We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 800600725 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Data is everywhere, but it’s only valuable when organised and meaningful. This is where data processing comes in, transforming raw data into usable information through steps like collection, preparation, and analysis. But What is Data Processing, and why does it matter?
This blog delves into What is Data Processing, exploring its importance, key steps, and its transformative role in decision-making. Unlock the secrets of turning data into actionable insights, and discover how it drives success in today’s data-driven world!
Table of Contents
1) What is Data Processing?
2) 6 Steps of the Data Processing
3) Different Types of Data Processing
4) Examples of Data Processing
5) The Future of Data Processing
6) Conclusion
What is Data Processing?
Data processing is collecting and translating data into usable information. This task is usually performed by a data scientist or a team of data scientists. Doing this correctly is crucial to avoid negatively impacting the final data output.
The process begins with raw data, which is then converted into a more readable format, like graphs or documents. This makes it easier for computers to interpret and for employees to use throughout an organisation.
6 Steps of the Data Processing
Data processing involves several key stages in converting raw data into useful information. Here's a breakdown of these stages:
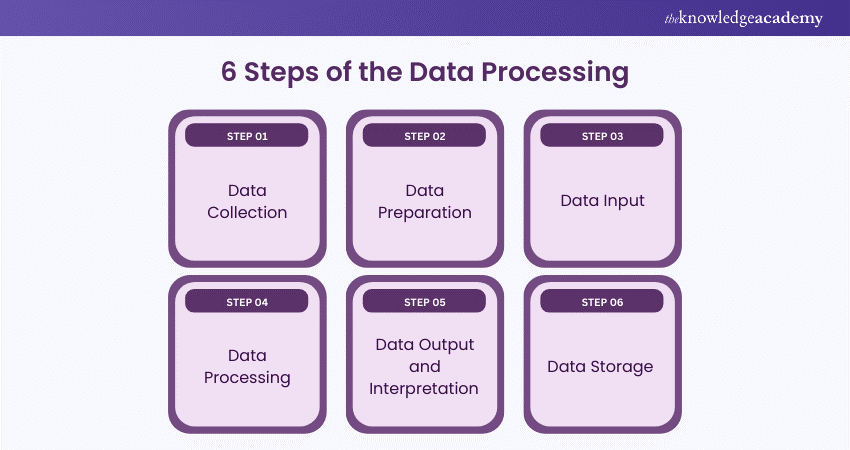
Step 1: Data Collection
Collecting data is the first step. Data is gathered from sources like data lakes and data warehouses. It's crucial to ensure these sources are reliable to collect high-quality data for later use.
Step 2: Data Preparation
Once collected, data enters the preparation stage, often called "pre-processing." Here, raw data is cleaned and organised. Errors are checked, and bad data (redundant, incomplete, or incorrect) is eliminated to create high-quality data for business intelligence.
Step 3: Data Input
Clean data is then entered into its destination, such as a CRM like Salesforce or a data warehouse like Redshift. This stage translates raw data into a usable format.
Step 4: Data Processing
During this stage, the data inputted in the previous step is processed for interpretation. Machine learning algorithms are used, though the process may vary depending on the data source and its intended use (e.g., advertising patterns, medical diagnosis, customer needs).
Step 5: Data Output and Interpretation
This stage makes data usable for non-data scientists. Data is translated into readable formats like graphs, videos, images, or text. It can now be used by company members for data analytics projects.
Step 6: Data Storage
The final stage is storing the processed data for future use. Properly stored data can be easily accessed when needed and is crucial for compliance with data protection laws like GDPR. While some data is used immediately, much of it serves future purposes.
Elevate your career with our Advanced Data Science Certification Course - master cutting-edge skills and stand out in the field!
Different Types of Data Processing
Data processing involves various methods to convert raw data into useful information. Each type suits different scenarios and needs.
Batch Processing
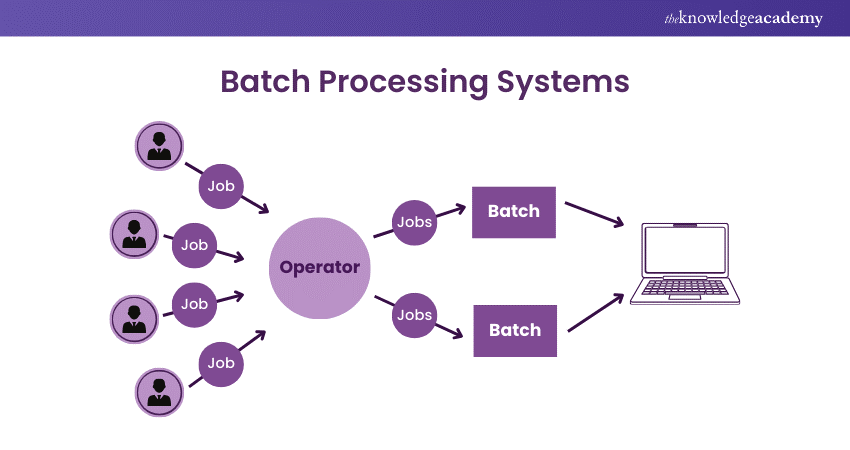
Handles large volumes of data at set times, ideal for non-urgent tasks. This method aggregates data and processes it during off-peak hours to minimise impact on daily operations.
Example: Financial institutions process checks and transactions overnight, updating account balances in one go.
Real-time Processing
Processes data immediately upon receipt, providing instant feedback. Crucial for tasks where delays are unacceptable, ensuring timely decisions and responses.
Example: GPS navigation systems offer real-time turn-by-turn directions based on live traffic and road conditions.
Multiprocessing
Uses multiple CPUs to handle tasks simultaneously, improving efficiency, especially for complex computations that can be split into smaller tasks.
Example: Movie production uses multiprocessing for rendering 3D animations, speeding up project completion and improving visual quality.
Online Processing
Enables interactive data processing over a network with continuous input and output for immediate responses. Essential for e-commerce and online services.
Example: Online banking systems process financial transactions in real-time, allowing instant fund transfers and account updates.
Manual Data Processing
Requires human intervention for data input, processing, and output, typically without electronic devices. Prone to errors but was common before computers.
Example: Libraries used to catalogue books manually, recording details by hand for inventory purposes.
Cloud Computing
Provides computing resources like servers and storage over the internet, offering flexibility and scalability without physical infrastructure.
Example: Small businesses use cloud computing for data storage and software services, allowing easy scaling as the business grows.
Mechanical Data Processing
Uses machines or equipment for data tasks, a prevalent method before the digital era, involving tangible devices to input, process, and output data.
Example: Early 20th-century voting machines tallied votes by pulling levers, simplifying counting and reducing errors.
Distributed Processing
Spreads computational tasks across multiple devices to improve speed and reliability, handling large-scale tasks more efficiently than a single computer.
Example: Video streaming services store videos on multiple servers for smooth playback and quick access worldwide.
Automatic Data Processing
It uses software to automate routine tasks, reduce manual input, and increase efficiency by streamlining processes and minimising errors.
Example: Automated billing systems in telecommunications calculate and send monthly charges to customers, streamlining operations and reducing errors.
Electronic Data Processing
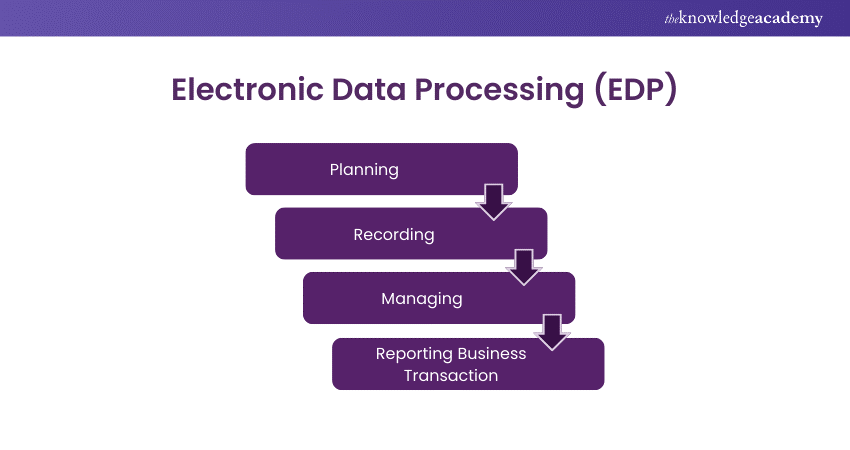
Uses computers and digital technology for efficient data handling, allowing rapid processing, vast storage, and easy retrieval.
Example: Retail checkouts use barcode scans to update inventory and process sales quickly.
Transform your Data Analysis skills with our Pandas For Data Analysis Training - learn to unlock powerful insights from your datasets!
Examples of Data Processing
Data processing is crucial in many industries and applications, showcasing its versatility and essential role in digital operations. Here are some examples highlighting its importance:
Digital Marketing
Digital marketing companies use demographic data to create targeted marketing campaigns. By processing this data effectively, they identify target audiences, understand their preferences, and optimise marketing efforts for better engagement and conversion rates.
Financial Transactions
Data processing is essential for financial transactions like bank transfers, online payments, and stock trades.
Navigation Systems
Real-time data processing is vital for GPS navigation systems, which process satellite data instantly to provide turn-by-turn directions.
Supply Chain Optimisation
Data from various supply chain points is processed to identify bottlenecks, predict demand, and optimise production logistics.
Weather Forecasting
Weather forecasting relies on multiprocessing (parallel processing), where data from satellites and weather stations is processed simultaneously. This enables rapid analysis of complex meteorological data to accurately predict weather conditions.
Advance your career with our Data Mining Training - gain essential skills to analyse data and extract valuable insights today!
The Future of Data Processing
Various innovative trends and technologies are shaping the future of data processing:
Cloud Computing
More data processing is moving to the cloud as organisations prefer cloud computing over on-premises resources. Serverless computing and function as a service make cloud data processing tasks easier and more efficient.
Edge Computing
Driven by the rise of IoT devices and 5G deployment, edge computing processes data closer to its source. This reduces latency and bandwidth use, enabling real-time processing capabilities.
ML and AI Integration
Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence are increasingly integrated with data processing technologies. This integration automates data analysis, predictive modelling, and decision-making processes.
Privacy-Preserving Data Processing
With increasing worries over data privacy and stricter regulations, technologies that support privacy-preserving data processing are becoming more important.
Conclusion
Data processing transforms raw data into valuable insights, driving smarter decisions and efficient operations. It’s the backbone of modern businesses and technology. We hope you understand What is Data Processing and its importance in businesses. Its potential paves the way for smarter solutions and improved outcomes.
Unlock the secrets of Data Science with our expert-led Data Science Courses and start transforming data into actionable insights today!
Frequently Asked Questions

Data processing tools are software or systems used to collect, process, and analyse data efficiently. Examples include Excel, SQL, Hadoop, and Python-based tools. These tools streamline workflows, handle large datasets, and ensure accuracy, enabling faster decision-making and improved data management.

Data storage is crucial in data processing as it securely holds raw, intermediate, and processed data for analysis and retrieval. It ensures data availability, reliability, and organisation, enabling smooth processing and supporting decision-making by maintaining structured access to information.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Data Science Courses, including Data Mining Training, Python Data Science Course, Advanced Data Science Certification and Data Science With R Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Data Mining Tools.
Our Data, Analytics & AI Blogs cover a range of topics related to Data Mining, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Data, Analytics & AI skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Data, Analytics & AI Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Python Data Science Course
Python Data Science Course
Mon 6th Jan 2025
Mon 24th Mar 2025
Mon 26th May 2025
Mon 28th Jul 2025
Mon 20th Oct 2025
Mon 1st Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


