We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Imagine a retail company relying on customer data to tailor its marketing strategies, only to find that half of its data is inaccurate. How can they make informed decisions? This is where Veracity in Big Data becomes crucial. Have you ever wondered how much of your data is truly reliable?
Moreover, Statista states the value of the global Big Data Analytics market is forecasted to increase to £79.45 billion by 2027. Given this circumstance, this blog delves into the importance of Veracity in Big Data, exploring how it impacts decision-making, operational efficiency, and overall business success. Let’s dive in!
Table of Contents
1) What is Veracity in Big Data?
2) What are the Sources of Data Veracity?
3) Importance of Veracity in Big Data
4) What are Some use Cases for Data Veracity?
5) Conclusion
What is Veracity in Big Data?
Veracity in Big Data refers to the trustworthiness and accuracy of the data. It is one of the critical dimensions that determine the quality and reliability of data used for analysis and decision-making. Here’s a closer look at related concepts:
1) Validity
Validity ensures that the data accurately represents the real-world scenarios it is intended to model. It involves verifying that the data is correct, consistent, and useful for its intended purpose. High validity means the data is relevant and reliable, which is essential for making sound business decisions.
2) Volatility
Volatility refers to the rate at which data changes over time. In the context of Big Data, it is crucial to manage and analyse data that is constantly evolving. Understanding data volatility helps organisations to update their strategies and operations in real-time, ensuring they remain responsive to market dynamics and other external factors.
3) Volume
Volume pertains to the sheer amount of data generated and collected. In the era of Big Data, organisations deal with vast quantities of information from various sources. Managing this volume effectively requires robust storage solutions and efficient processing capabilities to extract meaningful insights without compromising Data Veracity.
What are the sources of Data Veracity?
Identifying the sources of Data Veracity is essential for implementing effective strategies to ensure the reliability and accuracy of the information being processed. Here are the key sources contributing to Data Veracity challenges:
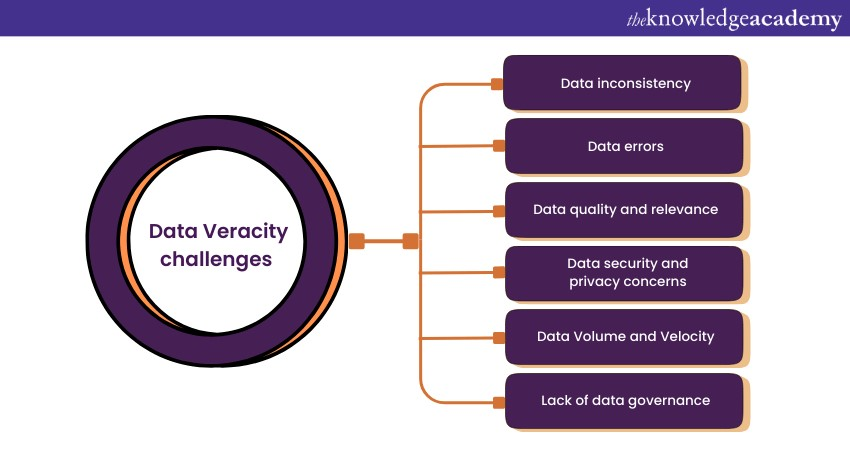
a) Data Inconsistency:
1) Diverse Data Origins: Big Data often integrates information from heterogeneous sources. Inconsistencies in data formats, units, and structures across these sources can lead to inaccuracies.
2) Data Integration Issues: Merging data from different platforms and databases can result in inconsistencies, making it challenging to establish a uniform dataset.
b) Data Errors:
1) Human Errors: Mistakes made while entering data entry, processing, or interpretation can introduce errors. These errors might be typographical, computational, or contextual.
2) Sensor Errors: In fields like the Internet of Things (IoT), sensor inaccuracies can lead to noise in data, affecting the overall reliability.
3) Missing Data: Incomplete datasets can misrepresent trends and patterns, impacting the accuracy of analytical models.
c) Data Quality and Relevance:
1) Outdated Information: Data might become obsolete over time, especially in fast-changing environments. Using outdated data can lead to misguided conclusions.
2) Lack of Context: Data might need more contextual information, making it easier to interpret. Understanding the context is crucial for accurate analysis.
d) Data security and Privacy Concerns:
1) Data Tampering: Malicious intent can lead to data tampering, altering the values to misguide analyses and decision-making processes.
2) Privacy Regulations: Anonymising data to comply with privacy regulations can sometimes strip away crucial information, affecting the analysis's accuracy.
e) Data Volume and Velocity:
1) Overwhelming Volume of Data: The sheer volume of Big Data can overwhelm traditional processing systems, leading to errors or incomplete analyses.
2) Velocity Challenges: High-speed data streams can result in processing delays, which might cause discrepancies in time-sensitive analyses.
f) Lack of Data Governance:
1) Absence of Standards: With proper data governance policies and standards, there can be consistency in data definitions, leading to clarity and accuracy.
2) Data Ownership Issues: Ambiguity about data ownership and stewardship can impact the overall quality and reliability of the data.
Elevate your expertise with our hands-on Big Data Architecture Training – join us now!
Importance of Veracity in Big Data
In the context of Big Data, the significance of Veracity becomes even more critical due to the vast and diverse nature of the datasets involved. Here's why ensuring Veracity in Big Data is essential:
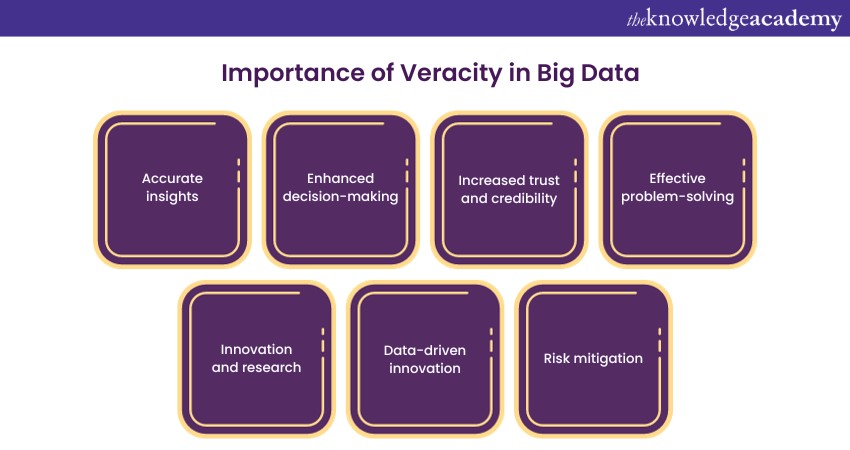
1) Accurate Insights: Accurate data leads to precise insights. Only accurate and reliable data can skew analytical results, leading to misguided conclusions and faulty business strategies. Veracity ensures that the insights derived from Big Data analyses are reliable and reflective of the actual scenarios.
2) Enhanced Decision-making: Reliable data is the source of informed selection-making. Whether it's predicting marketplace developments, understanding customer behaviour, or optimising operations, decision-makers depend on sincere data to make strategic decisions. Veracity guarantees that these decisions are based totally on a major foundation, leading to better outcomes.
3) Increased Trust and Credibility: Businesses regularly share facts-derived insights with stakeholders, investors, and clients. Trust in these insights is paramount. Veracious information builds consider among stakeholders, improving the credibility of the agency. It ensures that the records offered isn't always best convincing however also correct, fostering confidence inside the agency's talents.
4) Effective Problem-solving: Big Data Analytics is instrumental in figuring out and fixing complex business problems. However, misguided information can result in misdiagnosis of troubles. These information make certain that the root reasons of troubles are effectively recognised, leading to sensible solutions and procedure upgrades.
5) Customer Experience: In industries like e-commerce and social media, know-how customer behaviour is critical. Accurate data approximately client choices, purchasing styles, and remarks is important for personalised advertising and improving consumer experience. Veracity in customer records guarantees that businesses can tailor their offerings to satisfy client expectations as it should be.
6) Compliance and Legal Considerations: Many industries, such as healthcare and finance, are bound to use strict rules concerning data accuracy and privacy. Ensuring Veracity isn't just exact practice, however also a legal requirement. Non-compliance can purpose intense consequences and reputational harm.
7) Innovation and Research: Researchers rely on accurate data to draw meaningful conclusions and increase new technologies. Inaccurate records can misguide research efforts, leading to wasted assets and misleading findings.
8) Data-driven Innovation: Veracity facilitates innovative solutions by providing a solid foundation for experimentation. Researchers and innovators rely on accurate data to explore new ideas, test hypotheses, and develop groundbreaking technologies.
9) Predictive Analytics: Reliable ancient data is used to expect future traits and behaviours. Inaccurate information can result in improper predictions, impacting corporations' capacity to anticipate marketplace modifications and customer choices.
10) Risk Mitigation: In sectors like finance, accurate Data Analysis is vital for risk evaluation. Veracious facts helps in figuring out potential risks, allowing companies to enforce proactive strategies for risk mitigation and compliance with regulatory necessities.Reliable data is the foundation of informed decision-making. Whether it's predicting market trends, understanding customer behaviour, or optimising operations, decision-makers rely on trustworthy data to make strategic choices. Veracity ensures that these decisions are based on a solid foundation, leading to better outcomes.
11) Brand Reputation: Veracity ensures that the data shared with the public and media is accurate. A piece of inaccurate information can tarnish a company's reputation. Reliable data builds brand credibility and trust, enhancing the organisation's image in the eyes of the public and potential investors.
12) Resource Optimisation: Veracious data leads to better resource allocation. Whether it's optimising supply chains, managing inventory, or planning workforce distribution, accurate data insights enable organisations to optimise their resources efficiently, minimising waste and maximising productivity.
13) Customer Trust: In the age of information, customers are discerning about the businesses they engage with. Veracious data ensures that customer information is handled accurately and responsibly. This builds trust, fostering long-term relationships and customer loyalty.
14) Fraud Detection: For industries like banking and online transactions, Veracity is vital for fraud detection algorithms. Accurate data patterns helps identify anomalies and potentially fraudulent activities, protecting businesses and customers from financial losses.
15) Performance Evaluation: Veracity in performance data is necessary for assessing the effectiveness of marketing campaigns, product launches, and other business initiatives. Reliable performance metrics provide actionable insights for future strategies, improving overall business performance.
16) Cross-departmental Collaboration: Veracious data acts as a common language across departments within an organisation. Accurate data ensures that marketing, sales, finance, and other departments are working with the same trustworthy information, promoting collaboration and unified decision-making.
17) Ethical considerations: Ensuring Veracity is also an ethical responsibility. Responsible data management, which includes maintaining its accuracy and integrity, demonstrates an organisation's commitment to ethical practices, contributing to a positive societal impact.
18) Regulatory Compliance: Many industries, including healthcare and finance, are bound by strict regulatory frameworks. Veracious data is crucial for compliance. Accurate Data Management ensures that organisations adhere to legal requirements, avoiding legal repercussions and financial penalties.
19) Disaster Preparedness and Recovery: Accurate data is essential for disaster preparedness and recovery planning. In emergencies, organisations rely on data to make critical decisions. Veracious data ensures that emergency response strategies are based on reliable information, leading to effective disaster management and faster recovery processes.
20) Social Impact and Public Policy: Veracity in Data plays a vital role in shaping public policies and social initiatives. Governments and non-profit organisations rely on accurate data for demographics, economic indicators, and public health statistics. Reliable data is crucial for making informed policy decisions, leading to effective social programs and initiatives that benefit communities and societies at large.
Take your data skills to the next level with our comprehensive Advanced Data Analytics Course.
What are Some use Cases for Data Veracity?
Data Veracity is not just a theoretical concept; it has tangible implications across various industries. Here are several use cases that highlight the practical applications of ensuring Data Veracity:
1) Healthcare and Patient Records: In the healthcare sector, accurate and reliable patient data is critical. Ensuring Veracity in Electronic Health Records (EHRs) is essential for diagnosis, treatment, and patient safety. Veracious data ensures that healthcare providers have access to precise medical histories, medication records, and allergy information. Therefore, it enables them to make informed decisions about patient care.
2) Financial Fraud Detection: Veracity is crucial in the finance industry, especially in detecting fraudulent activities. By analysing transaction data with high Veracity, financial institutions can identify patterns associated with fraud, ensuring the security of customer accounts and transactions. Accurate data helps in distinguishing legitimate transactions from suspicious ones, enabling timely fraud prevention measures.
3) Supply Chain Optimisation: Veracity in supply chain data ensures the efficient movement of goods and minimises disruptions. Accurate data about inventory levels, demand patterns, and supplier performance allows businesses to optimise their supply chains. By relying on trustworthy data, companies can reduce excess inventory, minimise stockouts, and enhance overall supply chain efficiency.
4) Smart Energy Management: Utility companies analyse data from various sources to optimise energy distribution and consumption. Accurate data helps in predicting energy demand, identifying inefficiencies, and integrating renewable energy sources effectively. By ensuring Data Veracity, energy providers can reduce wastage, lower costs, and promote sustainable energy practices.
5) Disaster Response and Management: Accurate information about affected areas, population density, and infrastructure vulnerabilities helps emergency responders plan their actions effectively. Reliable data aids in resource allocation, evacuation planning, and humanitarian aid distribution, ultimately saving lives and mitigating damages.
6) Personalised Marketing: Accurate customer data, including preferences, purchase history, and browsing behaviour, enables businesses to create targeted marketing campaigns. By ensuring Data Veracity, companies can enhance customer engagement, increase conversion rates, and build long-term customer relationships.
Join our Big Data Analysis Course and develop the abilities to analyse and interpret complex data!
Conclusion
Understanding Veracity in Big Data is essential for leveraging accurate and reliable data to drive informed decisions. By prioritising Data Veracity, organisations can enhance their analytical capabilities, reduce risks, and improve overall efficiency. Implementing robust data validation ensures that your data remains a valuable asset.
Enhance your knowledge on techniques and drive innovation in your career with our Data Science Analytics Training now!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 5 V's of Big Data Veracity?

The 5 V's of Big Data include Volume (scale of data), Velocity (speed of data processing), Variety (types of data), Veracity (accuracy and trustworthiness), and Value (benefits derived from data).
What are the 5 P's of Big Data?

The 5 P's of Big Data refer to Purpose, Protection, Performance, Privacy, and Provenance, focusing on responsible Data Management and utilisation.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Big Data and Analytics Trainings, including the Data Science Analytics Course, Big Data Analysis Course, and Big Data Architecture Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Couchbase vs Cassandra.
Our Data, Analytics & AI Blogs cover a range of topics related to Big Data, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Data Analytics and Artificial Intelligence (AI) skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Data, Analytics & AI Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Hadoop Big Data Certification
Hadoop Big Data Certification
Thu 20th Mar 2025
Thu 22nd May 2025
Thu 17th Jul 2025
Thu 18th Sep 2025
Thu 20th Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


