We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +30 2111995372 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Psychology is a branch of science that takes a scientific approach to understanding human thought, behaviour, development, and personality. By learning Psychology, you can understand the behaviour of people, which will make it easy for you to collaborate with them in the workplace and also in personal life. Further, people eager to study and build a career in Psychology will find the salient Features of Science in Psychology very useful. These features will give you a basic understanding of Psychology and how it benefits society.
Psychology helps you understand why people react to certain situations in a particular way. Hence understanding the features will help you tailor your approach to different people when interacting with them on a day-to-day basis. Furthermore, read this blog to learn the various Features of Science in Psychology, namely Systematic Empiricism, Empirical Questions, and Public Knowledge.
Table of Contents
1) A Brief History of Psychology
2) What are the different types of Psychology?
3) Features of Science in Psychology
4) How can Psychology be approached through a scientific process?
5) Conclusion
A Brief History of Psychology
Wilhelm Wundt and William James are known as the founding fathers of Psychology. The first person to be referred to as a "psychologist" was Wilhelm Wundt (1832–1920). He was one of the first people who considered psychology a branch of science and believed in approaching the subject with scientific principles. However, due to a lack of sufficient scientific data, the idea of structuralism by Wundt fell through. William James (1842–1910) was among the first to test Darwin’s theory of Natural Selection, and he tried to uncover what goes on in people's minds.
When talking about Psychology, Sigmund Freud is an indispensable part of history. His principles and theories are both loved and hated by people in the Psychology community. Freud was obsessed with the unconscious mind and how it affects the emotions of patients suffering from hysteria and neurosis. He tried to access the unconscious mind through dream analysis, which is still a research topic to date.
The next addition to this branch was made by Max Wertheimer (1880–1943), Kurt Kofka (1886–1941), and Wolfgang Kohler (1887–1967), who introduced Gesalt principles. In addition to these principles, Pavlov, and Skinner added the theory of behaviourism as another part of Psychology. To continue these new world discoveries, Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs greatly impacted this modern scientific approach. Carl Rogers (1902–1987), with his new psychotherapy, or client-centred therapy, made great ripples which, to date, courses through this branch of science. We have listed some pioneers without whom, the study of Psychology would be incomplete.

Gain expert knowledge with our comprehensive course on Psychological Skills Training For Human Wellness Training.
What are the different types of Psychology?
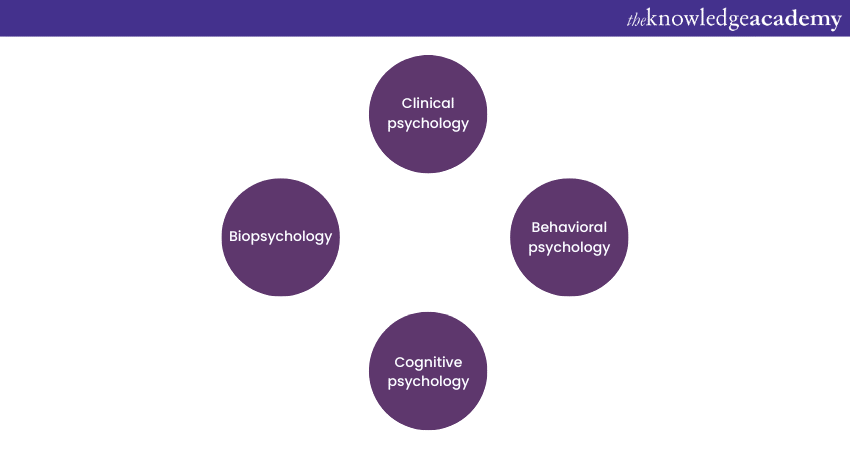
There are mostly four different Types of Psychology:
1) Clinical Psychology: This refers to counselling and therapeutic services provided for the mental health of individuals. This area of psychology deals with discovering, diagnosing, and treating mental illnesses such as eating disorders, depression, trauma, or phobias.
2) Behavioural Psychology: This area of psychology studies why people think and act upon those thoughts. Generally, this branch of Psychology is studied based on classical and instrumental conditioning. In classical conditioning, a neutral stimulus is paired with an existing natural stimulus, and the subjects' behaviour is studied. Whereas, in instrumental conditioning, the subject's behaviour is studied by implementing a desirable (reward) or undesirable (punishment) response.
3) Cognitive Psychology: This branch of Psychology helps people understand their behaviours, perception, attention, thinking, memory, and consciousness to overcome several disorders such as anxiety, depression, personality disorders, etc.
4) Biopsychology: The study of this branch helps to understand human behaviours from a biological point of view. This branch of psychology is often used to understand the human brain and evolution in general. Biopsychology is also used to understand non-mammals functioning by observing their sensory processes, memory, learning, excitement, and cognitive behaviours.
Here are some more types of Psychology for your reference:
Gain expertise in understanding various personalities with our Introduction to Psychology of Personality Course.
Features of Science in Psychology
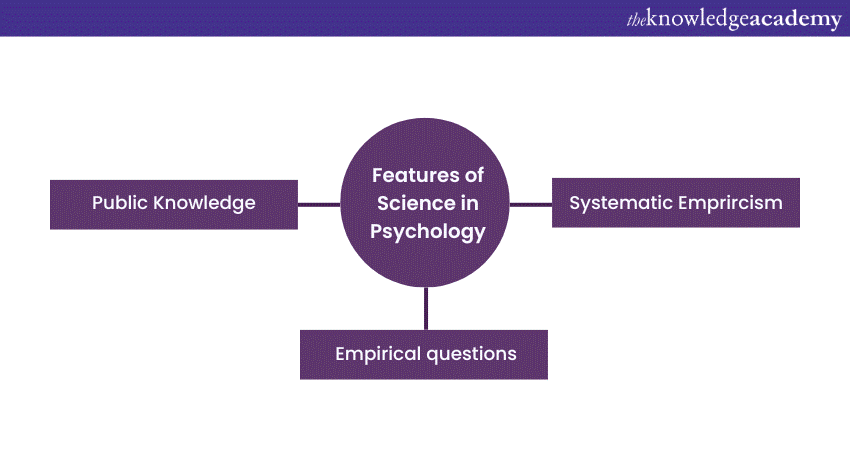
To understand the Salient Features of Science in Psychology, let’s look at some of these points:
1) Systematic empiricism: Systematic empiricism means emphasising the importance of using objective and measurable evidence to investigate psychological phenomena. This also involves meticulously observing and measuring variables in a controlled manner that can be replicated. Researchers employ some rigorous methodologies, ensuring that their studies are reliable and valid, minimising bias and subjectivity.
Systematic Empiricism is evident in all kinds of experimental designs, observational studies, and psychometric assessments. Through controlled experiments, psychologists manipulate independent variables to observe their effects on dependent variables, which leads them to establish casual relationships. These empirical data are collected and analysed to draw objective conclusions, which helps scientists to understand human behaviour.
Systematic Empiricism helps to minimise subjective biases and personal interpretations. This ensures that psychological research is grounded only in objective observations and measurements. The research then becomes credible and trustworthy.
2) Empirical question: Empirical questions are based on observable phenomena. It drives the acquisition of new knowledge in psychology. These questions are answerable through systematic observation and data collection. This helps the researchers by guiding them towards unravelling the complexities in human behaviour.
The researchers develop testable hypotheses, which in turn can be empirically tested using systematic observation, experimentation, or data analysis. One of the two ways this research is done is through quantitative research. This involves collecting and analysing numerical data, enabling statistical inference and generalisations.
In this second way, the qualitative research the researchers employ helps capture the rich and contextualised data through interviews, focus groups, and case studies. Formulating these Empirical Questions that address real-world problems or challenges helps psychologists comprehensively understand human behaviour. They then make informed decisions based on reliable data rather than relying on assumptions, anecdotal evidence, or personal beliefs.
3) Public Knowledge: After any scientific discovery, scientists publish their journals, which are accessible to both scientists and non-scientists. They publish these journals to let the public know of their discoveries. These journals are then studied and discussed on a much broader scale by various scientists and the public.
This Public Knowledge in Psychology ensures transparency and accountability in this advancing field. This process of publication of scientific journals opens the collective accumulation of knowledge upon the existing theories and frameworks. Public Knowledge also enables the application of psychological principles in various domains, such as education, mental health, and organisational settings. This also helps in conducting evidence best practices for the betterment of society.
We have listed the Features of Science in Psychology, for you. Let’s have a look:

How can Psychology be approached through a scientific process?
As Psychology is a branch of science, it also requires data and research to derive results from the experiments done on subjects. There are various ways in which Psychology can be approached through scientific processes. They are:
1) Case Study: There are several scenarios where an observation is recorded to interpret the data from that study. Psychoanalysts sometimes use this data to draw a conclusion or make an observation that helps them in their research.
2) Analysing Content: There are many articles, interviews, journals, and research materials alike that scientists use to analyse previous data. This helps them draw conceptual and relational conclusions from their projects on relevant topics.
3) Conducting a survey: Surveys are a great way to predict mass behaviour or opinions. Scientists often use this method to draw relevant observations and conclusions for their research. For example, numerous surveys are conducted asking people about their mental health. This helps the scientists know the ratio of the number of people with good mental health to the number of people struggling with their mental health.
Here are some ways where you can approach Psychology in a scientific manner:

Enhance the workplace environment of your organisation with our Workplace Stress and Mental Health Identification for Manager Course.
Conclusion
Understanding the Features of Science in Psychology makes it easy to discover and analyse people's mental wellness. Through conducting thorough research and cross-referencing previously published journals, it becomes easy for psychoanalysts and researchers alike to build meaningful analyses for future reference.
Want to learn more about Psychology? Register for our Psychology Masterclass Today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Health & Safety Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Psychology Course
Psychology Course
Fri 6th Dec 2024
Fri 14th Feb 2025
Fri 11th Apr 2025
Fri 13th Jun 2025
Fri 15th Aug 2025
Fri 10th Oct 2025
Fri 12th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


