We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 800600725 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Information Security Professionals often find themselves navigating through a myriad of certifications to enhance their skills and career prospects. Two such notable certifications are Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) and Certified Incident Response and Security Consultant (CRISC).
While both certifications focus on different aspects of information security, it's crucial to understand their nuances to make an informed decision about which one aligns better with your career goals. In this blog, we will undertake a comprehensive comparison of CISM and CRISC, delving into their differences, domains, benefits, and potential career paths.
Table of Contents
1) What is CISM?
2) What is CRISC?
3) Comparison between CISM and CRISC
a) Focus and expertise
b) Domains
c) Eligibility and prerequisites
d) Career trajectories
e) Exam format and preparation
f) Skill emphasis
4) CISM career paths
5) CRISC career paths
6) Conclusion
What is CISM?
CISM is a globally recognised certification offered by ISACA (Information Systems Audit and Control Association) that targets professionals aspiring to manage, design, and assess an enterprise's information security program. It emphasises a holistic approach to information security management and is ideal for individuals who want to develop skills in governance, Risk Management, and compliance (GRC) aspects of security.
What is CRISC?
CRISC, on the other hand, is a certification that concentrates on incident response and Security Consulting. Offered by renowned Cybersecurity training organisations, CRISC equips professionals with the skills required to effectively respond to and manage Cybersecurity incidents. It is designed for those who are interested in handling real-time security incidents, conducting investigations, and providing security consultancy services.
Comparison Between CISM and CRISC
While both Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) and Certified Incident Response and Security Consultant (CRISC) certifications are highly respected in the field of information security, they exhibit significant differences in terms of their focus, domains, prerequisites, benefits, and career trajectories. Understanding these distinctions can greatly aid professionals in choosing the certification that aligns best with their career aspirations. Here, we delve into the key differences between CISM and CRISC.

1) Focus and Expertise
CISM: CISM places a strong emphasis on information security governance, Risk Management, and compliance. It equips professionals with the skills needed to manage and lead information security programs effectively. The certification is tailored for individuals who aspire to take on managerial roles, overseeing security strategies, policies, and processes within an organisation.
CRISC: In contrast, CRISC is centred around incident response, digital forensics, and security consultancy. It trains professionals to handle Cybersecurity incidents, conduct investigations, and provide strategic security advice. CRISC is ideal for those who thrive in fast-paced environments, tackling real-time security challenges and mitigating risks.
2) Domains
CISM: CISM covers domains such as Information Security Governance, Information Risk Management, Information Security Program Development and Management, and Information Security Incident Management. These domains encompass a broader spectrum of governance, control frameworks, and Risk Assessment Methodologies.
CRISC: The domains of CRISC include Incident Response and Recovery, Digital Forensics and Investigations, Security Consultancy and Advisory, and Cyber Threat Intelligence. These domains revolve around practical incident handling, forensic analysis, and providing strategic security guidance, highlighting the worth of CRISC in addressing these critical areas.
3) Eligibility and Prerequisites
CISM: Candidates seeking the CISM certification typically require five years of work experience in information security management, with three years of experience in at least three CISM domains. Alternatively, candidates with specific security-related qualifications can also fulfil some of these requirements.
CRISC: The prerequisites for CRISC vary among training providers. While prior Cybersecurity knowledge is beneficial, some training programs may not mandate extensive work experience, making it relatively more accessible for professionals starting their Cybersecurity journey.
4) Career Trajectories
CISM: Holding a CISM Certification can lead to roles such as Information Security Manager, Compliance Officer, IT Auditor, or Risk Manager. Professionals with CISM are well-suited to oversee security programs, ensure compliance with regulations, and manage risks effectively.
CRISC: Graduates of CRISC often find themselves in roles like Incident Responder, Security Consultant, Digital Forensics Analyst, or Cybersecurity Investigator. They are equipped to handle security incidents, analyse breaches, and provide strategic security advice to organisations.
5) Exam Format and Preparation
CISM: The CISM exam typically consists of multiple-choice questions that assess a candidate's understanding of security concepts, governance frameworks, and risk management practices.
CRISC: CRISC exams usually incorporate scenario-based questions and practical challenges that test a candidate's ability to respond to incidents, conduct investigations, and provide security recommendations.
6) Skill Emphasis
CISM: This certification hones skills related to strategic planning, risk assessment, and regulatory compliance. It develops a comprehensive understanding of security frameworks and their application in business contexts.
CRISC: CRISC focuses on hands-on skills such as incident response strategies, digital forensics techniques, and the ability to assess an organisation's security posture.
Secure your future with CRISC-certified risk management skills- sign up for our Certified In Risk And Information Systems Control (CRISC) Course today!
CISM Career Paths
Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) and Certified Incident Response and Security Consultant (CRISC) certifications offer unique avenues for career growth, allowing individuals to excel in different niches within the Cybersecurity landscape. Let's explore the potential career paths that each certification can unlock.
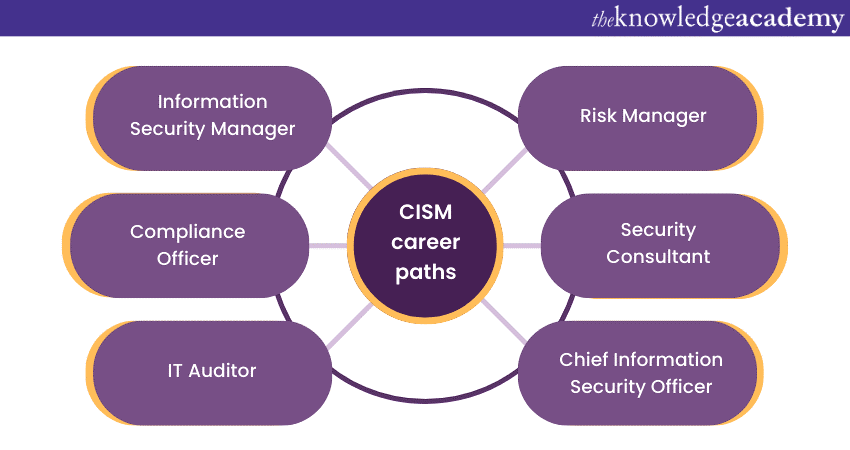
1) Information Security Manager: As the name suggests, CISM equips professionals with the skills needed to manage information security programs. In this role, you'll oversee the design, implementation, and maintenance of security measures across an organisation, ensuring that policies and procedures align with business goals.
2) Compliance Officer: Many industries are subject to regulations and standards. CISM-certified individuals are well-suited to becoming compliance officers, ensuring that their organisations adhere to industry-specific security standards and regulations.
3) IT Auditor: CISM's focus on governance and risk management makes it an excellent fit for IT Auditing Roles. IT auditors assess an organisation's IT systems, processes, and controls to identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance.
4) Risk Manager: Managing risks is a critical aspect of information security. CISM equips professionals with risk assessment skills that are vital for roles such as risk manager. You'll be responsible for identifying, evaluating, and mitigating security risks.
5) Security Consultant: CISM-certified professionals can transition into security consultancy roles. Here, you'll advise clients on security best practices, assess their security postures, and recommend improvements to enhance their overall security strategies.
6) Chief Information Security Officer (CISO): With experience and additional qualifications, CISM holders can aspire to become CISOs. In this executive role, you'll lead an organisation's entire security strategy, overseeing teams' budgets and ensuring the protection of sensitive information.
Interested in a career in information security? Download the CISM Career Path guide now and discover how to navigate the steps toward becoming a certified security expert.
CRISC career paths
Certified Incident Response and Security Consultant (CRISC) certifications offer exciting career growth, guiding individuals along their CRISC Career Path to excel in different niches within the Cybersecurity ecosystem.

1) Incident Responder: CRISC is tailor-made for incident response roles. As an incident responder, you'll be at the forefront of dealing with security incidents, investigating breaches, and orchestrating response plans to mitigate damage.
2) Digital Forensics Analyst: CRISC equips individuals with skills in digital forensics. This role involves collecting, analysing, and preserving digital evidence to support investigations and legal proceedings.
3) Cybersecurity Investigator: Similar to digital forensics, Cybersecurity investigators focus on uncovering the origins and motives behind cyberattacks. This role requires a deep understanding of attack methods and patterns.
4) Security Consultant: CRISC-certified professionals can specialise in security consultancy. Your expertise in incident response and digital forensics will enable you to guide organisations in enhancing their security posture and responding effectively to threats.
5) Threat Intelligence Analyst: Cyber threat intelligence involves monitoring and analysing the cyber threat landscape to predict and prevent potential attacks. CRISC skills can be invaluable in understanding and interpreting threat data.
6) Security trainer or Educator: With experience, CRISC-certified individuals can contribute to the field by training and educating aspiring Cybersecurity professionals sharing their practical insights and skills.
Secure critical assets through our Chief Information Security Officer Training- sign up today!
Conclusion
We hope you understand the CISM vs CRISC comparison. CISM and CRISC offer unique perspectives and expertise, catering to different niches within the industry. Hence, before deciding, assess your professional goals carefully, your current skill set, and the role you see for yourself in Cybersecurity. Regardless of your path, continuous learning and dedication will be your allies in achieving success in the dynamic system of Information Security.
Become proficient in Security Architecture with our ISSAP Training- register now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Who Should Consider Obtaining the CISM or CRISC Certification?

Professionals in Risk Management, IT security, and governance-related fields should consider CISM or CRISC certification. Moreover, CISM is ideal for aspiring Information Security Managers who are looking to take up leadership roles.
How Much Does It Cost to Renew the CISM or CRISC Certification?

Renewing CISM or CRISC costs approximately £33.75/year for ISACA (Information Systems Audit and Control Association) members and £63.75/year for non-ISACA members. Additional certifications costs include £18.75/year for members and £37.50/year for non- ISACA members.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various CISM Training, including CISM Certified Information Security Manager. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into 25+ Chief Information Security Officer Interview Questions & Answers.
Our IT Security & Data Protection Blogs cover a range of topics related to Cybersecurity and data protection, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your IT security skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 CISM Certified Information Security Manager
CISM Certified Information Security Manager
Sat 3rd May 2025, Sun 4th May 2025
Tue 6th May 2025
Mon 2nd Jun 2025
Sat 7th Jun 2025, Sun 8th Jun 2025
Sat 5th Jul 2025, Sun 6th Jul 2025
Mon 7th Jul 2025
Sat 2nd Aug 2025, Sun 3rd Aug 2025
Mon 4th Aug 2025
Mon 1st Sep 2025
Sat 6th Sep 2025, Sun 7th Sep 2025
Sat 4th Oct 2025, Sun 5th Oct 2025
Mon 6th Oct 2025
Mon 3rd Nov 2025
Sat 8th Nov 2025, Sun 9th Nov 2025
Mon 1st Dec 2025
Sat 6th Dec 2025, Sun 7th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


