We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +30 2111995372 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Business Resilience in this ever-shifting society becomes key to adapting to ever looming risks around the corner. It’s not about getting to the storm and huddling until it passes, no, it is being keen enough to enjoy the rain. Whether the situation is caused by business cycles, new technologies, or other unplanned occurrences, organisations that demonstrate Business Resilience can respond tactfully, rebound effectively, and come out of the process as future-green field organisations.
To call this strategy is actually putting it mildly—it’s the science of how to survive against all the odds. In simplest terms, Business Resilience is the capacity of transforming threats into opportunities. It allows organisations to remain flexible, continue operation, and promote trust from all the stakeholders. It is not only a defense mechanism against all odds.
Table of Contents
1) What is Business Resilience?
2) Why Business Resilience?
3) The Seven Pillars of Resilience
4) Importance of Business Resilience
5) Inclusion in a Business Resilience Plan
6) Guidelines and Standards for Business Resilience
7) Differences Between Business Resilience and Business Continuity
8) Strategies for Building Business Resilience
9) Conclusion
What is Business Resilience?
Business Resilience then can be defined as the capacity of an organisation to withstand and continually overcome adversity in scenarios such as downturns, physical disasters, or system breakdowns. It embodies a mix of planning in advance, risk mitigation, and contingency in order to facilitate unhampered key processes.
Through an analysis of risk profiles, it becomes possible to develop viable risk management solutions to help organisations sustain their operations, make good on promised results, and remain viable despite a volatile economy. These are highlighted beyond mere coping mechanisms to the proactivity to turn infirmity into strength.
Why Business Resilience?
Here are some key pointers that will help to understand why it is important and why there is a need of Business Resilience:
a) Crisis Preparedness: Supports organisations in absorbing moments like pandemics or economic crises.
b) Customer and Stakeholder Trust: Establishes reliability and thus builds a better working relationship between the firm and its stakeholders.
c) Competitive Advantage: Increasing adaptability makes it easier for resilient companies to leverage change, thereby placing them in a better spot.
d) Financial Stability: Maintains the company’s property and guarantees an unperturbed cash stream in the period of industry fluctuations.
e) Regulatory Compliance: Thus, supports compliance to industry standards and laws and regulations with regard to risk and continuity management.
The Seven Pillars of Resilience
As a result, leaders and employees should address seven pillars of resilience, a model that has gained popularity of Ursula Neuber. The seven pillars are:
a) Optimism: Crisis management is rooted in the assumption that the difficulties we face at any given time are unique only for a transitory period. These include the existence of luck as a factor in influencing events.
b) Acceptance: These above concerns call for a premise that it is first imperative to acknowledge challenges as an important pre-requisite to overcome them. Only those who have the full perspective of the problems that must be solved can advance to the next issues in strategic planning.
c) Solution Orientation: Adaptive businesses remain fit and can respond correctly and promptly in a crisis and seek out solutions.
d) Leaving the Role of Victim: Hence, it is crucial to pay much attention to the strengths and weaknesses found in the process and define directions for improvement in the future.
e) Taking Responsibility: The four facets of resilience define the ability to take personal responsibilities for one’s choices and outcomes.
f) Network Orientation: For handling challenges it is crucial to have a stable network.
g) Future Planning: In this context, risk management enables organisations to either prevent or else prepare for contingencies when adverse occurrences occur.
Enhance your Emotional Intelligence with our Emotional Intelligence Training – Sign up today!
Importance of Business Resilience
From protecting core values to reducing risks, Business Resilience is crucial for many reasons. Let's explore some of them below:
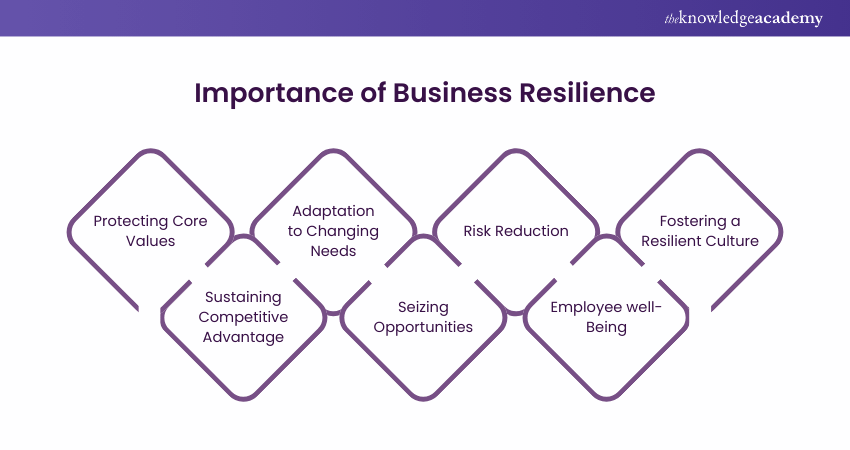
1) Protecting Core Values: It helps an organisation to protect its core values, vision, and mission. By maintaining these principles even during times of crisis, a business can uphold its identity and remain true to its founding principles.
2) Sustaining Competitive Advantage: Business Resilience allows an organisation to maintain its competitive gain and market share. While competitors may falter during disruptions, resilient businesses can continue to serve their customers, retaining their market position.
3) Adaptation to Changing Needs: It enables an organisation to react swiftly and effectively to changing customer needs and expectations. Resilient companies can pivot their strategies and offerings to meet evolving customer demands, ensuring long-term customer satisfaction.
4) Seizing Opportunities: Resilience equips organisations to seize new opportunities and create value, even in the face of adversity. By being agile and adaptable, businesses can identify and capitalise on emerging trends and markets.
5) Risk Reduction: It reduces the risk of various negative outcomes, including financial losses, legal liabilities, operational failures, reputational damage, and the loss of trust and confidence among customers, partners, and stakeholders.
6) Employee Well-being: Business Resilience enhances employees' morale, motivation, and productivity. Employees who feel secure in their workplace are likelier to contribute their best efforts and remain committed to the organisation's success.
7) Fostering a Resilient Culture: Resilience promotes a culture of collaboration, creativity, and resilience within an organisation. Employees who are trained in resilience practices can work together effectively to navigate challenges and find innovative solutions.
Master Sentiment Analysis techniques with our Sentiment Analysis Training – Sign up now!
Inclusions in a Business Resilience Plan
A Business Resilience plan is a document that outlines the strategies, actions, and resources that an organisation will use to achieve its Business Resilience objectives. A Business Resilience plan should include the following elements:
1) Business Impact Analysis (BIA): This involves identifying the organisation's critical functions, processes, and resources and assessing the potential threats and impacts that could affect them. The BIA provides insights into what parts of the business are most vulnerable during disruptions.
2) Risk Assessment: It evaluates the likelihood and severity of the identified threats and impacts, prioritising them based on their potential effect on the organisation's objectives. This helps organisations allocate resources to address the most significant risks first.
3) Risk Mitigation Strategy: This strategy defines the measures and controls that will be put in place to prevent, reduce, or transfer risks. It outlines the proactive steps an organisation will take to minimise the impact of potential disruptions.
4) Business Continuity Plan (BCP): The BCP specifies the procedures and arrangements that will be activated to ensure the continuity of critical functions and processes in the event of a disruption. It outlines the immediate actions to be taken to maintain essential operations.
5) Crisis Management Plan (CMP): This plan outlines communication and escalation protocols to follow during a crisis. It also specifies the roles and responsibilities of the Crisis Management team. Moreover, it ensures a coordinated response when faced with unexpected events.
6) Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP): The DRP details the steps and resources that will be utilised to restore the organisation's normal operations after a disruption. It focuses on recovery efforts to get the business back on track.
7) Testing and Review Schedule: This schedule defines the frequency and methods for testing and reviewing the Business Resilience plan. It outlines the process for updating and improving the plan using the feedback and lessons learned from simulations and real-life incidents.
These components together form a comprehensive Business Resilience plan that prepares organisations to face and overcome disruptions effectively.
Guidelines and Standards for Ensuring Business Resilience
In the pursuit of Business Resilience, organisations often turn to established guidelines and standards that serve as beacons of best practices. These guidelines and standards provide organisations with valuable frameworks and best practices to enhance their Business Resilience. Let's explore some of them below:
1) ISO 22301:2019: This standard outlines the requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and improving a Business Continuity Management System (BCMS). It offers a framework for organisations to enhance their resilience against disruptions.
2) ASIS SPC.1-2009: It is a standard published by ASIS International that provides guidelines for developing and implementing a risk assessment and management program. It focuses on finding and mitigating security risks to protect assets and operations.
3) ISO 27001:2013: ISO 27001 sets forth the requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and improving an Information Security Management System (ISMS). A robust ISMS helps protect critical information assets, contributing to overall Business Resilience.
4) ISO 22316:2017: It is an international standard that offers guidance on organisational resilience. It provides principles and a framework for enhancing an organisation's ability to anticipate, respond to, and recover from disruptions, whether related to security, operational, or other risks.
Difference Between Business Resilience & Business Continuity
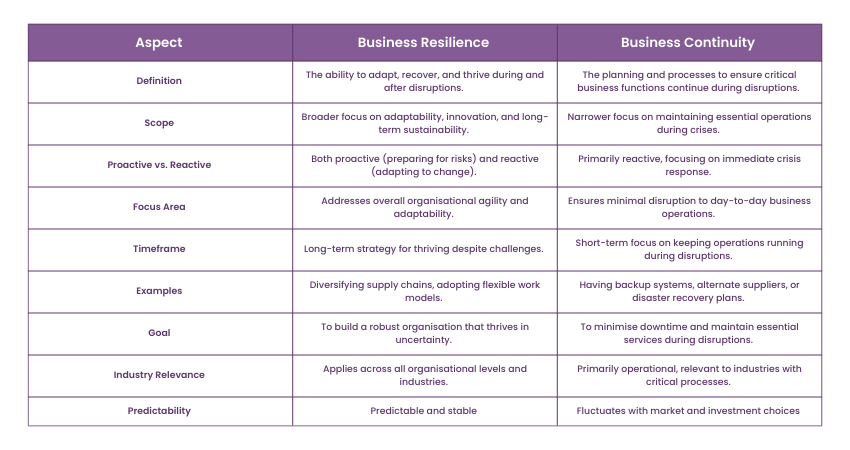
Business Resilience and Business Continuity are related but distinct concepts. Business Continuity is a subset of Business Resilience. It focuses on ensuring the continuity of an organisation's critical functions and processes during a disruption. Business Resilience, on the other hand, is a broader concept. It entails adapting to change, recovering from disruptions, and ensuring uninterrupted delivery of products and services to stakeholders.
Strategies for Building Business Resilience
Following are the key pointers for the Strategies for Building Business Resilience:
a) Develop a Risk Management Framework: Find out possible risks, determine their consequences, and define how to minimise threats.
b) Foster a Resilient Organisational Culture: Promote flexibility, creativity and teamwork of the employees to ensure that an organisation is ready to tackle problems.
c) Invest in Technology and Digital Transformation: Opt for reasonably adaptable facilities like cloud systems that would enable a business to maintain the smooth running of operations in the face of technical challenges.
d) Diversify Supply Chains: Minimise supply dependence on a single supplier by developing other supplying companies and collaboration for uninterrupted business operations during emergence of hitches.
e) Enhance Financial Resilience: Create, strengthen, and develop operational capital structures, periodically prevent unnecessary wastages on operational activities, and diversify the sources of revenue in order to avoid the outsiders’ volatility factors affecting the business.
f) Strengthen Leadership and Decision-making: Teach leaders on how to make decisions very fast and ensure staff during emergencies.
g) Establish Business Continuity Plans (BCP): Develop and review schedules to guarantee key processes can keep going in the event of disruptions.
Conclusion
We hope you read and understand everything about Business Resilience and its importance. In today's unpredictable business landscape, Business Resilience is not just a luxury; it's a necessity. Organisations can minimise downtime, protect their reputation, and ensure long-term sustainability by anticipating, preparing for, and adapting to disruptions.
Learn how to thrive in the face of challenges with our Resilience Training – Sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions

A Business Resilience Plan may have elements which include risk evaluation to spot weaknesses, a sound crisis management plan, effective communication procedures, business continuity plans, and regular tests and training of employees. These enable fast responses or recovery during any disruption.

Business Resilience is beneficial for organisations of all sizes. While the specific strategies and resources may vary, small businesses can also benefit by identifying risks, developing plans, and building the capacity to withstand disruptions. This will help them thrive in the face of adversity.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. By tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Personal Development Courses, including Resilience, Emotional Intelligence, and many more. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Business Skills methodologies.
Our Business Skills blogs cover a range of topics related to Resilience, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Business Skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Resilience Training
Resilience Training
Fri 28th Feb 2025
Fri 4th Apr 2025
Fri 27th Jun 2025
Fri 29th Aug 2025
Fri 24th Oct 2025
Fri 5th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


