We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Every business dream of thriving on unwavering quality and trust. But is there a surefire blueprint to ensure that? ISO 9001 provides an answer. As the world's most recognised Quality Management standard, it offers a framework for organisations to deliver consistent, high-quality products and services. In this blog, we’ll unpack the key ISO 9001 Requirements in a way that’s easy to grasp, ensuring you are ready to turn quality aspirations into reality. So read on and unlock the secrets of delivering excellence, one requirement at a time!
Table of Contents
1) What are the Requirements for ISO 9001?
2) Structure of ISO 9001
3) What are the Six Mandatory Procedures for ISO 9001?
4) How Much Does ISO 9001 Certification Cost?
5) Conclusion
What are the Requirements for ISO 9001?
The ISO Requirements are established in ten clauses that include both mandatory and non-mandatory Requirements. As the term implies, mandatory requirements must be met to be certified as compliant with the ISO 9001 Standard. The Requirements help in ensuring the successful performance of the QMS within an organisation.
An example of a mandatory Requirement is a document outlining the features of the products produced or services provided. These types of ISO 9001 Documentation are essential for the process of creating a QMS to the ISO 9001 Standard. Non-mandatory Requirements contain documents which may or may not be required based on the type or size of the organisation.
The first three clauses under ISO 9001 Requirements encompass the scope, references and terms of the ISO 9001 Standard. Although these clauses do not include mandatory Requirements, they deliver useful information to the organisation. Clauses four to 10 cover seven scopes of the organisation and contain the mandatory Requirements and actions for the standard.

Structure of ISO 9001
The ISO 9001 Standard requires that your organisation address the 10 ISO 9001 clauses which are put in place to help achieve continual improvement within your Quality Management System (QMS). These clauses, supported by Quality Management principles, help your business implement an effective QMS. Let's explore them in details:
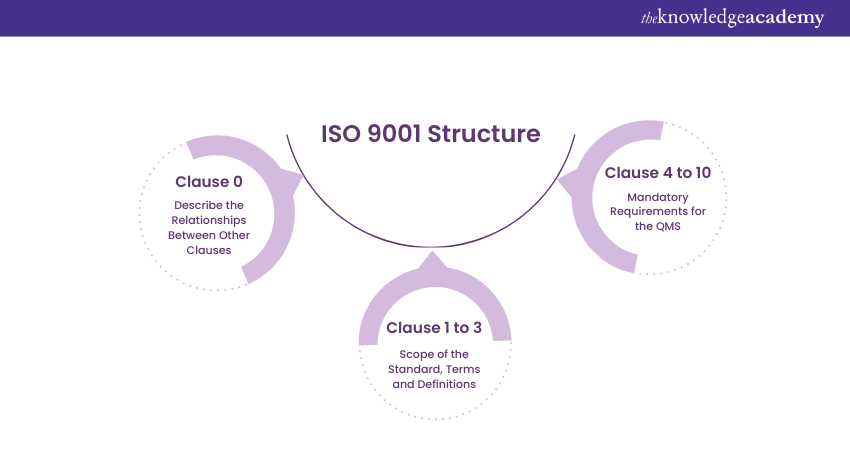
Clauses 0 – 3: Introduction, Scope, References, Terms and Definitions
Clauses numbered 0 to 3 of the ISO 9001 Standard offer foundational elements, setting the stage for the remaining ISO 9001 Requirements. While they are not mandatory for implementation, having a good grasp of them can help your organisation effectively use the standard. Here’s a breakdown:
a) Introduction (Clause 0): This clause delivers an overview of the Standard, its purpose, and the advantages of implementing a QMS. Additionally, it introduces key concepts, like the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle, the process approach, and risk-based thinking.
b) Scope (Clause 1): This clause outlines the scope of the ISO 9001 Standard by outlining what it covers and doesn’t cover.
c) References (Clause 2): This section outlines any normative references. These are external documents that ISO 9001 refers to for additional information.
d) Terms and Definitions (Clause 3): This clause highlights prominent terms used throughout the Standard to ensure clarity and consistent understanding.
Clause 4: Context of the Organisation
Clause 4 is where you set out your business's purpose and strategic direction regarding quality. It covers the following points:
a) Determining the internal and external factors as spotlighted by ISO 9001 Internal Audit that impact the quality of your services.
b) Identifying stakeholders in your business including suppliers, staff, and other interested parties.
c) Understanding customers and their needs.
Clause 5: Leadership and commitment
This section on Leadership Requirements and Commitments explains the Requirements of top management. These include the following:
a) Fostering an organisation-wide customer focus
b) Creating and upholding a quality policy that sets direction and alignment
c) Identifying responsibilities and authorities across the QMS to offer clarification regarding who has the decision-making authority and what's expected of the functions operating within the system.
Do you wish to unlock your organisation's potential? Grab the chance with ISO 9001 Certification Courses - register now!
Clause 6: Planning for the QMS
An effective QMS operates on risk-based thinking, putting measures in place to address risks and opportunities. As an important part of the ISO 9001 Clauses, clause 6 requires companies to:
a) Document potential risks, including their chance of occurrence and severity.
b) Plan for prevention or reduction of undesired effects.
c) Integrate plans for enhancing desirable effects.

Clause 7: Support and Resource Management
ISO 9001 Clause 7 states that your organisation offers adequate resources to operate an effective QMS. This includes providing resources for:
a) Robust infrastructure
b) Efficient working environments
c) Effective HR Management
Clause 8: Operational Planning and Control
Clause 8, or the operation section within ISO 9001:2015, describes a company's work developing and delivering goods or services to its customers. The ISO 9001 processes will set out:
a) The requirements and quality objectives of products or services.
b) The process guides, resources and documents employees need to successfully create products or services.
c) The monitoring, inspection or testing the company needs to ensure top quality of products and services.
d) The rules governing the development and storage of records.
Clause 9: Performance Evaluation
This section outlines the ISO Quality Standards for measuring customer satisfaction, internal audit, monitoring, analysis, and process performance as outlined in this section, align with the ISO 9001 Audit Checklist. The prerequisites for the management review, such as the inputs and outputs, are also mentioned.

Clause 10: Improvement Actions
The final ISO 9001 Clause focuses on the importance of continual improvement within a business. Clause 10 states that measures must be put in place to:
a) Improve products and services for the growth of the business.
b) Better match customer needs and improve customer satisfaction.
c) Identify instances of processes not achieving the goals and update them accordingly.
Want to become an expert in Internal Auditing? Join ISO 9001 Internal Auditor Training now!
What are the Six Mandatory Procedures for ISO 9001?
The six mandatory procedures for ISO 9001 are:
1) Control of Documents
2) Control of Records
3) Internal Audit
4) Control of Non-Conforming Products
5) Corrective Action
6) Preventive Action
How Much Does ISO 9001 Certification Cost?
The ISO 9001 certification cost depends on factors such as the complexity and size of the organisation. The cost of this certification, including accreditation and implementation, ranges from £3,000 to £6,000.
Conclusion
In conclusion, focusing on the ISO 9001 Requirements is your gateway to consistent quality, customer satisfaction, and business success. By understanding and implementing its key principles, such as Risk Management, process optimisation, strong leadership, and continuous improvement, you can set the stage for excellence. Remember, embracing ISO 9001 isn’t just about the certification; it’s about building a foundation for sustainable growth and long-term trust in your organisation.
Learn to incorporate and manage Quality Management Systems in our comprehensive ISO 9001 Lead Implementer Certification Course – Sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the Seven Principles of Quality Management?

The seven crucial principles of ISO 9001 guide organisations to maintain of effective Quality Management Systems. Those principles include engagement of people, customer focus, leadership, process approach, continual improvement, factual approach to decision-making and Relationship Management.
Who Needs to Comply with ISO 9001?

While ISO Certification can offer advantages to various industries, certain sectors particularly reap substantial benefits from obtaining ISO Certification. These sectors encompass Construction Management, Information Technology (IT), Hospitality, Healthcare, Manufacturing, Engineering firms, and Community Services.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are Related Courses And Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various ISO 9001 Certification Courses, including the ISO 9001 Foundation Course, ISO 9001 Lead Auditor Course, and ISO 9001 Internal Auditor Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into What is ISO.
Our ISO & Compliance Blogs cover a range of topics related to ISO 9001 Requirements, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your ISO 9001 knowledge base, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Business Improvement Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 ISO 9001 Foundation course
ISO 9001 Foundation course
Mon 17th Feb 2025
Mon 3rd Mar 2025
Mon 7th Apr 2025
Mon 12th May 2025
Mon 2nd Jun 2025
Mon 7th Jul 2025
Mon 4th Aug 2025
Mon 1st Sep 2025
Mon 20th Oct 2025
Mon 10th Nov 2025
Mon 1st Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


