We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +30 2111995372 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Imagine a cutting-edge fuel that powers modern IT infrastructures and turbocharges efficiency by creating virtual avatars of physical resources! That's the innovation brought on by Virtualisation in Cloud Computing. This integration of virtualisation tech with the Cloud lets multiple virtual environments run on a single system, opening doors for boundless scalability.
This blog unravels the magic behind this technology that allows businesses to accomplish far more with far less. So, let's plug in and explore how Virtualisation in Cloud Computing narrows the gap between the present and the future.
Table of Contents
1) What is Virtualisation in Cloud Computing?
2) What is a Virtual Machine?
3) How Does Virtualisation Work?
4) Types of Virtualisation in Cloud Computing
5) Virtualisation Technologies in Cloud Computing
6) Benefits of Virtualisation in Cloud Computing
7) Challenges of Virtualisation in Cloud Computing
8) Use cases of Virtualisation in Cloud Computing
9) Conclusion
What is Virtualisation in Cloud Computing?
To have a firm grasp on Virtualisation in Cloud Computing, you must begin with the fundamental concepts of Virtualisation and Cloud Computing. Virtualisation is creating a virtual version of something, like a virtual computer, server, storage, or network. This virtualised environment can exist on a single physical hardware system or across multiple physical systems. Virtualisation aims to optimise resource utilisation, improve scalability, and expand the flexibility of managing and deploying IT resources.
Cloud Computing, on the other hand, is a technology that delivers on-demand access to a shared pool of computing resources, such as storage, databases, servers, software, networking, and more, over the internet. It allows organisations and individuals to access and use these resources without owning or managing the underlying hardware and software infrastructure.
Virtualisation in Cloud Computing, therefore, refers to the integration of Virtualisation technologies into Cloud environments. This integration enables the efficient utilisation of physical resources by creating virtual computing, storage, and network instances. These virtualised resources can be allocated and managed as cloud users require, making Cloud Computing a powerful and flexible solution for multiple applications.
Importance of Virtualisation in Cloud Computing
When it comes to the cloud, Virtualisation is a very important element. From segmenting networks to cloning Virtual Machine, it offers many important functionalities. Let's explore some of them below:
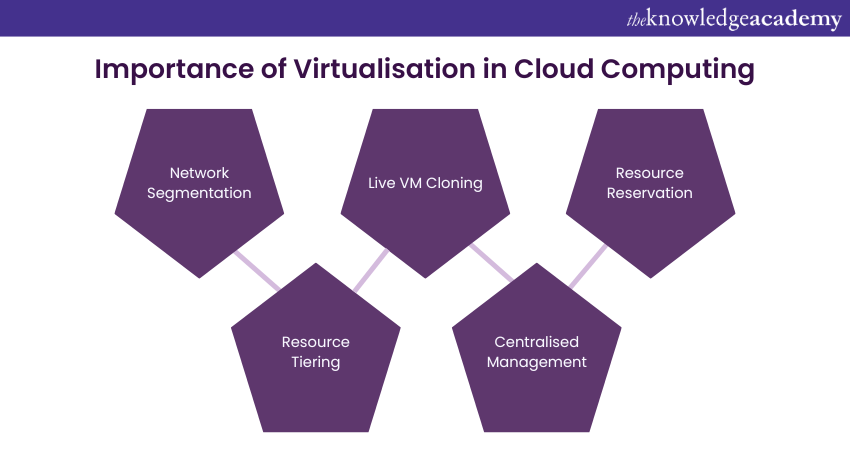
1) Network Segmentation: Virtualisation enables network segmentation, where Virtual LANs (VLANs) or virtual networks can be created within a physical network. This isolation is vital for security and separating different departments or customer environments.
2) Resource Tiering: Virtualisation allows for resource tiering, where workloads can be categorised into different performance tiers, ensuring optimal allocation of resources based on application requirements.
3) Live VM Cloning: Virtualisation technology allows for live cloning of VMs. This is particularly useful in scenarios where you need to replicate a running environment quickly, such as for creating development or testing environments.
4) Centralised Management: Virtualisation solutions often come with centralised management tools that simplify the administration of virtual resources, reducing the complexity of managing diverse IT environments.
5) Resource Reservation: Virtualisation platforms offer resource reservation capabilities, allowing users to allocate specific resources to critical applications, ensuring consistent performance even during peak loads.
Elevate your tech prowess and reach for the digital skies with our Cloud Computing Courses – Sign up now!
What Is a Virtual Machine?
A Virtual Machine (VM) is a computing environment functioning as an isolated system which comprises its own CPU, memory, network interface, and storage, created from a pool of hardware resources. A Software names hypervisor is responsible for managing VMs, isolates and allocates these resources, enabling the creation and management of VMs.
The physical machine running the VMs is known as the host machine, host computer, host Operating System, or simply host. The VMs utilising its resources are referred to as guest machines, guest computers, guest Operating Systems, or simply guests. The hypervisor manages compute resources—such as CPU, memory, and storage—as a pool that can be easily redistributed among existing guests or new VMs.
VMs allow multiple Operating Systems to run simultaneously on a single computer. For example, you can run a Linux® distribution on a MacOS or Windows system. Each Operating System operates as it would on the host hardware, providing an end-user experience within the VM that is nearly identical to running the OS on a physical machine.
Understand Virtualisation vs Containerisation for optimized performance and resource management solutions.
How Does Virtualisation Work?
A hypervisor is software that enables you to build a virtual layer over the hardware system to manage the interaction between the Virtual Machines and the system's hardware resources. Hypervisors are installed as any other software application and perform virtualisation tasks.
It connects the physical system with Virtual Machines to ensure proper access to hardware resources and manages the Virtual Machines so that they don't interfere with each other's memory and computing resources.

Types of Virtualisation in Cloud Computing
Virtualisation in Cloud Computing can be categorised into several types, each with its own set of use cases and benefits. Let's explore some of the most common types:
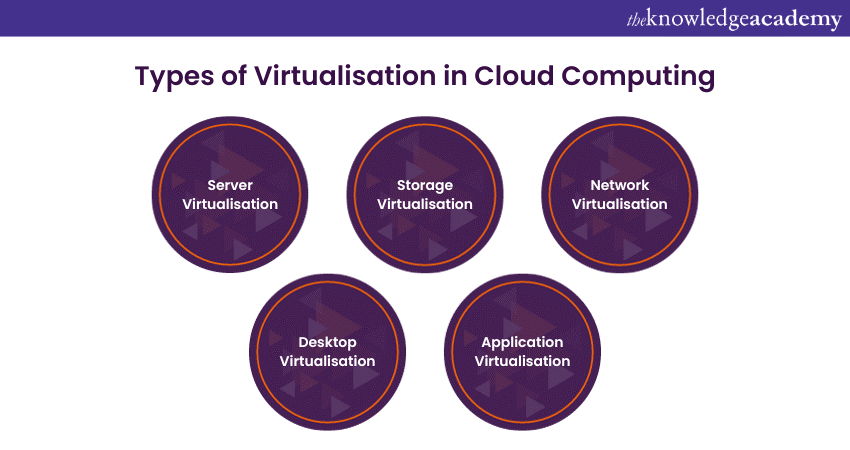
1) Server Virtualisation:
This is perhaps the most well-known form of Virtualisation which involves running multiple Virtual Machines (VMs) on a single physical server. Every VM functions as an independent server with its very own OS, applications, and resources. This type of Virtualisation is highly efficient in utilising server hardware and is widely used in Cloud data centres.
2) Storage Virtualisation: This approach abstracts storage resources from the physical hardware, allowing for greater flexibility and efficient data management. It allows you to pool storage resources from multiple devices and manage them centrally, making it easier to allocate and expand storage as required.
3) Network Virtualisation: This involves abstracting network resources, such as routers, switches, and firewalls, from their physical counterparts. This virtualisation allows for the creation of virtual networks with customised configurations and is vital in enabling secure and isolated network environments within the cloud.
4) Desktop Virtualisation: Desktop Virtualisation, also known as Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI), enables users to access virtualised desktops from anywhere. These virtual desktops are hosted on central servers and can be accessed using various devices, providing flexibility and simplifying desktop management.
5) Application Virtualisation: Application Virtualisation abstracts individual applications from the underlying Operating System. This allows applications to run in isolated containers, enablign easy deployment and management of software without conflicts.
6) Data Virtualisation: From the Cloud to on-premise software and hardware, modern enterprises store data from multiple applications using multiple file formats in numerous locations. Data virtualisation enables any application to access all that data, regardless of format, source, or location.
Data virtualisation tools create a software layer between the applications that access the data and the systems storing it. The layer translates an application’s data request as needed and returns results that can cover multiple systems. This can help break down data silos when other types of integration aren’t feasible or affordable.
7) Cloud Virtualisation: As already mentioned, the Cloud Computing model depends on virtualisation. By virtualising storage, servers, and other physical data centre resources, Cloud Computing providers can deliver a range of services to customers, including the following:
a) Platform as a Service (PaaS): Virtualised databases, development tools, and other Cloud-based services can be used to build your Cloud-based applications and solutions.
b) Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): You can configure virtualised storage, servers, and network resources according to their requirements.
c) Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS is a Cloud-based service abstracted from the hardware.
9) GPU Virtualisation: A Graphic Processing Unit (GPU) is a multi-core processor that improves overall computing performance by handling heavy graphic or mathematical processing. It lets multiple VMs utilise all or some of a single GPU’s processing power for faster AI, video, and other graphic or math-intensive applications. The two prime categories of GPU virtualisation are:
a) Pass-through GPUs: This approach makes the entire GPU available to a single guest OS.
b) Shared vGPUs: This approach divides physical GPU cores among various virtual GPUs (vGPUs) to be used by server-based VMs.
Master the best AI techniques for automating Cloud infrastructure and enhancing security through our Certified Artificial Intelligence (AI) For Cloud Professionals Course - Sign up now!
Virtualisation Technologies in Cloud Computing
Several Virtualisation technologies are commonly used in Cloud Computing. Let's take a look at a few of them below:
1) Hypervisors: Hypervisors (also called Virtual Machine Monitors (VMMs)), are software or hardware components that create and manage VMs. The two main categories of hypervisors are: Type 1 (bare-metal) and Type 2 (hosted). While Type 1 hypervisors run directly on the host hardware, Type 2 hypervisors run on top of an existing Operating System. Popular hypervisor options include VMware vSphere, Microsoft Hyper-V, and open-source solutions like KVM and Xen.
2) Containerisation: Containers are lightweight, portable, and efficient Virtualisation technologies that package applications and their dependencies. Unlike traditional VMs, containers share the host OS kernel, which makes them faster and more resource-efficient. Docker is a well-known containerisation platform.
3) Virtual Machine Images: Virtual Machine images are pre-configured templates used to create VM instances. Cloud providers often offer a marketplace of VM images that users can choose from, simplifying the process of deploying new VMs.
Benefits of Virtualisation in Cloud Computing
Virtualisation in Cloud Computing offers a wide range of benefits for businesses and individuals. Let’s explore some of its key benefits:
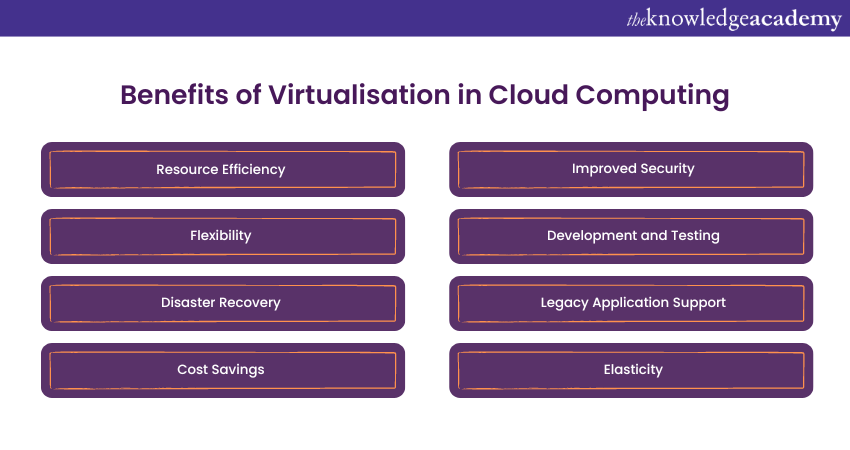
1) Resource Efficiency: Virtualisation optimises resource utilisation by allowing multiple virtual instances to share a single physical server. This consolidation significantly reduces hardware requirements. It reduces data centre space, lowers power consumption, and enhances cost savings. As a fundamental pillar of green computing, it promotes a more environmentally responsible and sustainable approach to IT infrastructure.
2) Flexibility: Virtualisation provides the flexibility to scale resources up or down as needed. Whether adding more computing power during peak traffic or reducing resources during off-peak hours, Virtualisation ensures optimal performance. This adaptability is essential in today's ever-changing business landscape. It ensures that resources align precisely with current demand and budgetary constraints.
3) Disaster Recovery: Virtualisation's use of VM snapshots and backup capabilities simplifies disaster recovery processes. In the event of system failures, data loss, or other unforeseen disasters, these features facilitate the swift restoration of virtual environments to their previous states. This minimises downtime, reduces data loss, and enhances overall business continuity planning.
4) Cost Savings: Virtualisation fosters cost savings through resource sharing. Cloud providers leverage this by pooling physical resources, and users adopt a pay-as-you-go model. It eliminates any need for upfront capital expenditures and enables organisations to pay only for the resources they consume. This results in significant financial advantages and streamlined budget management.
5) Improved Security: The isolation between Virtual Machines enhances security by preventing vulnerabilities in one VM from affecting others. This security feature ensures the integrity of both data and applications, particularly in multi-tenant Cloud environments. It supports the protection of sensitive information and maintains the confidentiality and privacy of user data.
6) Development and Testing: Virtualisation empowers developers to create and test applications within isolated virtual environments, free from conflicts with the host Operating System or other applications. This results in higher-quality software, shorter development cycles, and reduced operational risks during deployment. It fosters innovation and supports agile development practices, enabling organisations to offer quick response to changing market demands.
7) Legacy Application Support: Virtualisation serves as a lifeline for legacy applications that may not be compatible with modern hardware or operating systems. By encapsulating these applications in VMs, they can run seamlessly on contemporary infrastructure. This preservation of historical data and business processes enables organisations to transition smoothly to modern technologies while maintaining vital legacy systems.
8) Elasticity: Virtualisation empowers developers to create and test applications within isolated virtual environments, free from conflicts with the host Operating System or other applications. This results in higher-quality software, shorter development cycles, and reduced operational risks during deployment. It fosters innovation and supports agile development practices, enabling organisations to offer quick response to changing market demands.
Challenges of Virtualisation in Cloud Computing
While Virtualisation offers many advantages in Cloud Computing, you must be aware of the potential challenges associated with this technology. Let's explore some of them below:
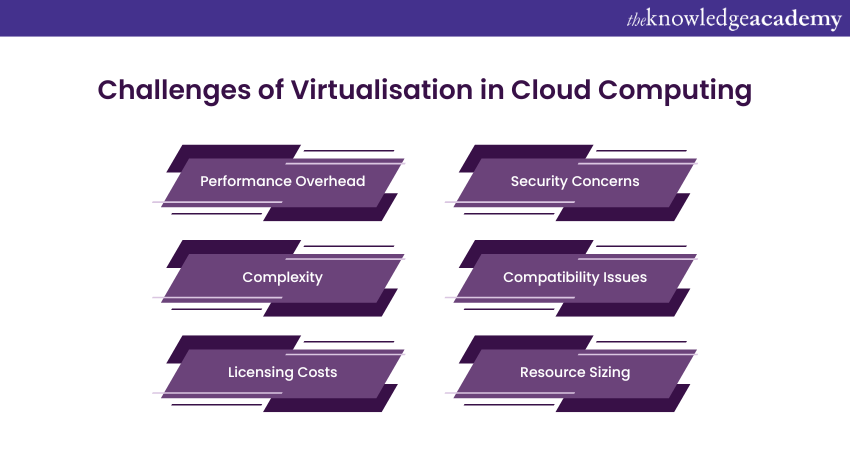
1) Performance Overhead: Running VMs can introduce a performance overhead compared to running applications on physical hardware. Proper resource allocation and management are vital to mitigate this issue.
2) Complexity: Managing virtualised environments can be complex, especially as they scale. Tools and automation are often required to streamline operations.
3) Licensing Costs: Some Virtualisation technologies and tools come with licensing costs, which need to be factored into the overall budget.
4) Security Concerns: While Virtualisation enhances Cloud Computing Security, it also introduces new attack surfaces. It's crucial to implement proper security measures to protect virtualised resources.
5) Compatibility issues: Ensuring compatibility between VMs and applications is essential to avoid conflicts and ensure smooth operations.
6) Resource Sizing: Over or under-provisioning resources can lead to inefficiencies or performance bottlenecks. Proper resource sizing and monitoring are vital.
Use cases of Virtualisation in Cloud Computing
Virtualisation in Cloud Computing has a wide range of use cases across various industries. Let's take a look at some of them below:
1) Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Cloud providers use server Virtualisation to offer scalable computing resources to users.
2) Desktop as a Service (DaaS): DaaS solutions leverage desktop Virtualisation to provide remote access to virtual desktops.
3) Database Virtualisation: Virtualised databases enable efficient data management and scalability for applications.
4) Software Development and Testing: Developers create virtual environments to test applications and reduce development costs.
5) Disaster Recovery: VM snapshots and backups make disaster recovery more efficient and cost-effective.
6) Classic Application Support: Organisations use Virtualisation to run legacy applications on modern hardware and operating systems.
7) Hybrid Cloud: Virtualisation is a key component of hybrid cloud solutions, allowing seamless integration between on-premises and cloud environments.
Dominate the digital landscape with our Terraform Training – Sign up now!
Conclusion
Running VMs can introduce a performance overhead compared to running applications on physical hardware. Proper resource allocation and management are vital to mitigate this issue.
Unlock the future of technology with our Cloud Computing Training – Sign up today!
Frequently Asked Questions

The three types of virtualisation technologies include:
a) Full virtualisation (Includes Oracle VM Virtualbox and Windows Virtual PC)
b) Para-virtualisation (Supported by Xen and IBM LPAR)
c) OS-level virtualisation technologies (Common containers include Oracle Solaris
d) and Linux LCX )

The two most common methods of virtualisation are hardware-assisted virtualisation and binary translation.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Cloud Computing Courses, including the Microservices Architecture Course and the Certified Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Cloud Professionals Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Common Challenges of Cloud Computing.
Our Cloud Computing Blogs cover a range of topics related to Cloud technology, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Cloud Computing skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Cloud Computing Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Cloud Computing Training
Cloud Computing Training
Thu 13th Feb 2025
Thu 10th Apr 2025
Thu 12th Jun 2025
Thu 14th Aug 2025
Thu 9th Oct 2025
Thu 11th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


