We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 800600725 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

As our world becomes increasingly digital, the question What is Cyber Security has become more crucial than ever. As we rely more on technology, protecting personal data, financial information, and sensitive secrets from attacks becomes imperative. This blog delves into the essentials of Cyber Security, highlighting its significance in our interconnected world.
Are you equipped to handle the latest cyber threats targeting individuals and businesses? Do you have the knowledge to implement effective Cyber Security measures? This blog provides insights and practical advice to enhance your understanding and strengthen your defences. Join us to explore Cyber Security, answering: What is Cyber Security, and how can we stay ahead in this vital field?
Table of Contents
1) What is Cyber Security?
2) Types of Cyber Security
3) Common Cyber Security Threats
4) Latest Cyber Security Threats
5) Advantages of Cyber Security
6) Cyber Security Best Practices
7) Cyber Security Jobs and Salaries
8) Conclusion
What is Cyber Security?
Switching to Cyber Security involves safeguarding computers, networks, and data from digital threats like hacking, malware, and phishing. It consists of using various tools and techniques to secure systems and prevent Cyber Security attacks. Key areas include network security, application security, and information security. It also involves detecting, responding to, and recovering from cyber incidents.
Effective Cyber Security, with its advantages and disadvantages, requires a blend of advanced technology, regular updates, employee training, and robust policies. By implementing these measures, organizations can enhance data safety and privacy while maintaining its integrity and availability in an increasingly connected world.
Types of Cyber Security
Cyber Security is a broad field encompassing various disciplines, which can be categorised into seven main pillars, each representing different types of cyber security.
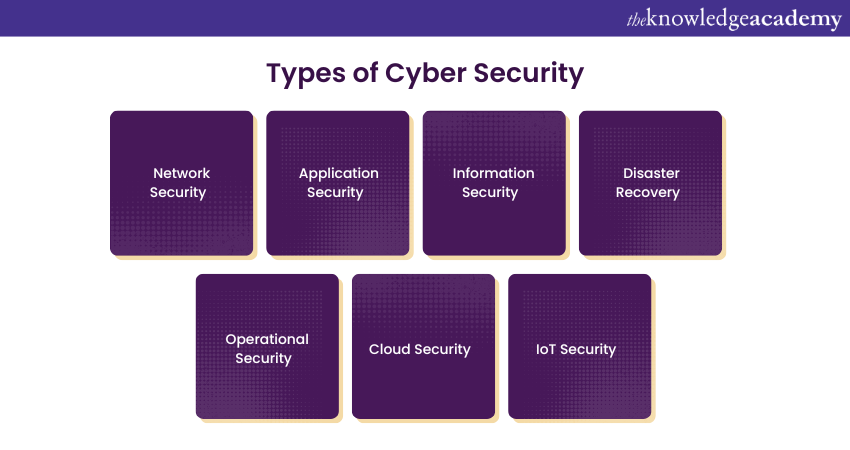
1) Network Security
Network security in Cyber Security involves strategies, technologies, and policies to safeguard computer networks from unauthorised access, data breaches, and disruptions, which is a key aspect when considering Network Security Vs Cyber Security. Network security uses access control, firewalls, encryption, VPNs, and monitoring to protect networks from cyber security breach, Cyberbullying, and other cyber threats.
2) Application Security
Application security involves securing software from vulnerabilities and attacks by implementing robust coding practices, regular security testing, and patch management. It ensures that applications protect data integrity and user privacy, mitigating risks associated with unauthorized access and cyber threats. This expertise in application security can have a significant impact on Cyber Security Analyst salaries, as companies value professionals who can safeguard critical systems and information.
3) Information Security
Information security encompasses practices and technologies that protect sensitive data from unauthorised access, alterations, or destruction. It includes access controls to limit who can access information. Regular audits confirm cyber security compliance with security policies and regulations, maintaining data integrity and confidentiality.
4) Disaster Recovery
Disaster recovery focuses on preparing for and recovering from potential disasters or disruptions that could impact business operations. It involves planning and testing contingency plans, setting up backups, and defining roles for quick response and recovery.
5) Operational Security
Operational security addresses risks related to day-to-day business operations, including physical security of facilities, access control measures for employees and visitors, and training staff on security best practices. It aims to protect assets, facilities, and personnel from threats such as theft, espionage, and sabotage.
6) Cloud Security
Cloud security involves protecting data, applications, and infrastructure hosted in cloud environments. This includes implementing strong authentication mechanisms, encryption for data protection, and monitoring for suspicious activities.
7) IoT Security
IoT security focuses on securing interconnected devices and networks from cyber threats. It involves implementing secure communication protocols, regularly updating firmware to patch vulnerabilities, and segregating IoT networks from critical systems. Security measures are intended to prevent unwanted access and possible misuse of IoT devices.
Explore the impact of Artificial Intelligence vs Cyber Security in shaping a safer digital future.
Common Cyber Security Threats
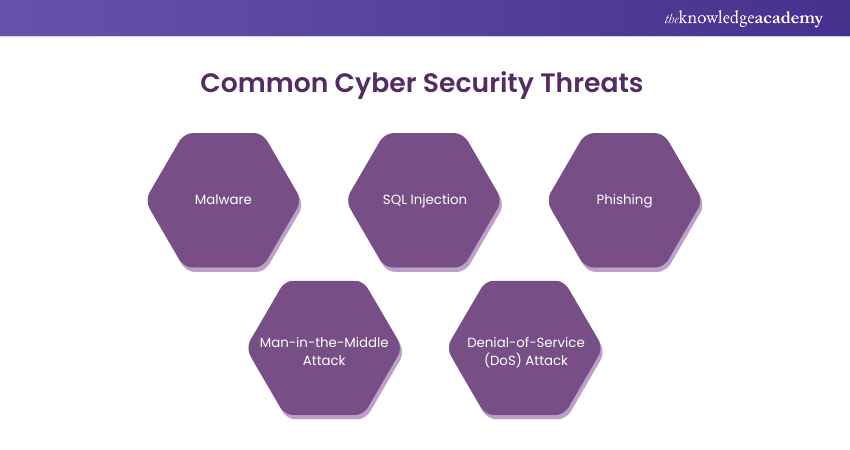
1) Malware
Malware refers to software that is malicious. One of the most common cyber threats is malware, which is designed by a cybercriminal or hacker to disrupt or damage an authorised user's computer. Malware, spread through unsolicited emails or legitimate downloads, is used by cybercriminals for financial gain or political attacks. Understanding and mitigating malware attacks is a crucial Cyber Security skill, and plays a key role in the 3 Pillars of Cyber Security, which focus on protecting confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Here are some common Malware Cyber threats:
a) Viruses: A virus is self-replicating software that flows through a computer system, infecting documents with malicious code.
b) Trojans: Malware masquerading as legal software. Cybercriminals mislead people into installing Trojans on their computers, which inflict damage or collect data.
c) Spyware: This is an application that secretly records a user's actions, which hackers are able to use. For example, spyware might record credit card information.
d) Adware: This is advertising software that can be used to transmit malware.
e) Botnets: These are networks of malware-infected computers used by hackers to conduct internet activities without user permission.
f) Ransomware: This is a type of malware that takes a victim’s sensitive data or device hostage, threatening to lock it or cause further harm unless a ransom is paid to the attacker.
2) SQL Injection
SQL Injection is a type of cyber-attack that targets vulnerabilities in data-driven applications. By inserting malicious SQL code into input fields, attackers can manipulate the database to gain unauthorised access to sensitive information.
3) Phishing
Phishing is a cyber-attack where criminals send fraudulent emails that seem to originate from reputable sources. Similar to phishing, pharming aims to deceive individuals into disclosing sensitive personal information.
4) Man-in-the-Middle Attack
Man-in-the-Middle Attack is a cyber-attack where an attacker intercepts the communication between two parties (such as a user and a website). By eavesdropping on the data exchange, the attacker can steal sensitive information or alter the communication.
5) Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attack
A Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attack is a cyber-attack that overwhelms a computer system, network, or server with excessive traffic, making it unusable. Cybercriminals flood the target with requests, disrupting normal cyber security operations and preventing legitimate users from accessing services.
Protect your digital assets by mastering Malware Analysis by joining our expert-led Malware Analysis Training and enhancing your Cyber Security skills!
Latest Cyber Security Threats
Here are some of the latest cyber threats reported by the governments of the UK, US, and Australia.
Dridex Malware
In 2019, the US Department of Justice charged the leader of a cyber-criminal group involved in a global Dridex malware attack. This campaign impacted the public, government, infrastructure, and businesses worldwide.
Dridex, a financial trojan active since 2014, infects computers through phishing emails or existing malware. It steals passwords, banking details, and personal data, leading to significant financial losses, particularly when it targets sensitive information related to Cyber Security In Banking. The UK’s National Cyber Security Centre advises keeping devices patched, anti-virus software updated, and files backed up.
Romance Scams
In 2020, the Federal Bureau of Investigation warned US citizens about confidence fraud on dating sites, chat rooms, and apps. Cybercriminals exploit individuals seeking new partners, tricking them into revealing personal information. In 2019, romance scams affected 114 victims in New Mexico, resulting in $1.6 million in financial losses.
Emotet Malware
In late 2019, the Australian Cybersecurity Centre alerted national organisations to a global threat from Emotet malware. Emotet is a sophisticated trojan that can steal data and load other malware. It often exploits weak passwords, highlighting the need for strong, secure passwords to protect against cyber threats.
Boost Your Confidence with Essential Cyber Security Interview Questions!
Advantages of Cyber Security
Businesses and individuals (such as MSSPs) can safeguard themselves and others from the entire range of Cyber Security dangers listed below by installing security solutions and experiencing the benefits of Cybersecurity.
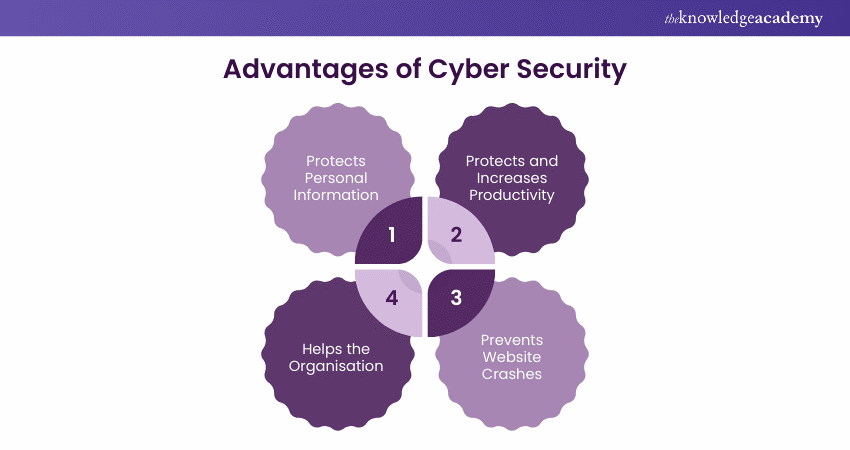
1) Protects Personal Information: In today's technologically advanced society, personal information is one of the most important resources. It is possible that if a virus is able to gather personal data about your workers or customers, it will be sold or exploited to steal their money.
2) Protects and Increases Productivity: When viruses attack your computers and network, they stop working, making it nearly impossible to continue working. As a result, your employees' productivity will suffer, and there will be waste that will halt operations throughout the entire business.
3) Prevents Website Crashes: Preventing website crashes is crucial for small businesses hosting their own sites. If infected, downtime not only leads to lost transactions but also risks customer loss and significant system damage from malware.
4) Helps the Organisation: A strong security system often provides your business and employees with the best tools, strategies, and support in defending against cyberattacks and criminals.
Transform your career with Fraud Analytics Training - join today and become a Cyber Security expert!
Cyber Security Best Practices
To reduce the possibility of a cyberattack, it is essential to develop and stick to a set of best practices that include the following:
1) Keep Software Up to Date: Software updates are released by companies for three main reasons: to introduce new features, fix known bugs, and enhance security. When considering CSO vs CISO, both roles emphasize the importance of keeping software updated to safeguard against new and existing security vulnerabilities. Always ensure you update your software to the latest version to maintain optimal security.
2) Stay away from suspicious emails: If an email appears suspicious, do not open it, as it could be a phishing scam. Cybercriminals may impersonate individuals or companies to steal your personal information. These emails might also contain attachments or links that can infect your devices.
3) Use Strong Passwords: Encourage employees to use complicated passwords that contain a combination of letters, numbers, and symbols. Regularly changing passwords is essential.
4) Implement Multifactor Authentication (MFA): Require at least two identity components for access, reducing the risk of unauthorised entry.
5) Train Employees on Security Awareness: Educate staff about potential risks and how to recognise suspicious emails (phishing attacks).
6) Use a Secure File-sharing Solution to Encrypt Data: For sharing confidential information, use a secure file-sharing solution instead of regular email, which can be intercepted.
7) Use Anti-virus and Anti-malware Software: Complete protection from malware is impossible while connected to the internet. However, you can significantly reduce your vulnerability by installing both anti-virus and anti-malware software on your computers.
8) Use a VPN to Privatise Your Connections: For a more secure and private network, use a Virtual Private Network (VPN). It encrypts your connection, safeguarding your private information from possible eavesdroppers, including your internet service provider.
9) Double-check for HTTPS on Websites: Ensure a website uses HTTPS before sharing personal or private information. Without HTTPS, the data transfer between you and the site’s server isn’t guaranteed to be secure.
10) Avoid Using Public Networks: Connecting to a public network means sharing it with everyone else connected, making your information vulnerable. Avoid using public networks or use a VPN to secure your connection if you must connect to one.
Empower yourself with expert knowledge - sign up for our Cyber Security Risk Management Course and stay ahead of cyber threats!
Cyber Security Jobs and Salaries
The field of Cyber Security is currently experiencing remarkable growth, with a staggering 13 percent increase. This surge is expected to create 2,700 new jobs in the UK, as per Gov.UK. In this section, we will outline a Roadmap for Cyber Security that highlights the key areas and skills needed to thrive in this rapidly expanding industry. we will explore about Cyber Security jobs and their respective salaries in the UK:
|
Job Roles |
Average Annual Salary |
|
Security Architect |
£83,000 |
|
Software Security Engineer |
£50,000 |
|
Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) |
£97,000 |
|
Information Security Analyst |
£49,000 |
|
Penetration Tester |
£59,000 |
|
Security Consultant |
£55,000 |
Source: Glassdoor
Gain essential skills in system and network security - join our Introduction to System And Network Security Course and secure your digital future now!
Conclusion
Understanding What is Cyber Security is vital in our increasingly digital world. Protecting personal data, financial information, and sensitive organisational secrets from cyber threats, including Smishing in Cyber Security or Spamming in Cyber Security is essential for maintaining security and trust. Taking the right steps on the Cyber Security Certification Path will help you implement effective measures to safeguard your digital assets. For a clearer understanding, it’s useful to consider the difference between cyber security and Information Security and how they intersect in protecting your digital assets. As we explore Data Science vs Cyber Security, it's clear that both disciplines play crucial roles in securing digital environments, with data science offering insights through analytics and cyber security focusing on proactive defence strategies.
Learn more about how to ensure Cyber Security practices in your business- sign up for Cyber Security Training courses now!
Frequently Asked Questions
What Career Opportunities are Available in Cyber Security?

Career opportunities in Cyber Security include roles such as Cyber Security Analyst, Ethical Hacker, and Network Security Engineer. Other positions are Cyber Security Consultant, Incident Responder, and Chief Information Security Officer (CISO).
What does a Cyber Security Analyst do?

A Cyber Security Analyst protects an organisation's computer systems and networks from cyber threats. They monitor breaches, analyse vulnerabilities, implement security measures, and respond to incidents to protect data and ensure system integrity.
What are the Other Resources and Offers provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Cyber Security Training, including Certified Cyber Security Professional (CCS-PRO), Cyber Security Awareness, and Cyber Security Risk Management. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Internet Security.
Our IT Security & Data Protection Blogs cover a range of topics related to Cyber Security, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Cyber Security skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Certified Cyber Security Professional (CCS-PRO)
Certified Cyber Security Professional (CCS-PRO)
Fri 21st Mar 2025
Fri 23rd May 2025
Fri 22nd Aug 2025
Fri 5th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


