We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +30 2111995372 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Two critical performance measurements in Project Management are the schedule baseline, which evaluates project duration, and the cost baseline, which assesses cost performance. Clients prioritise the schedule as it directly impacts project delays and business outcomes. This is the reason why project managers use tools like the PERT Estimation Technique, PERT Charts, CPM diagrams, and Gantt charts to develop precise programs.
Creating a schedule is complex work that demands expertise in schedule network diagram techniques and practical experience. In this blog, we will understand how PERT Estimation Technique helps people figure out how long different tasks in a project might take.
Table of contents
1) Introduction to PERT Estimation Technique
2) Understanding the basics of PERT
3) The three-point Estimation method
4) Creating a PERT analysis
5) Benefits of using PERT Estimation
6) Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
7) Conclusion
Introduction to PERT Estimation Technique
Before starting any project-related activities, it is crucial to have a well-founded and accurate time estimate in place. Without such an estimate, projects risk running over budget and missing their intended completion dates. Estimating the time required for a project is an intricate task, mainly when dealing with large-scale projects involving numerous stakeholders. Therefore, various methods have been designed to improve the accuracy of project estimation.
Among these methods, PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) has emerged as a successful and proven approach. PERT stands out among a multitude of other techniques, including CPM, Function Point Counting, Top-Down Estimating, WAVE, and more.
The genesis of PERT dates back to the late 1950s when the U.S. Navy initially developed it for a pioneering project involving the development of Ballistic Missiles. This experience engaged thousands of contractors. As a testament to its efficacy, the implementation of PERT led to the project's completion two years ahead of its original schedule.
Understanding the basics of PERT
At its core, PERT revolves around managing probabilities, making it heavily dependent on various statistical methods. While some may tend to put PERT and CPM (Critical Path Method) together, it's important to note that although they share specific characteristics, PERT maintains a distinct focus.
Like many other estimation techniques, PERT begins by breaking down tasks into detailed activities. These activities are then demonstrated in a Gantt Chart to showcase their interdependencies. Later, a network of activities and their interrelationships is displayed in a visually informative manner.
Within this network, each event is represented by a node, and the activities are denoted as arrows, connecting events based on their sequence. The next step involves determining both the Earliest Time (TE) and the Latest Time (TL) for each activity and identifying the careless time associated with each.
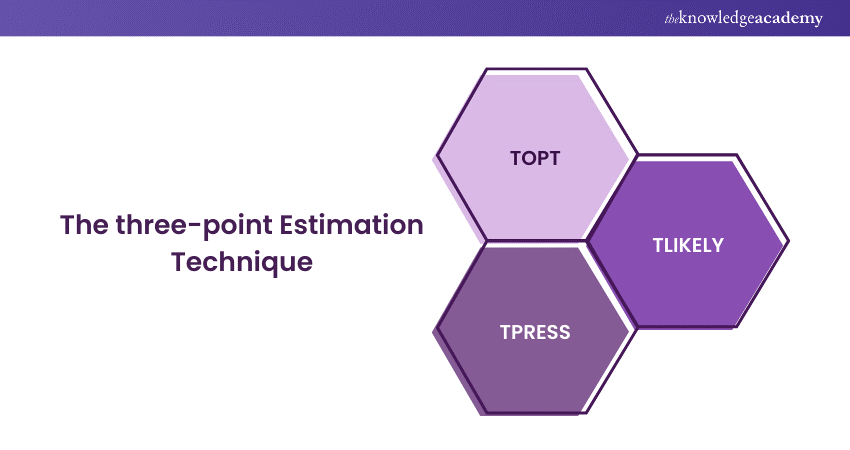
The three-point Estimation method
In PERT, the estimation process involves three distinct time estimates: Optimistic Time Estimate (TOPT), Most Likely Time Estimate (TLIKELY), and Pessimistic Time Estimate (TPESS).
For each activity in a PERT analysis, these three estimated times are calculated, resulting in a time range for each activity, with TLIKELY representing the most probable value.
Here's a closer look at each of these estimates:
a) TOPT: TOPT represents the shortest possible time required to complete an activity. It assumes ideal conditions, where all necessary resources are readily available, and all prior activities occur without delays.
b) TLIKELY: Often, project managers are required to provide a single estimate. In such cases, TLIKELY is the estimate submitted to upper management. It represents the most likely and realistic time frame for completing the activity.
c) TPESS: TPESS estimate represents the maximum time necessary to complete an activity. It assumes that a variety of factors may go wrong during the activity, including rework, resource unavailability, and other potential setbacks.
Elevate your project management skills today with our Project Management Courses - Explore now!
Creating a PERT analysis
The PERT formula, which is used to calculate the PERT estimate, is defined as follows:
PERT Estimate = (Tp + 4Tm + To) / 6
Additionally, the Standard Deviation (SD) is calculated as:
SD = (Tp – To) / 6
The Variance, which is the square of the Standard Deviation, can also be computed using this value.
Let's break down these components:
a) Most Likely Estimate (Tm): This represents the duration with the highest probability of completing an activity.
b) Optimistic Estimate (To): This is the best-case scenario, considering ideal conditions and the shortest possible duration for task completion.
c) Pessimistic Estimate (Tp): This is the worst-case scenario, factoring in unfavourable conditions and the longest potential duration for task completion.
The PERT estimate method reduces uncertainties around the duration estimate by providing a range of possibilities. It's a practical approach, especially when meeting project deadlines is crucial.
By considering various scenarios, PERT offers a more robust estimate. For example, if a project manager estimates a task will take two days without considering pessimistic scenarios, unexpected events like heavy rainfall could lead to a day's delay in the project. PERT, with its range of scenarios, allows intelligent decision-making:
Identifying potential sources of pessimism.
Exploring ways to improve optimistic scenarios.
Implementing measures to reduce the likelihood of pessimistic durations.
PERT serves as a valuable Project Planning Software Tool for estimating project completion times. It also finds utility in risk analysis, utilising its three estimates. Additionally, it enables Monte Carlo simulations, which generate statistical analyses regarding the likelihood of completing a project within budget and on schedule.
In essence, PERT offers a quantitative approach to address uncertainties and risks, making it a versatile asset in Project Management.
Benefits of using PERT Estimation
Now that we understand PERT formula, let us understand a few benefits it offers:
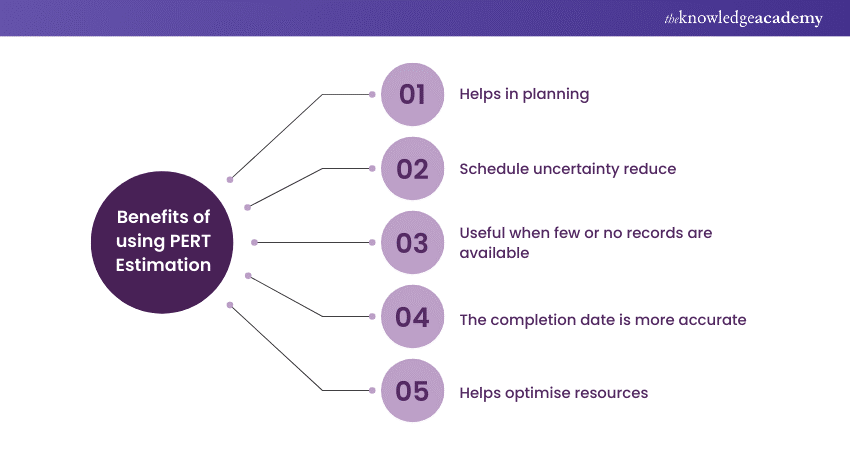
a) Help in planning: PERT assists project managers in developing a well-structured project plan by breaking down complex tasks into manageable activities. This careful planning allows for a clear roadmap to project success and ensures that each step is well-defined and achievable. It also assists in setting realistic milestones and deadlines while helping teams stay on track. This ensures that project goals are met efficiently.
b) Schedule uncertainty reduce: PERT's blend of optimistic, most likely, and pessimistic time estimates significantly reduces the uncertainty associated with project schedules. By considering a range of scenarios, it accounts for potential delays and setbacks. This reduction in schedule uncertainty is invaluable in managing client expectations and maintaining stakeholder confidence, as it provides a more accurate representation of the project's expected timeline.
c) Useful when few or no records are available: In cases where historical data or prior project records are scarce or unavailable, PERT remains a viable option. By relying on expert judgment and a thorough analysis of task dependencies, it can provide reliable estimates even in data-deficient situations. Its support of three distinct estimates (optimistic, most likely, and pessimistic) ensures that the project schedule is grounded in a comprehensive understanding of potential timeframes.
d) The completion date is more accurate: PERT's three-point estimation method results in a more precise completion date. By including both the best and worst-case scenarios, it offers a balanced estimate that considers a full range of potential outcomes. This improved accuracy in determining project completion dates helps in better resource allocation, budget planning, and overall project management.
e) Helps optimise resources: PERT's ability to identify the critical path, along with the Expected Time (TE) for each activity, allows project managers to allocate resources efficiently. By focusing efforts and resources on necessary activities, productivity is maximised. This optimisation of resources not only improves project efficiency but also reduces unnecessary costs, making PERT an essential tool for resource management.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
To understand PERT better, let's focus on some important factors that impact its application in project management.
a) Subjective analysis and estimations: Subjective estimates in PERT can skew schedules and outcomes, and accuracy depends on the experience and impartiality of the estimator.
b) Critical path management challenges: Managing the critical path can be challenging with PERT due to changing project dynamics. Continuous monitoring and adaptation are necessary to cope with evolving conditions.
c) Optimistic assumptions: PERT's optimism assumes resource availability and uninterrupted activity flow. Real-world conditions can often differ from these assumptions, necessitating proactive adaptation by project managers.
d) Updating and maintenance challenges: Keeping the PERT diagram up-to-date is time-consuming, but crucial. Neglecting updates can result in being disconnected from project realities, leading to uninformed decisions. Regular maintenance is necessary.
Take the first step towards mastering project management with our Introduction To Project Management Certification Course - Register Now!
Conclusion
PERT is known for its ability to incorporate time estimation uncertainties. By analysing a range of assumptions that could speed up or slow down project progress, PERT Estimation Technique provides project managers with valuable insights into potential delivery time variations. This enables managers to offer their clients more accurate delivery dates, making the project more reliable.
Unlock the power of Project Management with our Project Management Office Fundamentals Certification Course– Sign up for success!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Project Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Introduction to Project Management Course
Introduction to Project Management Course
Thu 1st Jan 1970







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


