We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

When it comes to financial regulations and corporate governance in the United States, the Sarbanes Oxley Act, often abbreviated as SOX, stands as a cornerstone of accountability and transparency. Enacted in the wake of corporate scandals, the Sarbanes Oxley 101 was to restore investor confidence and safeguard the integrity of financial reporting.
According to a report by Stanford Business, in the 1990s, corporate profits increased by 88 percent while worker pay increased by 42 per cent. On the other hand, CEO pay was raised by a staggering 463 percent. These inequalities led to the downfall of the likes of Enron and WorldCom. In this introductory guide, we’ll dive into Sarbanes Oxley 101, the act’s significance, implementation strategies and its impact on the corporate landscape.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding Sarbanes Oxley Act: A brief overview
a) Key provisions of Sarbanes Oxley
b) Significance and impact
2) Sarbanes Oxley 101: Simplifying compliance
3) Conclusion
Sarbanes Oxley Act - An Overview
Named after its co-sponsors, Senator Paul Sarbanes and Representative Michael Oxley of the United States Congress, the Sarbanes Oxley Act became law in 2002 as a response to the high-profile accounting scandals that shook the corporate world, including those involving Enron and WorldCom. The primary objective of the act is to enhance corporate governance, improve financial reporting accuracy, and strengthen the oversight of public companies.
Key Provisions of Sarbanes Oxley
The Following are the explained key provisions of Oxley:
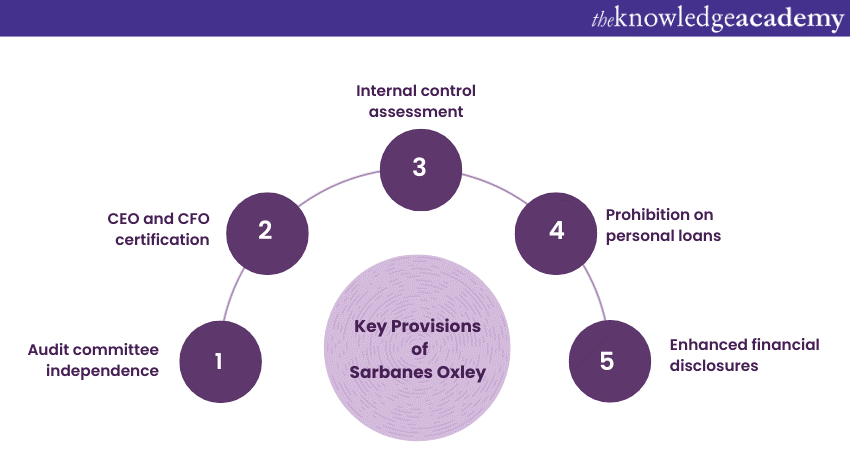
a) Audit Committee Independence: The act mandates that public companies have an independent audit committee to oversee the financial reporting process and the relationship with external auditors.
b) CEO and CFO Certification: CEOs and CFOs of public companies are obligated to personally certify the accuracy of financial statements and disclosures, increasing their individual accountability.
c) Internal Control Assessment: Public companies must assess and report on the effectiveness of their internal controls over financial reporting to avoid fraud and errors.
d) Prohibition on Personal Loans: The act prohibits companies from making personal loans to executives and directors, curbing potential conflicts of interest.
e) Enhanced Financial Disclosures: The act calls for clearer and more comprehensive financial disclosures, ensuring that investors have accurate information to make informed decisions.
Significance and Impact:
a) Investor Confidence: Sarbanes Oxley aims to restore investor trust by ensuring that financial information is accurate and transparent, reducing the risk of corporate fraud.
b) Corporate Accountability: The act holds CEOs, CFOs, and other executives personally responsible for the accuracy of financial statements, discouraging unethical practices.
c) Improved Corporate Governance: The act promotes better corporate governance through independent audit committees, ensuring checks and balances within organisations.
d) Internal Control Effectiveness: The requirement to assess internal controls enhances the accuracy and reliability of financial reporting, reducing the likelihood of errors.
e) Global Influence: Sarbanes Oxley's principles have influenced corporate governance and reporting standards worldwide, shaping a global commitment to transparency.
Boost your knowledge with Sarbanes-Oxley Training – Secure your spot and excel in compliance!
Sarbanes Oxley 101: Simplifying Compliance
Compliance with the Sarbanes Oxley Act can be a complex endeavour, especially for organisations navigating its intricacies for the first time. Here are some steps to simplify the compliance process:
a) Understand Applicability: Determine whether your organisation falls under the jurisdiction of Sarbanes Oxley based on factors like public company status and market capitalisation.
b) Establish Internal Controls: Develop robust internal controls over financial reporting to ensure accuracy and reliability.
c) Educate Personnel: Train employees, especially executives and financial professionals, on the requirements of Sarbanes Oxley to ensure proper implementation.
d) Conduct Regular Assessments: Regularly assess the effectiveness of your internal controls and address any weaknesses promptly.
e) Seek Expertise: Engage legal and financial experts with expertise in Sarbanes Oxley compliance to guide your organisation through the process.
Conclusion
The Sarbanes Oxley Act has significantly transformed the landscape of corporate governance and financial reporting. By emphasising accountability, transparency, and improved internal controls, the act seeks to prevent corporate malfeasance and enhance investor confidence. Hopefully, through this blog, we have cleared up your doubts regarding Sarbanes Oxley 101 and set you on the path of financial compliance.
Elevate your expertise with our Sarbanes Oxley Certified Professional Course for enhanced governance and compliance.
Frequently Asked Questions

The Sarbanes-Oxley Act defines internal controls as processes ensuring accurate financial reporting, compliance with laws, and operational efficiency. Section 404 mandates management to assess and report on controls, and auditors must verify their effectiveness, ensuring reliability and fraud prevention.

The Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) was passed in July 2002 in response to major corporate scandals like Enron and WorldCom. It aims to protect investors by improving corporate transparency, enforcing stricter financial reporting standards, and holding executives accountable for fraud.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers Sarbanes-Oxley Training, including the Sarbanes-Oxley Certified Professional. This course caters to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Sarbanes Oxley Act.
Our ISO and Compliance Blogs cover a range of topics related to Sarbanes Oxley, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Finance Management Skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming ISO & Compliance Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Sarbanes-Oxley Certified Professional
Sarbanes-Oxley Certified Professional
Mon 6th Jan 2025
Mon 17th Mar 2025
Mon 26th May 2025
Mon 14th Jul 2025
Mon 22nd Sep 2025
Mon 24th Nov 2025
Mon 8th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


