We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +30 2111995372 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

As projects become more complex and dynamic, the need for effective Risk Management in Project Management becomes increasingly vital. Risk Management involves systematically identifying, assessing, and addressing potential risks that could impact project objectives.
It helps Project Managers to minimise disruptions, optimise decision-making, and improved project success rates. So, why lag behind in the race to effectively manage your projects? Incorporate Risk Management in Project Management and deliver the best services!.
Not sure how you would do that? What is Management of Risk? How is it helpful in Project Management? Read this blog to explore the importance of Risk Management in Project Management. Also, learn to identify, assess, and mitigate risks to ensure project success.
Table of Contents
1) What is Risk Management in Project Managment?
2) Why do organisations need to manage risks?
3) What are the different types of project risks?
4) How to manage project risks?
5) Tools for managing risks
6) Conclusion
What is Risk Management in Project Management?
Risk Management in Project Management refers to the systematic approach of identifying, assessing, and responding to risks that may affect the successful completion of a project. In simple terms, it involves the identification of potential threats and opportunities, evaluating their potential impact on project objectives, and developing strategies to mitigate them.
Further, Risk Management provides a structured framework for evaluating and addressing risks, ensuring that projects are delivered within time, cost, and quality constraints.
The goal of this technique is to proactively manage uncertainities and minimise the negative impact of risks while maximising opportunities for project success. As a result, the technique assists the Project Managers in achieving the following:
1) Anticipating potential obstacles
2) Making informed decisions
3) Allocating resources efficiently
4) Enhancing overall project outcomes

Why do organisations need to manage risks?
Organisations involved in Project Management require managing risks for several important reasons. Let’s explore why Risk Management is crucial in the project management context.
a) Minimise project disruptions: Risks can disrupt project activities, leading to delays, cost overruns, and even project failure. By implementing Risk Management practices, organisations can identify potential threats early on and develop strategies to mitigate or address them proactively.
b) Optimise resource allocation: Risks can impact the allocation of resources, including time, budget, and personnel. By managing risks, organisations can identify potential resource constraints and make necessary adjustments to ensure optimal resource allocation.
c) Enhance stakeholder confidence: Clients, investors, and sponsors are vested in project success. By demonstrating effective Risk Management practices, organisations instil confidence in stakeholders that potential risks are being managed proactively.
d) Improve decision-making: Risk Management provides valuable insights that inform decision-making processes. By assessing and analysing risks, Project Managers gain a deeper understanding of potential uncertainties and their potential impacts.
e) Comply with regulatory and legal requirements: Many projects are subject to regulatory and legal requirements specific to their industry or location. Failure to manage risks effectively can lead to non-compliance, resulting in legal issues, fines, and reputational damage. By implementing Risk Management processes, organisations can demonstrate their commitment to compliance and mitigate potential legal and regulatory risks.
f) Ensure project success: Managing risks increases the chances of project success. This includes developing contingency plans, allocating resources effectively, and making informed decisions based on risk assessments. Therefore, it enhances project outcomes and increases the likelihood of achieving project goals.
What are the different types of project risks?
In Project Management, various types of risks can potentially impact project objectives and outcomes. Understanding the different types of project risks is essential for effective Risk Management. So, let's learn about some common types of project risks:
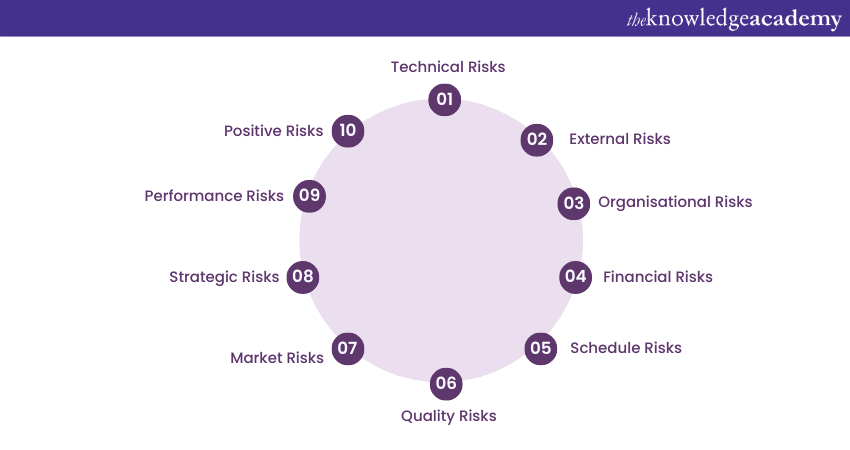
a) Technical Risks: These risks relate to the technical aspects of a project, such as the complexity of the technology or tools used, potential system failures, or compatibility issues. Technical risks can arise from inadequate technical expertise, insufficient resources, or technological changes during the project’s lifecycle.
b) External Risks: External risks are beyond the control of the project team and arise from external factors such as economic conditions, political instability, legal and regulatory changes, market trends, or natural disasters. These risks can significantly impact project schedules, costs, and resources.
c) Organisational Risks: These stem from internal factors within the organisation. This includes poor Project Management practices, inadequate project governance, lack of stakeholder support, inadequate communication, or resource constraints.
d) Financial Risks: Financial risks involve the potential for cost overruns, budget constraints, currency fluctuations, or funding uncertainties. Changes in financial markets, unexpected expenses, or inaccurate cost estimations can pose significant financial risks to projects.
e) Schedule Risks: Schedule risks pertain to potential delays or disruptions in project timelines. Factors such as dependencies, resource availability, scope changes, or unforeseen events can impact project schedules and deadlines.
f) Quality Risks: Quality risks involve the potential for defects, errors, or subpar quality in project deliverables. Insufficient quality control measures, inadequate testing, or poor adherence to quality standards can lead to customer dissatisfaction, rework, and project setbacks.
g) Market Risks: Market risks relate to changes in market demand, competition, or customer preferences. Factors such as shifts in consumer behaviour, market saturation, or introduction of new technologies can impact project viability and success.
g) Strategic Risks: Strategic risks are associated with the alignment of projects with the overall strategic objectives of the organisation. These risks may include ineffective project prioritisation.
h) Performance Risks: These relate to the potential for projects to fall short of performance expectations. These risks may include issues with choosing the right methodology, efficiency, or meeting project timelines.
i) Positive Risks (Opportunities): Not all risks are negative; there are also positive risks. These risks arise from favourable events or circumstances that enhance project outcomes or create additional benefits.
Become a skilled Risk Management Professional and give a boost to your career with our MoR® Management of Risk training.
How to manage project risks?
Risk Management in Project Management is based on several key concepts that provide the foundation for effective practices. Understanding these concepts is essential for Project Managers to navigate the complexities of Risk Management. The following are the key concepts of Risk Management:
1) Risk identification
Identifying risks involves systematically identifying potential risks that may affect the project. This includes identifying both internal and external risks that could impact project objectives.
The team uses various techniques such as brainstorming, checklists, historical data analysis, and expert judgment to identify risks.
2) Risk assessment
Risk assessment means evaluating the identified risks in terms of their possibility of occurrence and potential impact on project objectives. Risks are particularly assessed based on their probability, severity, and detectability. This assessment helps Project Managers prioritise risks and allocate appropriate resources for risk mitigation.
3) Risk analysis
While analysing the risks, the team or Project Managers often indulge in a detailed examination of identified risks. This is particularly done to understand their root causes, potential consequences, and interdependencies.
Therefore, this analysis helps Project Managers gain a deeper insight into the nature and characteristics of risks, enabling them to develop effective risk response strategies.
4) Risk response
Risk response involves developing strategies to address identified risks. There are four main risk response strategies:
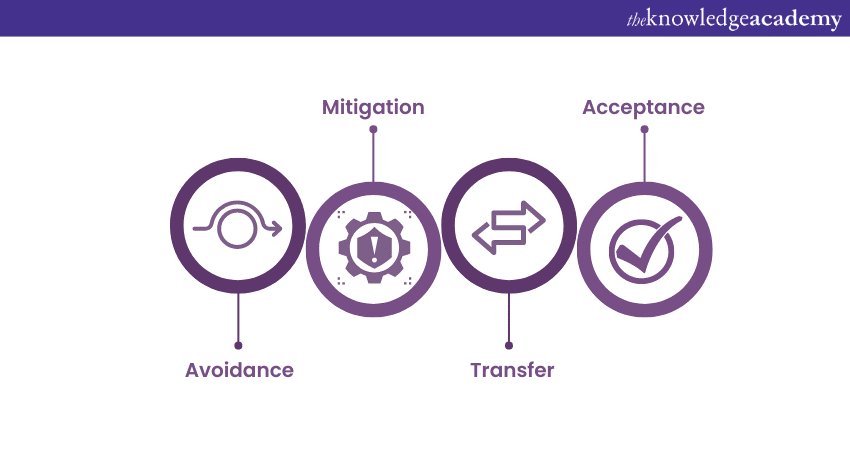
a) Avoidance: Taking actions to eliminate or avoid the risk altogether. This may involve changing project plans, resources, or approaches to eliminate the risk.
b) Mitigation: Implementing measures to reduce the likelihood or impact of the risk. This may include developing contingency plans, conducting additional testing, or enhancing project controls.
c) Transfer: Shifting the risk to another party, such as through insurance, outsourcing, or contract agreements.
d) Acceptance: Acknowledging the risk without taking any specific action. This strategy is typically used for risks with low likelihood or low impact.
5) Risk monitoring and control
Risk monitoring and control include continuously tracking identified risks, assessing their effectiveness, and adjusting as necessary. It means that the Project Team implements risk mitigation measures, monitors risk indicators, and reviews Risk Management plans.
Build a solid foundation in effective Risk Management practices with our Management Of Risk (MoR®) Foundation course.
Tools for managing risks
Effective Risk Management is crucial to Project Management. But how can organisations do that? Well, they require various tools and techniques. These tools provide valuable support in managing risks throughout the project lifecycle. Here are some commonly used tools for managing risks in Project Management:
a) Risk register: This tool is a central repository that captures and documents all identified risks, their likelihood, impact, and assigned owners. It provides a dynamic overview of the project risks.
b) Probability and impact matrix: It is a visual tool that helps assess risks based on their probability of occurrence and potential impact on project objectives. It allows Project Managers to prioritise risks and determine appropriate risk response strategies.
c) SWOT analysis: SWOT analysis is another technique used to examine the strength, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats associated with a project. It helps identify potential risks and opportunities by assessing internal and external factors that may impact the project.
d) Risk assessment workshops: These workshops bring together project stakeholders to identify, assess, and analyse risks. They include brainstorming sessions, knowledge sharing, and consensus building, leading to a more comprehensive understanding of project risks.
e) Risk data quality assessment: This tool assesses the quality and reliability of data used in Risk Management processes. It ensures that risk information is accurate, up-to-date, and sufficiently detailed to support informed decision-making.
f) Monte Carlo analysis: Monte Carlo analysis is a simulation technique used to model and analyse the impact of uncertainities and risks. It provides probabilistic forecasts by running multiple iterations based on probability distributions of input variables.
g) Decision trees: This tool helps in evaluating and visualising the potential outcomes of different decisions and their associated risks. They assist Project Managers in making informed decisions by considering the risks, probabilities, and expected values of each decision path.
h) Risk response planning: Risk response planning means developing strategies to address identified risks. This includes creating contingency plans, defining risk mitigation measures, setting up fallback options, and establishing risk monitoring mechanisms.
i) Risk reporting: It involves regular communication of risk-related information to project stakeholders. The project Manager summarises risk status, provides updates on risk response actions, and highlights emerging risks.
j) Lessons learned repository: This repository captures insights and experiences from previous projects. It is valuable for identifying and addressing risks by drawing on past lessons and best practices.
Conclusion
Risk Management in Project Management is vital. By understanding the key concepts, employing appropriate strategies, and following best practices, organisations can effectively manage risks throughout the project lifecycle. The successful management of risks leads to improved project outcomes, stakeholder satisfaction, and overall project success.
Gain in-depth knowledge of risk identification and Risk Management principles with our Certified Risk Management Professional CRMP course.
Upcoming Project Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Certified Risk Management Professional CRMP
Certified Risk Management Professional CRMP
Thu 22nd May 2025
Thu 24th Jul 2025
Thu 23rd Oct 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


