We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +30 2111995372 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Sage is a renowned software company that offers a range of accounting, payroll, and business management solutions. Aspiring candidates seeking roles related to Sage software often face interviews that assess their technical skills, knowledge, and suitability for the position. This blog aims to provide a list of the most asked Sage Interview Questions and offers comprehensive answers to help candidates prepare effectively.
Table of Contents
1) Sage interview process
2) Technical Sage Interview Questions
a) What is Sage software, and what are its key features?
b) Differentiate between Sage 50, Sage 100, and Sage 300.
c) Why do companies choose Sage software over other accounting solutions?
d) Can you explain the different modules in Sage software?
e) How does Sage software help with financial management?
f) Behavioural interview questions
3) Conclusion
Sage interview process
Before diving into the interview questions, it's crucial to lay the foundation for a successful interview preparation strategy. Research the company, understand the role you're applying for, review your resume, and practice your communication skills. Most importantly, brush up on your knowledge of accounting principles, software functionality, and industry trends related to Sage.
The Sage interview process typically unfolds in three key steps, aiming to assess candidates' suitability for roles involving Sage software:
1) Application and screening: The process begins with an initial screening, which may include submitting your resume and completing an online application. This stage assesses your qualifications, experience, and alignment with the role's requirements.
2) Technical assessment: In the next stage, you may be asked to participate in a technical assessment, which can include written tests, case studies, or practical exercises related to Sage software. This stage evaluates your proficiency in using Sage tools and your understanding of its functionalities.
3) In-person or virtual interview: Shortlisted candidates proceed to interview rounds. These can encompass a mix of technical, behavioural, and situational questions. Expect to discuss your experience with Sage software, problem-solving skills, and how you handle challenges. Interviews may be conducted by HR, managers, or team members.
Discover the fundamentals of payroll management through our Introduction to Payroll Training Course – Sign up today to advance your financial skillset.
Technical Sage Interview Questions
Technical questions in a Sage interview are designed to assess your knowledge of the software's features and functionalities and how well you can navigate its tools. Here are some commonly asked technical questions, along with their answers:
1) What is Sage software, and what are its key features?
Sage software is a robust accounting and business management solution designed to streamline financial processes for organisations of all sizes. Its key features encompass a wide range of functionalities that empower businesses to handle their financial tasks efficiently. Among its notable features is financial reporting, which enables users to generate detailed and customisable reports to analyse company finances and performance.
Budgeting tools help organisations plan and allocate resources effectively, ensuring that financial goals are met. Additionally, Types of Sage Accounting Software offer comprehensive inventory management, allowing businesses to track stock levels, manage orders, and optimise inventory control. With features tailored to various industries, Sage software adapts to the unique needs of businesses, making it a versatile tool for managing financial operations.
Differentiate between Sage 50, Sage 100, and Sage 300.
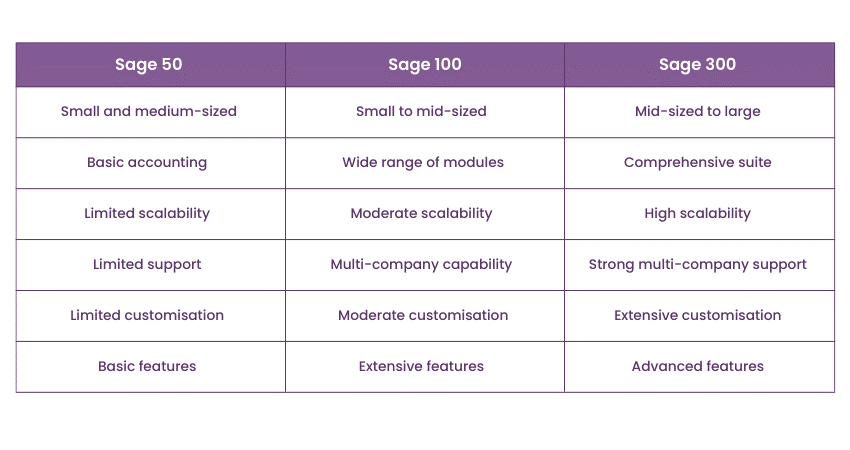
Sage offers a range of software solutions tailored to businesses with diverse needs. Understanding the differences between these versions is important for choosing the right fit for an organisation. However, note that Sage 50 interview questions are the commonly asked ones. Here are the differences between each:
1) Sage 50: Designed for small to medium-sized businesses, Sage 50 (formerly known as Peachtree) provides tools for managing accounting, invoicing, cash flow, and basic inventory. It's ideal for businesses seeking entry-level accounting software.
2) Sage 100: Positioned as a middle-ground solution, Sage 100 (formerly known as MAS 90 and MAS 200) caters to small and medium-sized businesses with more complex financial needs. It offers advanced inventory management, manufacturing, and distribution features.
3) Sage 300: Geared towards larger enterprises, Sage 300 (formerly known as Accpac) provides a comprehensive suite of tools for financial management, including multi-currency support, advanced reporting, and customisable features to accommodate different business processes.
Why do companies choose Sage software over other accounting solutions?
Companies often opt for Sage software due to its unique combination of features, scalability, and user-friendliness. It offers a vast array of functionalities that cater to various business needs, making it suitable for both small businesses and large enterprises, highlighting the Advantages and Disadvantages of Sage Accounting Software. Its customisable nature allows companies to tailor the software to their specific requirements, enhancing overall efficiency. Moreover, Sage's reputation for reliability and its track record of assisting businesses in streamlining financial processes play a significant role in companies' preference for it.
Can you explain the different modules in Sage software?
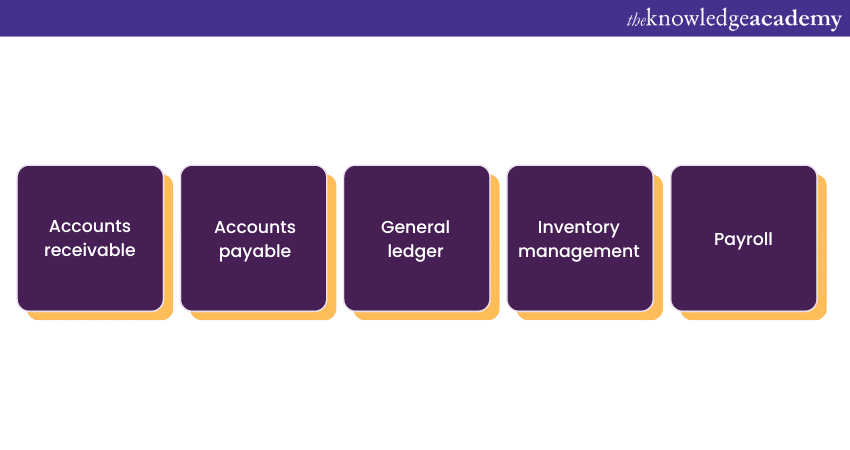
Sage software is modular, meaning it consists of distinct modules that cater to specific financial tasks. Some common modules in Sage software include:
a) Accounts receivable: This module manages customer invoices, receipts, and accounts receivable tracking.
b) Accounts payable: It handles vendor invoices, payments, and accounts payable tracking.
c) General ledger: The general ledger module is the core of financial accounting, recording all financial transactions and providing a snapshot of a company's financial position
d) Inventory management: This module helps businesses manage their inventory, track stock levels, and optimise supply chain processes.
e) Payroll: The payroll module automates payroll calculations, tax deductions, and employee payment processes.
How does Sage software help with financial management?
By automating routine financial tasks and providing comprehensive financial visibility, Sage software contributes to efficient and effective financial management practices.
1) Bookkeeping: Sage simplifies the recording and tracking of financial transactions, ensuring accurate and up-to-date records.
2) Invoicing: With Sage, businesses can generate professional invoices, track payments, and manage outstanding balances efficiently.
3) Financial reporting: Sage's reporting capabilities enable businesses to generate comprehensive financial statements, helping in analysis and decision-making.
4) Budgeting: Sage aids in setting and tracking budgets, enabling organisations to monitor expenses and revenue against predetermined targets.
5) Cash flow management: By providing insights into cash flow patterns, Sage assists in managing cash effectively and preventing liquidity issues.
6) Compliance: Sage software often incorporates tax calculation features, helping businesses adhere to tax regulations and avoid penalties.
Master the art of bookkeeping with our comprehensive Book Keeping Training Course - Register now!
How is data security ensured in Sage software?
Sage software places a strong emphasis on data security to protect sensitive financial information from unauthorised access, breaches, and cyber threats. One of the primary security measures is data encryption, which safeguards data during transmission and storage. This process renders data indecipherable to unauthorised parties unless they possess the necessary decryption key. User access controls play a crucial role by letting administrators define user roles and permissions, ensuring that only authorised personnel can access specific data and perform designated actions.
Regular software updates are necessary to patch vulnerabilities and address potential security risks, keeping the software up-to-date with the latest security protocols. Sage also employs multi-factor authentication to add an extra layer of protection to user accounts, requiring users to provide extra verification before accessing sensitive data. By implementing these security measures, Sage software maintains a robust security framework that helps organisations confidently manage their financial data.
Can you explain the concept of the Chart of Accounts and its significance in Sage?
The Chart of Accounts is a fundamental element of accounting that categorises and organises a company's financial transactions. It comprises a list of all accounts used to record income, expenses, assets, liabilities, and equity. Each account is assigned a unique code and description, facilitating easy identification and classification of transactions.
What is Bank reconciliation, and how is it performed in Sage?
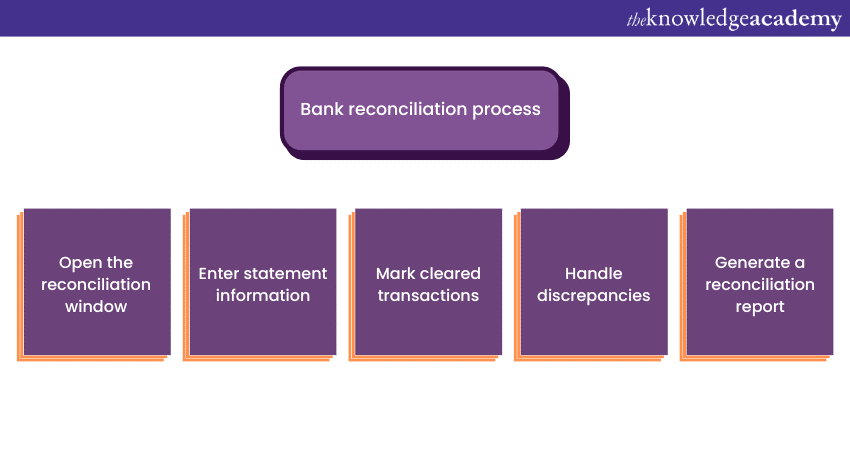
Bank reconciliation is simply the process of comparing a company's internal financial records with its bank statement to ensure accuracy and identify any discrepancies. It helps in reconciling discrepancies between the company's records and the bank's records, such as outstanding checks, deposits in transit, and bank charges.
Bank reconciliation in Sage ensures that the company's financial records accurately reflect its actual bank transactions, enhancing financial transparency and minimising errors. In Sage, performing bank reconciliation involves these steps:
1) Opening reconciliation window: Navigate to the reconciliation module in Sage and select the appropriate bank account.
2) Enter statement information: Enter the bank statement's beginning and ending balances, as well as any additional information provided on the statement.
3) Mark cleared transactions: Compare the transactions on the bank statement with those in Sage. Mark transactions as cleared or reconciled as they match.
4) Handle discrepancies: Address any discrepancies between the bank statement and Sage records. This may involve investigating and correcting errors or identifying outstanding items.
5) Reconciliation report: Once all transactions are reconciled, generate a reconciliation report to verify that the ending balance matches the bank statement balance.
How does Sage software handle budgeting and forecasting?
Sage software supports budgeting and forecasting by allowing businesses to set budget targets, allocate resources, and track actual performance against projected figures. Users can create detailed budgets for various departments, projects, or time periods. The software provides tools to compare actual financial data with budgeted amounts, helping businesses identify variances and make necessary adjustments. This feature aids in effective financial planning, resource allocation, and performance evaluation.
Can you explain how Sage software integrates with third-party applications?
Sage software offers integration capabilities through APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that enable seamless data exchange between Sage and other business systems. This integration facilitates the flow of information, such as customer data, sales transactions, and inventory levels, between Sage and CRM, ERP, e-commerce platforms, and more. By connecting Sage with third-party applications, businesses can streamline operations, eliminate data duplication, and enhance overall efficiency.
How does Sage handle sales Tax/VAT?
Sage software is equipped to handle the complex calculations and reporting associated with Sales Tax or VAT. The process involves:
1) Setting tax rates: Configure the appropriate tax rates based on the jurisdiction's regulations. Sage allows for multiple tax rates, exemptions, and different tax codes.
2) Assigning tax codes: Assign the relevant tax codes to products or services that are subject to taxation. This ensures accurate calculation during transactions.
3) Recording transactions: When creating invoices or sales orders, Sage automatically calculates the applicable tax based on the tax codes assigned. It adds the tax amount to the total payable by the customer.
4) Generating tax reports: Sage generates tax reports detailing the collected and payable tax amounts. These reports aid in compliance with tax regulations and facilitate timely tax remittance.
5) Tax filing: Depending on the jurisdiction, Sage might offer integration with tax filing systems, simplifying the process of submitting tax information to the authorities.
By automating tax calculations and reporting, Sage ensures accuracy and helps businesses adhere to tax laws, reducing the risk of errors and penalties.
How does Sage software help with tax compliance?
Sage software includes tax management features that help businesses stay compliant with tax regulations. It allows users to set up tax codes, rates, and rules specific to their jurisdiction. When recording transactions, the software automatically calculates taxes and applies them to invoices, purchases, and other financial activities. Sage software also generates tax reports and summaries for easy submission to tax authorities. This ensures accurate tax calculations and reporting, reducing the risk of errors and penalties.
Describe the process of generating financial reports in Sage.

Sage software empowers users to create a variety of financial reports to analyse the company's financial performance. Here's a general process to generate financial reports:
1) Access report menu: Navigate to the reporting or financial reports section within Sage.
2) Select report type: Choose the type of report you want to generate, such as a profit and loss statement, cash flow statement, or custom report.
3) Set parameters: Define the reporting period, which accounts to include, and any specific criteria. Sage allows for customisation to tailor the report to your needs.
4) Preview or generate report: Depending on the software version, you can preview the report to ensure accuracy before finalising it. Once satisfied, generate the report.
5) Export or share: Sage offers options to export reports in different formats like PDF or Excel. You can also share reports with colleagues or stakeholders.
How can Sage software aid in cost management and cost analysis for a project-based business?
Sage software can greatly assist project-based businesses in cost management and analysis. By utilising Sage's project accounting module, businesses can allocate costs to specific projects, track expenses, and monitor budget utilisation. Sage's reporting capabilities can generate detailed cost breakdowns for each project, highlighting areas of overspending or cost-saving opportunities. This information empowers project managers to make informed decisions to optimise resource allocation, improve profitability, and ensure that projects remain on track financially.
Upgrade your financial management expertise with our comprehensive Financial Management Training Course - seize the opportunity to enhance your skills now!
Can you explain the concept of Sage Intelligence Reporting?
Sage Intelligence Reporting is a module within Sage software that enables users to create custom, dynamic reports using real-time data from their Sage database. It offers a drag-and-drop interface to design reports tailored to specific business needs. Users can create financial statements, dashboards, and analytical reports that offer insights into key performance indicators (KPIs). Sage Intelligence Reporting empowers businesses to make data-driven decisions by visualising complex financial information in a comprehensible format.
Can you discuss the integration possibilities of Sage with other business systems?
Sage software offers robust integration capabilities through its Application Programming Interface (API). This API allows seamless data exchange between Sage software and other critical business systems like Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), and e-commerce platforms.
Integrating Sage with these systems facilitates real-time data synchronisation, enhances operational efficiency, and provides a holistic view of business processes. For example, integrating Sage with a CRM system enables sales teams to access up-to-date financial information, streamlining customer interactions and order management.
Explain the process of payroll management in Sage.
Sage software streamlines payroll management by automating tasks related to employee compensation, tax deductions, and compliance. The process involves several steps:
1) Employee setup: Enter employee information, including salary, deductions, and tax details, into Sage.
2) Time tracking: Capture employee work hours or time off within Sage, either manually or through integrations with time tracking systems.
3) Payroll calculation: Sage calculates employee wages, considering variables such as hourly rates, overtime, and deductions.
4) Tax calculation: Sage automatically calculates tax deductions, including income tax, social security, and other withholdings.
5) Generating payslips: Sage generates payslips detailing employee earnings, deductions, and net pay.
6) Tax filing: Sage may offer integrations or features to facilitate tax filing, ensuring compliance with tax regulations.
By automating payroll tasks, Sage minimises errors, saves time, and ensures accurate and timely payments to employees.
Explain the concept of Sage Business Cloud and its significance.
Sage Business Cloud is a suite of cloud-based accounting and business management solutions offered by Sage. It encompasses various software applications designed to address different aspects of financial management, including accounting, payroll, and financial reporting. The significance of Sage Business Cloud lies in its ability to provide businesses with flexibility, scalability, and accessibility.
By hosting software in the cloud, companies can access their financial data from anywhere, collaborate in real-time, and scale their software usage as their needs evolve. This cloud-based approach aligns with the growing trend of remote work and provides a secure environment for data storage and management.

Behavioural interview questions
Behavioural and scenario-based questions assess a candidate's problem-solving abilities, practical experience, and interpersonal skills. In the case of Sage software, these questions provide insight into how well a candidate can apply their knowledge to real-world situations. This section explores common behavioural interview questions related to Sage software and provides detailed answers to help you effectively showcase your skills.
1) How does your experience with Sage make you a suitable candidate?
Employer asks this interview question to evaluate your confidence and how well you are suited for that Sage role. Explain the experiences you had while working with Sage software and what all you accomplished. You can also describe any projects you have worked on. Here’s a sample answer:
Answer: “I have had the privilege of working extensively with Sage software in my previous roles, where I actively utilised its features to optimise financial processes. I've demonstrated my ability to navigate the software's modules, generate accurate financial reports, and effectively manage tasks such as accounts payable, accounts receivable and payroll. My experience has not only allowed me to become proficient in the technical aspects but has also honed my problem-solving skills as I tackled various challenges.”
2) Can you share an example of a challenging situation you resolved using Sage?
Provide a detailed example of a successful implementation, highlighting challenges faced, solutions applied, and positive outcomes achieved. Here’s an example:
Answer: “In my previous role as an Accountant, I faced a situation where our inventory management system was not syncing accurately with Sage. This led to discrepancies in stock levels, resulting in overstocking of some items and stockouts of others. To resolve this, I took the following steps:
1) Diagnosis: I conducted a thorough analysis to pinpoint the root cause of the syncing issue. I discovered that incorrect settings were causing data discrepancies between our inventory system and Sage.
2) Communication: I collaborated with our IT and inventory management teams to explain the issue and the importance of accurate data synchronisation. We identified the specific settings that needed adjustment.
3) Configuration changes: With input from the IT team, I made the necessary configuration changes in both the inventory management system and Sage to ensure proper data synchronisation.
4) Testing: After the changes were implemented, I conducted extensive testing to verify that stock levels were now accurate across both systems.
5) Training: I provided training to relevant team members on the correct data entry procedures and the importance of consistent data synchronisation practices.
6) Continuous monitoring: I established a routine to monitor data synchronisation regularly, ensuring that any potential discrepancies were addressed promptly.
By effectively diagnosing and resolving the syncing issue, I improved inventory accuracy and reduced unnecessary costs, demonstrating my problem-solving skills and ability to collaborate across departments.”
3) How do you ensure data accuracy and integrity when using Sage?
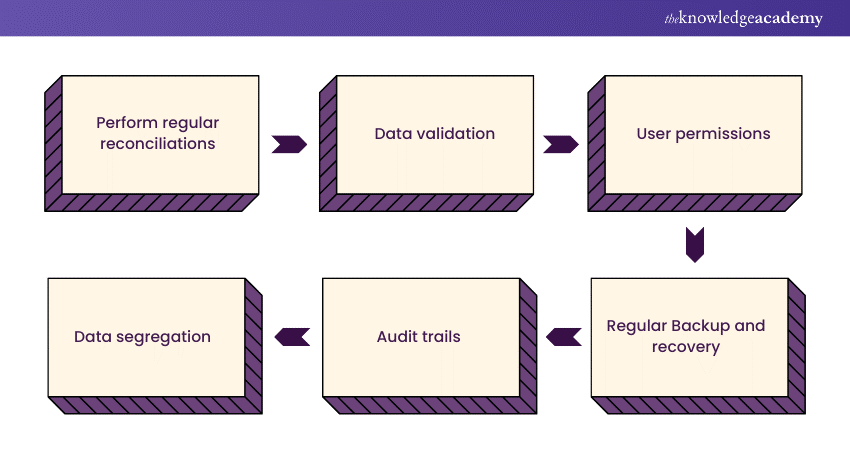
Describe what measures you take to ensure the accuracy and integrity of data within Sage software. Here’s a sample answer:
Answer: “Ensuring data accuracy and integrity is paramount when working with financial software like Sage. Here's my approach:
1) Regular reconciliation: I perform regular reconciliations, such as bank reconciliations and inventory audits, to identify and rectify any discrepancies between Sage records and external sources.
2) Data validation: Before entering data, I double-check to ensure accuracy and completeness. I also implement validation rules to prevent erroneous data entry.
3) User permissions: I assign appropriate user roles and permissions within Sage. This limits access to sensitive data and ensures that only authorised personnel can make changes.
4) Backup and recovery: I regularly back up Sage data to safeguard against data loss. This ensures that in case of any unexpected issues, I can restore accurate data quickly.
5) Audit trails: I enable audit trails within Sage, which track changes made to records and transactions. This helps in identifying any unauthorised or erroneous modifications.
6) Data segregation: I segregate data by departments, projects, or divisions where applicable. This helps maintain data integrity and prevents unauthorised access.
By implementing these measures, I maintain a high level of data accuracy and integrity, minimising errors and enhancing decision-making based on reliable information.”
4) Describe a time when you had to train team members on using Sage effectively.
Here, the employer wants to know your team handling and training approaches. Share an experience where you had to train colleagues on using Sage software effectively.
Answer: “In my previous role as a Financial Manager, I led the implementation of Sage software across our finance department. As part of the process, I had to train team members on using Sage effectively:
1) Needs assessment: I identified the specific needs of each team member to tailor the training accordingly. Some were new to Sage, while others needed to transition from another software.
2) Customised training: I organised interactive training sessions that covered the basics of Sage as well as specific modules relevant to each team member's role.
3) Hands-on practice: I encouraged hands-on practice with real-life scenarios, guiding them through entering transactions, generating reports, and reconciling accounts.
4) Q&A sessions: I scheduled regular Q&A sessions to address any queries or challenges the team members faced while using Sage.
5) Follow-up support: After the initial training, I provided ongoing support and guidance as team members applied their learnings in their day-to-day tasks.
6) Feedback loop: I established a feedback loop to gather insights from team members on their experience with Sage. This allowed us to identify areas for further improvement or additional training.
By effectively training my team on using Sage, I ensured a smooth transition to the new software, increased efficiency, and boosted their confidence in using Sage for various financial tasks.”
Conclusion
A Sage interview presents an opportunity to showcase your technical expertise, soft skills, and enthusiasm for contributing to a company's financial success. By preparing thoroughly, understanding the software, and practising your responses, you can confidently tackle any Sage Interview Questions that come your way.
Enhance your accounting skills with our Sage 50 Accounts Training Course - Register now to empower your financial expertise today!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
Upcoming Accounting and Finance Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Finance for Non Financial Managers
Finance for Non Financial Managers
Fri 21st Mar 2025
Fri 16th May 2025
Fri 18th Jul 2025
Fri 19th Sep 2025
Fri 21st Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


