you have people with ITIL Certification and proven expertise to lead the initiative. This might mean providing training or hiring new staff.
c) Start Small: Begin with one or a few ITIL practices as a trial project. Document the current process and its pros and cons. After implementing ITIL, reassess the process to see how it has improved business performance. If successful, gradually roll out more practices.
d) Focus on Results: ITIL is a means to an end, not the end itself. Determine what you want to achieve with ITIL, such as better customer satisfaction or lower service costs. Measure these outcomes using clear metrics to ensure you’re meeting your goals.
Need to pass your ITIL® 4 Foundation Exam Resit? Schedule now to boost your IT career! Register today!
How to Avoid Common ITIL Adoption Mistakes?
Adopting ITIL can be challenging, and many organisations make mistakes along the way. Here are some tips to help you guide the adoption process smoothly.

a) Avoid Taking ITIL too Strictly: ITIL provides guidelines, not strict rules. Be flexible in how you apply its practices to fit your organisation’s needs. Overly rigid adherence can hinder effectiveness and adaptability.
b) Tailor Your Implementation: Adapt ITIL practices to match your organisation’s size and requirements. Don’t force a large-scale implementation if it’s not necessary. Focus on what will work best for your specific situation.
c) Embrace Continual Improvement: Always be open to refining and enhancing your ITIL practices. Continual improvement helps address issues and adapt to changes. Regularly evaluate and update your processes for better results.
d) Choose the Right Tools: Select tools and software that align with your ITIL practices and organisational needs. Using the correct tools can significantly enhance efficiency and effectiveness. Avoid choosing tools just because they are popular; they should fit your specific requirements.
e) Identify and Manage Risks: Recognise potential risks in your ITIL implementation and address them proactively. Effective risk management helps prevent problems and ensures a smoother adoption process. Regularly review and adjust your risk management strategies as needed.
Learn best practices in IT Service Management with our ITIL® 4 Foundation Certification – Join today!
Conclusion
Understanding and implementing ITIL effectively can greatly enhance your IT Service Management. By following best practices, you can ensure a smoother adoption process and achieve better results. Additionally, knowing "What is ITIL" and how it can be applied will guide you in optimising your IT services. Embrace these strategies to make the most of ITIL and support your organisation's success.
Master asset management for cost-efficiency with our ITIL® 4 Specialist: IT Asset Management Training – Join today!
Frequently Asked Questions

ITIL provides a structured framework which helps in ensuring compliance with industry standards and regulations. It also helps organisations to establish a consistent process, maintain records, and document all procedures which adhere to legal requirements and industry-specific guidelines.

Here are some job roles which specifically require ITIL expertise:
a) Help Desk Analyst
b) Network Specialist
c) Network Analyst
d) Network Administrator
e) IT Analyst
f) Service Delivery Manager
g) Network Manager
h) IT Manager
i) IT Project Manager
j) Senior Project Manager

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bound.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy offers various ITIL® Certification, including ITIL 4 Foundation Certification Course, ITIL 4 Specialist: Create Deliver and Support Certification , and ITIL® 4 Specialist: IT Asset Management Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into ITIL 4 Guiding Principles.
Our IT Service Management Blogs covers a range of topics related to ITIL 4, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your IT Service Management skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming IT Service Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 ITIL® 4 Foundation Certification Course
ITIL® 4 Foundation Certification Course
Thu 1st Jan 1970







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


