We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 800600725 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
It's crucial to have a roadmap in the world of Business Analysis. That's where BABOK comes in. But What is BABOK, you ask? We'll answer that question not just once but twice in this blog. BABOK, or the Business Analysis Body of Knowledge, is a valuable guide for Business Analysts.
In simple terms, it's like a guide of knowledge and techniques, helping professionals in the field do their jobs better. Through this blog, explore What is BABOK, the Business Analysis Body of Knowledge, and gain a comprehensive overview of its significance in the field of Business Analysis.
Table of contents
1) Understanding BABOK
2) Key components of BABOK
a) Knowledge areas
b) Techniques
c) Underlying competencies
3) Importance of BABOK
4) Conclusion
Understanding BABOK
The Business Analysis Body of Knowledge (BABOK) is a comprehensive framework and guide that sets the standard for best practices and knowledge in the field of Business Analysis. It acts as a foundational resource, providing a structured approach to the tasks, techniques, and competencies required for effective Business Analysis. In essence, BABOK serves as the definitive reference for professionals engaged in Business Analysis, offering them a roadmap to excel in their roles.

Origin and Evolution
BABOK's origins can be traced back to the International Institute of Business Analysis (IIBA), a professional association that supports the Business Analysis community. The initial version of BABOK was published in 2005, and it has since gone through multiple iterations and updates to remain current with the evolving landscape of Business Analysis.
As the field of Business Analysis continued to mature and expand, the need for a standardised reference guide became evident. BABOK emerged as a response to this need, offering a consolidated body of knowledge that brings together the wisdom, experience, and best practices of seasoned professionals.
The ongoing evolution of BABOK is fuelled by the input and collaboration of experts in the field, ensuring that it stays relevant in an ever-changing business environment. It incorporates feedback from practitioners, educators, and organisations, making it a living document that adapts to the needs and challenges faced by Business Analysts worldwide. BABOK's constant evolution makes it a valuable and up-to-date resource for those looking to excel in the field of Business Analysis.
Key components of BABOK
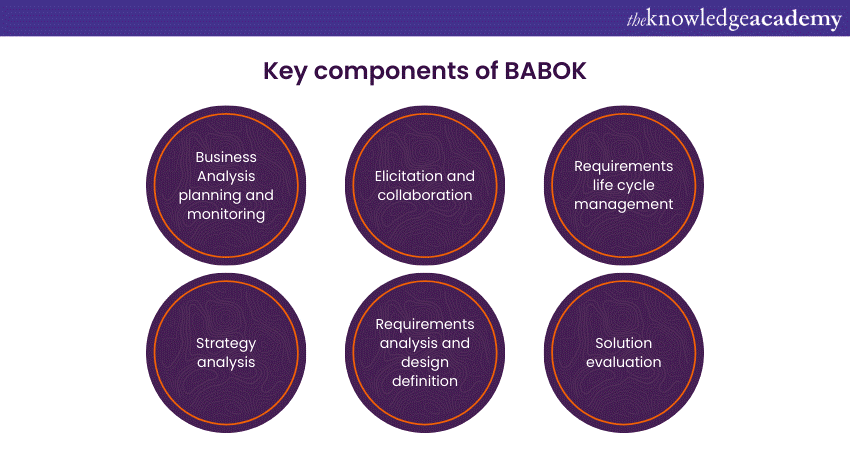
The Business Analysis Body of Knowledge (BABOK) consists of key components that provide a comprehensive framework for Business Analysis Professionals. These components are essential for understanding and executing the practices and techniques associated with effective Business Analysis. Here are the key components of BABOK:
Knowledge areas
Knowledge areas are the fundamental building blocks of BABOK, categorising and organising the knowledge and tasks that Business Analysts need to perform. They encompass the core areas of Business Analysis and serve as a roadmap for professionals to navigate the various aspects of their work. Here's a closer look at each knowledge area:
a) Business Analysis planning and monitoring
This knowledge area focuses on setting the stage for a successful Business Analysis effort. It involves tasks such as defining the scope of the analysis, creating a Business Analysis plan, and establishing metrics for project success. Planning and monitoring are important for ensuring that the analysis is carried out effectively and in alignment with project objectives.
b) Elicitation and collaboration
Elicitation and collaboration are about engaging with stakeholders to understand their needs, expectations, and requirements. This knowledge area includes techniques for gathering and documenting requirements, fostering collaboration among stakeholders, and ensuring that all voices are heard.
c) Requirements life cycle management
Managing requirements effectively is critical to the success of any project. This knowledge area encompasses tasks related to requirements identification, documentation, and Change Management. It ensures that requirements remain accurate, complete, and traceable throughout the project.
d) Strategy analysis
Strategy analysis involves identifying the business need, aligning it with strategic goals, and defining the business problem or opportunity. It helps ensure that project objectives align with the broader organisational strategy. Strategy analysis is a foundational step in the Business Analysis process.
e) Requirements analysis and design definition
This knowledge area focuses on the process of analysing requirements, understanding their relationships, and defining solutions. It includes activities like modelling, verifying, and validating requirements to ensure they meet the desired outcomes and can be effectively implemented.
f) Solution evaluation
Solution evaluation occurs throughout the project life cycle, ensuring that the solution aligns with the requirements and provides value to the organisation. This knowledge area involves assessing the performance of the implemented solution and making necessary adjustments.
Unlock your potential with the BCS Advanced International Diploma in Business Analysis Course – Take the next step towards becoming a master in your field today!
Techniques
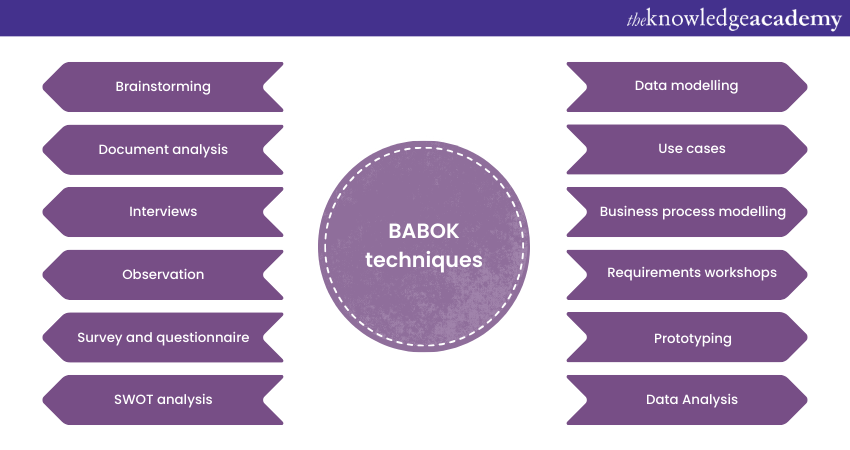
BABOK outlines numerous techniques that Business Analysts can employ to accomplish their tasks effectively. These techniques range from brainstorming, document analysis, and observation to more complex practices like data modelling, use cases, and business process modelling. The choice of techniques depends on the context of the project and the requirements of stakeholders. Here are some of the most commonly used BABOK techniques:
a) Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a creative technique that encourages collaboration among stakeholders to generate ideas, solutions, and potential requirements. It's a valuable method for exploring various possibilities and viewpoints.
b) Document analysis
Document analysis involves reviewing existing documentation, such as reports, business plans, and process diagrams, to extract relevant information and identify potential requirements. This technique helps in understanding the current state of the organisation.
c) Interviews
Business Analysts conduct interviews with stakeholders to elicit information and requirements. They ask questions and engage in discussions to understand their needs, concerns and preferences.
d) Observation
Observation involves directly witnessing how processes, systems, or individuals operate. This hands-on approach helps analysts understand the real-world context and can be especially valuable for uncovering implicit requirements.
e) Survey and questionnaire
Surveys and questionnaires are used to collect information from a large group of stakeholders. They are a structured way to gather data, opinions, and preferences. Surveys can be distributed electronically or on paper.
f) SWOT analysis
Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats (SWOT) analysis is a strategic technique used to assess an organisation's internal and external factors. It helps in identifying potential risks, opportunities, and areas for improvement.
g) Data modelling
Data modelling techniques like Entity-Relationship Diagrams (ERD) and Data Flow Diagrams (DFD) help in visualising and structuring data and information, which is essential for defining data-related requirements.
h) Use cases
Use cases are used to define system interactions from an end user's perspective. They describe how an actor (typically a user) interacts with a system to achieve a targeted goal.
i) Business process modelling
This technique involves creating process models, such as flowcharts and business process diagrams, to depict the steps involved in a business process. It aids in understanding and optimising business processes.
j) Requirements workshops
Requirements workshops are collaborative sessions where stakeholders and analysts come together to discuss, prioritise, and document requirements. Workshops facilitate communication and consensus-building.
k) Prototyping
Prototyping is a technique where a simplified, often interactive, model of a system or solution is created to validate and clarify requirements. It's particularly useful for visualising and refining user interfaces.
l) Data Analysis
Data Analysis techniques, like data mining and statistical analysis, help in extracting meaningful insights and trends from data to inform requirements and decision-making.
Underlying competencies
Underlying competencies are the personal and professional qualities that enable a Business Analyst to excel in their role. These competencies go include attributes like:
a) Analytical thinking and innovation
This competency involves the ability to think critically, analyse information, and approach problems and challenges with creativity and innovation.
Business Analysts often need to dissect complex problems, identify patterns, and generate innovative solutions. Analytical thinking and innovation enable them to make sense of data, see opportunities, and propose effective solutions.
b) Behavioural characteristics:
Behavioural characteristics encompass personal qualities that contribute to an individual's effectiveness, including adaptability, ethics, integrity, and professionalism.
These characteristics are vital in establishing trust with stakeholders, maintaining a high level of integrity in one's work, and adapting to changing circumstances or project requirements. Being ethical, adaptable, and professional helps in fostering positive relationships and maintaining a high level of credibility.
c) Business knowledge
Business knowledge involves understanding the industry, domain, organisation, and the specific context of the project. It includes knowledge of relevant business processes, practices, and terminology.
To be effective in Business Analysis, professionals must have a solid understanding of the environment in which they are working. Business knowledge enables analysts to comprehend the unique challenges, opportunities, and constraints faced by their organisation or industry.
d) Communication skills
Communication skills encompass the ability to convey ideas, thoughts, and information clearly and effectively. This includes active listening as well as both verbal and written communication.
Business Analysts constantly interact with stakeholders, document requirements, and facilitate discussions. Effective communication skills are important for ensuring that information is conveyed accurately and that stakeholders' needs and concerns are understood.
e) Interaction skills
Interaction skills are the ability to build and maintain strong relationships with stakeholders, foster collaboration, and manage conflicts or difficult conversations.
Interacting effectively with stakeholders is a critical aspect of Business Analysis. Building relationships, engaging stakeholders, and resolving conflicts are all necessary to ensure that projects progress smoothly and requirements are accurately captured.
f) Tools and technology
Proficiency in using various tools and technology to support Business Analysis activities, such as modelling software, requirements management tools, and collaboration platforms.
In the modern Business Analysis environment, tools and technology play a significant role in efficiently managing requirements, collaborating with stakeholders, and analysing data. Competency in these tools enhances productivity and accuracy.
Unlock your potential and enhance your career with the BCS Foundation Certificate in Business Analysis Course - your gateway to becoming a proficient Business Analyst. Join today and pave the way for professional success.
Importance of BABOK
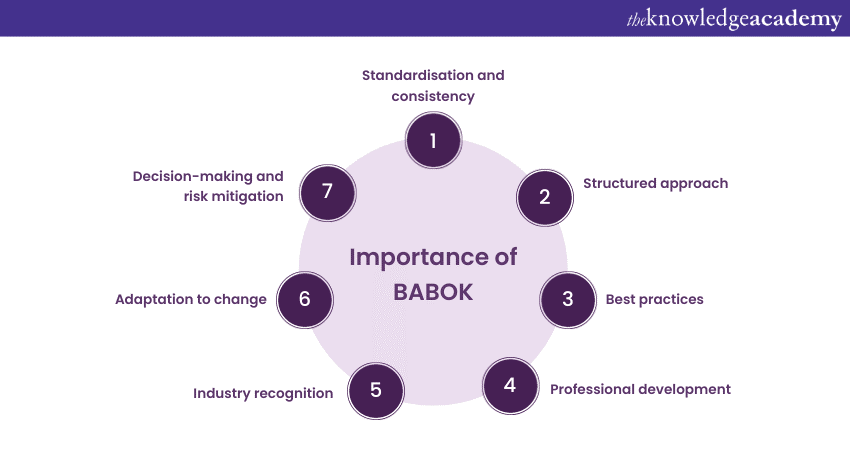
The Business Analysis Body of Knowledge (BABOK) is important in the field of Business Analysis for several compelling reasons:
a) Standardisation and consistency
BABOK serves as a universal reference guide that standardises Business Analysis practices. Establishing common terminology, methodologies, and best practices ensures that Business Analysts across the globe are on the same page. This consistency is crucial in fostering effective communication and collaboration within the profession.
b) Structured approach
BABOK provides a structured approach to Business Analysis, breaking down the complex process into manageable components. This structured framework aids analysts in tackling their roles systematically, from planning and requirements gathering to solution evaluation. It ensures that no critical steps are overlooked, reducing the risk of errors.
c) Best practices
BABOK incorporates the collective wisdom and experience of seasoned professionals in the field. It compiles and disseminates best practices, allowing Business Analysts to learn from the successes and challenges of others. This wealth of knowledge empowers professionals to make informed decisions and execute their roles more effectively.
d) Professional development
For individual Business Analysts, BABOK is a pathway to professional development and growth. It outlines the key competencies and skills required for success in the field, serving as a career development guide. By aligning with BABOK's recommendations, professionals can improve their skills, advance their careers, and become more valuable assets to their organisations.
e) Industry recognition
Organisations often look for professionals with a solid foundation in BABOK because it signifies a commitment to industry standards and best practices. Being BABOK-certified can enhance one's credibility and employability, making it an essential asset for Business Analysts seeking career advancement.
f) Adaptation to change
Business environments are constantly evolving, and so are the demands on Business Analysts. BABOK's continuous updates and revisions ensure that it remains relevant in the face of industry and technological changes. It equips analysts with the latest business analysis tools and knowledge they need to stay competitive.
g) Decision-making and risk mitigation
By following the guidelines and techniques outlined in BABOK, Business Analysts are better prepared to make informed decisions. This leads to more successful projects and reduces the likelihood of costly mistakes, ultimately contributing to improved organisational performance and profitability.
Conclusion
If you're still wondering, "What is BABOK?" - it's like a trusted map for Business Analysts. It guides them on their journey, helping them understand their tasks and responsibilities. By following its paths, Business Analysts can work more effectively and find success in their careers. BABOK, or the Business Analysis Body of Knowledge, brings structure, best practices, and standards to the field, making it a valuable resource for both newcomers and experienced professionals. So, remember, BABOK is your key to becoming a skilled and respected Business Analyst.
Unlock your potential with the BCS Certificate in Business Analysis Practice Training and chart a course for success in the world of Business Analysis.
Upcoming Business Analysis Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 BCS Certificate in Business Analysis Practice
BCS Certificate in Business Analysis Practice
Mon 6th Jan 2025
Mon 20th Jan 2025
Mon 3rd Feb 2025
Mon 17th Feb 2025
Mon 3rd Mar 2025
Mon 17th Mar 2025
Mon 7th Apr 2025
Mon 12th May 2025
Mon 9th Jun 2025
Mon 7th Jul 2025
Mon 4th Aug 2025
Mon 1st Sep 2025
Mon 6th Oct 2025
Mon 20th Oct 2025
Mon 3rd Nov 2025
Mon 17th Nov 2025
Mon 1st Dec 2025
Mon 15th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


