We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +30 2111995372 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Have you ever wondered what happens to your personal data when you share it online? In a world where data is often called the new oil, safeguarding personal information has become paramount. Explore the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) – a game-changer in the realm of data privacy. But What is GDPR, and why should you care? This regulation has transformed how businesses handle your data, ensuring its security like never before.
Discover the essentials of GDPR, from its foundational principles to practical compliance steps, as you dive into this blog. Curious about What is GDPR? Let's go on this fascinating adventure together to unravel its impact on you and the future of data protection. Ready to get started? Let's dive in!
Table of Contents
1) What is GDPR?
2) History and Evolution of GDPR
3) GDPR Scopes and Penalties
4) GDPR Breaches
5) Who Must Comply with GDPR?
6) GDPR Principles
7) New GDPR Consumer Rights
8) What Does GDPR Mean for the Future?
9) Criticism of the GDPR
10) Understanding GDPR Compliance
11) How to Prepare for GDPR Compliance?
12) What are the Basic Rules of GDPR?
13) What is GDPR Guideline?
14) Conclusion
What is GDPR?
The General Data Protection Regulation is a landmark data privacy law implemented by the European Union (EU) in May 2018. Its primary goal is to protect the personal data of EU citizens, ensuring their privacy and security in an increasingly digital world. GDPR sets stringent guidelines for organisations on how they collect, store, process, and share personal data.
GDPR strengthens individuals with greater control over their data, granting rights to access, rectify, erase, and restrict the processing of their information. Organisations must obtain explicit consent for data processing, implement robust data protection measures, and promptly report data breaches. Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties, making adherence to GDPR crucial for businesses handling personal data within the EU.
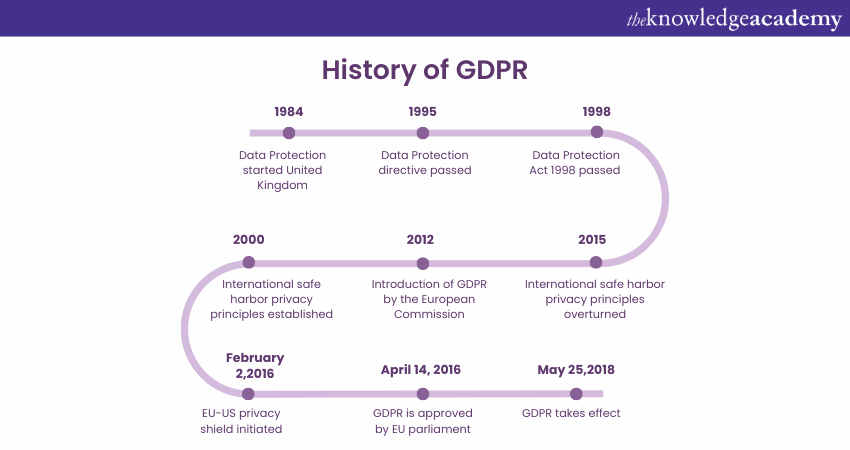
History and Evolution of GDPR
To replace the outdated Data Protection Directive of 1995, the European Union (EU) initiated the GDPR. The rapidly evolving digital environment and the rising volume of personal data being gathered, processed, and shared by businesses, organisations, and governments gave rise to the necessity for GDPR.
By giving EU citizens more control over their personal data and setting stricter laws on the organisations that manage it, the GDPR was developed to improve and standardise data protection for EU citizens. The regulation established standards for collecting, using, storing, and destroying personal data. It also specified procedures for disclosing data breaches and seeking consent before processing personal data. The EU officially adopted it in 2016, and it became enforceable on May 25, 2018.
Protect personal data and master GDPR regulations - join our in-depth GDPR Training today!
GDPR Scopes and Penalties
Your personal data can heavily suffer from a lack of regulations. Under these circumstances, an organisation is left to use it as it pleases. However, GDPR controls this by allowing the financial regulator to attack businesses that do not conform to ethical guidelines with hefty penalties. The scope and penalties of GDPR are as follows:
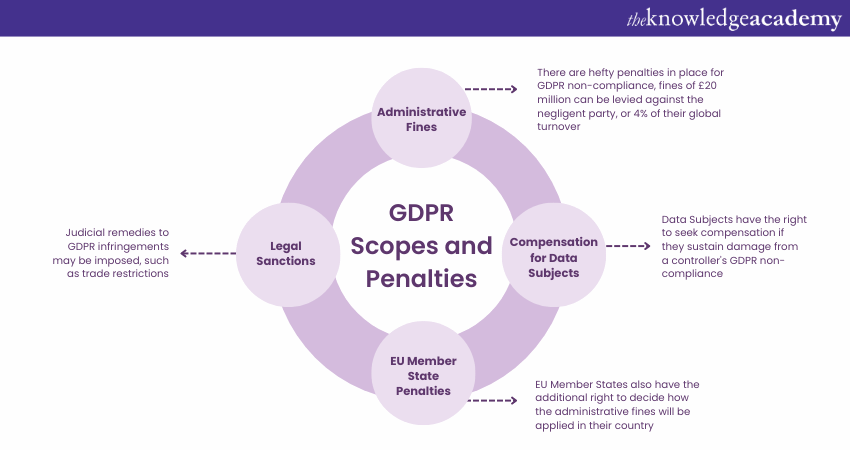
1) Scope
The Scope of GDPR applies to organisations that are within European Union (EU) as well as organisations which operate the personal data of EU residents.The scope of GDPR regulations extends to a different data type, such as name, location, email id’s, financial information, and health records. This leads to accountability when it comes to handling personal data in different sectors.
2) Penalties
An organisation can be imposed heavy fines if it does not deal with personal data carefully. Organisations handling personal data must abide by a set of laws and regulations mandated by the GDPR. Violations or any form of non-compliance to these regulations are subject to fines and other penalties.
An organisation may face fines and other penalties if it is determined that it has violated the GDPR. A GDPR breach carries a maximum penalty of €20 million, or 4% of the organisation's annual global revenue, whichever is higher. In the UK, Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) decides on fines for breaking Data Protection Laws. Any money collected goes back to the government.
The GDPR states that more minor breaches can result in penalties of up to £10 million or 2% of the company's worldwide revenue. Serious breaches can be fined up to £20 million or 4% of the company's global turnover. Before the GDPR, the ICO could only fine up to £500,000.
The severity of the breach and the organisation's cooperation level with authorities affect the exact fine amount. Enterprises may also face other penalties, such as legal action from individuals whose data has been breached or reputational damage. Therefore,They must take serious steps to ensure compliance with GDPR Requirements.
Become a certified GDPR expert and ensure your organisation's data protection compliance with our Certified EU GDPR Practitioner Course today!
GDPR Breaches
When an organisation disregard one or more GDPR regulations, it is considered a GDPR Breach. These breaches include accessing any personal data unlawfully, not implementing proper security measures or compromising the safety of personal data. Here are a few examples to help you understand GDPR Data Breach:
1) Lack of sufficient consent for the collection and use of personal data.
2) Failure at safeguarded personal information and unauthorised access prevention.
3) Denial of access or the ability to update or delete, personal data.
4) Failure to promptly inform people and authorities when a data breach happens.
Who Must Comply with GDPR?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) applies to any individual or organisation that collects, stores, and processes the personal data of EU citizens, irrespective of where the processing occurs. Consequently, companies outside the EU must comply with GDPR if they offer goods or services to, or monitor the behaviour of, EU residents.
Certain categories of sensitive personal data require enhanced protection. Examples include genetic information, biometric data, health details, political views, religious beliefs, trade union membership, and information regarding an individual's sexual life or orientation.
GDPR identifies two types of data handlers: Data Processors and Data Controllers. Here’s an explanation of each:
a) Data Processors: These are individuals or organisations that handle personal data on behalf of Data Controllers. Examples include marketing firms, cloud service providers, and IT service providers.
b) Data Controllers: These are individuals or organisations that determine the purposes and means of processing personal data. This can include businesses, non-profit organisations, and governmental bodies.
Become familiar with the principles of data protection and how they apply to personal data by signing up for our ertified EU GDPR Foundation Course today!
GDPR Principles

There are seven key GDPR Principles which serve as a guide to data handling. Let’s talk about them in detail:
a) Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency: Individuals must be informed about the processing activities and their rights, and personal data must be treated in a fair, lawful, and transparent manner.
b) Purpose Limitation: Personal data cannot be further processed in a method that is inconsistent with the original, stated, and legal purposes for which it was gathered.
c) Data Minimisation: Personal information must be sufficient, relevant, accurate and kept to a minimum required for processing purposes.
d) Accuracy: Personal information must be accurate and kept current, and all necessary steps must be taken to guarantee that errors are fixed or deleted.
e) Storage Limitation: When it is no longer required, personal data must be safely destroyed or anonymised. It must not be retained for longer than is necessary.
f) Integrity and Confidentiality: Personal data processing must be done in a secure manner that protects it against accidental loss, unauthorised or unlawful processing, destruction, or damage, among other risks.
g) Accountability: Organisations are accountable for adhering to GDPR, which includes maintaining records of processing operations, putting in place suitable security measures, and proving compliance when authorities ask for it.
Learn lawful processing of personal data, subject access requests and how to deal with them with the Certified EU General Data Protection Regulation (EU GDPR) Foundation Course today!
New GDPR Consumer Rights
The GDPR has updated the regulations regarding their data, as it is mentioned in the rights of the data subject, articles 12 to 23 in Chapter 3. The term data subject refers to people of the EU who trust an organisation with their personal data. These rules focus on the well-being of the data subjects, keeping them safe and defended from malicious reach of external attacks. Some of these rights are as follows:
1) Article 13-14 (The Right to be Informed): In this article, GDPR states that the data should always be transparent for the data subjects. It also states that the data subjects should be well-informed about the collection of their data andits uses.
2) Article 15 (The Right to Access): GDPR establishes the means for individuals to check their personal data if they choose to access it. This allows individuals to check the purpose of the data collected Additionally, any organisation under EU is bound by the law to provide this data if the data subject requests it, without any cost.
3) Article 16 (The Right to Rectification): Rectification in this article refers to an individual's ability to check if their data is correct or not. In case the data is not correct the subject is free to ask an organisation utilising their data, to make changes it. This extends to incomplete data, where an individual can ask an organisation to add the remaining information. GDPR mandates the rectification of the data on the earliest notice, and any organisation has a time limit of one month to correct this data.
4) Article 17 (The Right to Erasure): This segment of the updated rights allows users to delete their data which was utilised by an organisation. This deletion can be requested if the data is not relevant anymore or if subjects withdraw their consent regarding the usage of data. Organisations are not allowed to withhold data from deletion, and this regulation extends to all third parties that might have used or benefited from the collected data.
5) Article 18 (The Right to restrict Data Processing): GDPR allows a people under the protection of EU to choose how their data is processed. If the subjects discover the usage of their data is unlawful or they have objection to the way their data is processed, they have the right to restrict the processing. Data subjects are required to notify the third parties who are involved with this data, about this request as well under certain circumstances.
6) Article 20 (The Right to Data Portability): This segment of the GDPR article mandates the organisation to provide data relevant to the user in a coherent format. This data should be portable enough that another organisation should be able to easily use it (if necessary). Due to the regulations implemented by GDPR, an organisation cannot prevent the data subject from sharing this information with other organisations.
7) Article 21 (The Right to Objection): This segment of the GDPR article states that subjects have the right to object to the usage of their data. If people whose data has been collected by an organisation find objection to the way their data is being processed, for instance, for direct marketing purposes, they can object against it. According to the GDPR regulations, EU-based organisations will have to abide by the objection if they believe the reason for the objection is valid.
8) Article 22 (Automated Individual Decision-making): GDPR regulations mandate that people should not suffer by any means due to automated decision- making and profiling of their data. This regulation is applicable to all automated processing of data which may affect an individual in a legal manner.
Learn to handle sensitive and personal data with our Personal Data Protection Bill Training today!
What Does GDPR Mean for the Future?
GDPR has significantly changed how data and personal information is perceived by EU organisation. As regulations like these keep refining themself overtime, misuse or abuse of such data will become tougher with time. As a result, organisation and business who understand the essence of ethical data usage and privacy protection, will get higher preference in future.
There is no doubt businesses and organisations across the world are thriving on data in the current age. This data allows them to conduct predictive analytics on potential customers and future trends, thus making a larger profit than they could otherwise. However, the vital data thatis collected can also be used for malicious and unethical purposes.
Despite the potential of malicious usage of customer data, GDPR has shown that with correct regulations, this probability can be lowered. The EU regulator have the means and method to make sure the organisation that benefit from the data establish a data protection model. This enhanced security is bound to keep the people safer, and their data well defended against potential misuse.
One can say that it is too soon to draw a conclusion on how the future of GDPR rights will turn out. However, as times are changing the need for well- protected business models which keeps the data collection subjects safe, are becoming common. This is true for not just EU regions but also people outside it, such as USA.
There is a possibility that EU based GDPR model will become so popular that it may get accepted across various parts of world. Overall, it will lead to a safer and more transparent use of data with passage of time. This kind of data model is bound to make people safer, enabling greater cooperation among them.
Master GDPR essentials with our GDPR Awareness Training - safeguard personal data and achieve compliance!
Criticism of the GDPR
While the GDPR is a landmark in data protection, it has faced criticism for various reasons. Here’s a breakdown of the key challenges:
1) Administrative Burden
a) The requirement to appoint Data Protection Officers (DPOs) or assess the need for them is seen as an unnecessary strain, especially on smaller businesses.
b) The complexity of compliance demands significant time and resources.
2) Vague Guidelines
a) Companies struggle with unclear instructions on handling employee data, leading to confusion and potential compliance risks.
3) Data Transfer Restrictions
a) GDPR prohibits transferring data outside the EU unless the recipient ensures the same level of protection, disrupting traditional business practices.
b) Companies face increased costs and logistical challenges to meet these requirements.
4) Rising Compliance Costs
a) Educating employees and customers about data protection is an ongoing expense that many fears will grow over time.
b) The need for regular updates and audits adds to financial pressures.
5) Inconsistent Enforcement
a) There is scepticism about whether data protection agencies across the EU can uniformly enforce GDPR regulations.
b) Variability in enforcement and interpretation risks creating an uneven playing field for businesses.
Understanding GDPR Compliance
Understanding GDPR compliances has become a mandatory aspect of many organisations. It is one of the most significant privacy-based laws implemented in the past few years. Why is GDPR Important, to different organisations, as failing to abide by them can make them susceptible to penalties. These penalties generally come with hefty fines and as a result they act as a potential deterrent for any company to misuse the data.
The essence of complying with GDPR is based on the thought of protecting a person’s vital information and thus protecting the person’s fundamental rights. This compliance has led to an overall more ethically guided approach to data handling in the EU- based organisations. As a result of this mandated privacy standard, data protection has become much more accessible for a large majority of people across the EU.
This compliance became prominent and started to take a foothold due to rising concerns regarding the use of personal information. This compliance can be credited to the technical revolution that took place over last few years. This compliance to data protection is a successor for Data Protection Directive established previously.
The GDPR Compliance is particularly applicable to a certain set of companies and organisations that meet certain criteria. These companies need to strictly comply with the regulations if they do not wish to be penalised, or worse, considered to have breached GDPR. Some of the factors which can decide if an organisation or company is bound to comply with GDPR or not are as follows:
1) EU Based Operation: Any organisation operating within the EU region is directly under the GDPR laws. Hence, if they are dealing with data that may include health, biometrics, cookies, Internet Protocol (IP) addresses, and the race of the individual, they need to abide by GDPR regulations.
2) Data of EU Residents: This applies to companies who are operating outside EU grounds but are handling the data of people who reside in the EU region. Any company or organisation that operates with such data is bound by GDPR regulations and compliance.
3) Employee Count: An organisation that asks for the personal information of its employees is bound by GDPR in terms of how their vital data is handled. This is particularly for an organisation that has over 250 people working under the firm. This compliance not only keeps the resident safe but also the employee and their confidential information.
4) Frequency of Data Processing: Although EU based rules and regulations are applicable for large scale organisation and a business that operate within EU, GDPR is not limited there. GDPR compliance is also applicable for any organisation which may process sensitive information provided by citizens of EU region. Even if the company is not directly responsible for obtaining the data, how they handle it is still controlled by GDPR rules.
Interested in making an organisation more GDPR compliant? Try our Dealing With Subject Access Requests (SAR) - An Executive Briefing Course!
How to Prepare for GDPR Compliance?
The GDPR law emphasises "privacy by design," which means that all departments in a company must carefully examine their data and how they use it. To be GDPR compliant, companies need to take many actions. If you're starting your GDPR compliance journey, there are some steps you can start with:
1) Data Mapping
To prepare for GDPR compliance and improve Customer Relationship Management (CRM), it is essential to map out where all personal data in your business comes from and document how the data is used. This includes identifying where the data is stored, who can access it, and any risks to the data. Doing this lets you understand how personal data is used within your organisation and take steps to protect it.
2) Eliminate Unnecessary Data
To comply with GDPR, keeping the necessary information and removing unused data is essential. If your company has gathered excessive data that doesn't provide real value, evaluating which data is critical for your business is important to comply with the regulations. GDPR encourages companies to handle personal data with more care.
During the clean-up process, it's essential to ask yourself questions such as:
a) Consider why you are storing data instead of deleting it
b) Why are you keeping specific data?
c) What is the purpose of collecting certain personal information?
d) Whether it's better to delete the data instead of encrypting it
Answering these questions will help you decide what data to keep and what to remove.
3) Implement Data Protection Measures
To comply with GDPR, companies must protect personal data by implementing measures like encryption, access control, and monitoring. Encryption converts data into a coded format which is accessible only to authorised users and limits control over access of personal data. Monitoring helps identify potential security breaches quickly. These measures safeguard personal data and prevent data breaches, which can damage a company's finances and reputation.
For example, a company encrypts its customers' data when the data is stored on its servers. They could also limit access to this data to only authorised employees using access control measures. Additionally, they could set up monitoring systems to quickly detect and respond to any potential security breaches. These measures help ensure the data's confidentiality, integrity, and availability and protect it from unauthorised access or misuse.
4) Revaluate Your Documentation
Reviewing documentation is an important step in preparing for GDPR compliance, and it involves a thorough examination of a company's policies and procedures related to personal data. It should be prepared in the following manner:
a) To verify all the personal data that the company collects and processes.
b) Policies and procedures related to personal data should be reviewed, including privacy policies and data protection protocols.
c) Lastly, a plan should be developed to implement any necessary changes to the company's policies and procedures to ensure GDPR compliance.
Developing GDPR Policies and Procedures
Having discussed the eight rights of GDPR, developing GDPR policies and procedures for individuals to deal with certain situations effectively is also an essential step which includes:
a) It involves the creation of guidelines and protocols that outline how a company handles personal data.
b) Developing policies for handling personal data involves creating clear and concise guidelines that outline the processes for data collection, storage, processing, and sharing.
c) It also involves developing a data breach response plan, a subject access request process, and a data portability process.
By developing these policies and procedures, companies can ensure they are correctly handling personal data and are prepared to meet GDPR guidelines in the event of a data breach or other related issues.
What are the Basic Rules of GDPR?
GDPR rules include obtaining clear consent for data collection, ensuring data accuracy, providing individuals the right to access, correct, or delete their data, protecting data security, and notifying breaches promptly. Businesses must process data lawfully, transparently, and only for specific purposes.
What is GDPR Guideline?
GDPR guidelines are rules set by the EU to ensure organisations handle personal data responsibly. They outline how to collect, process, store, and protect data, emphasising user consent, transparency, and security. These guidelines aim to safeguard individual privacy while enabling lawful data use.
Conclusion
Understanding What is GDPR is crucial for protecting personal data and ensuring compliance. This regulation not only enhances data security but also imposes strict penalties for non-compliance. By adhering to GDPR, organisations can safeguard individuals' information and maintain trust in the digital age. Embrace GDPR to stay ahead in an evolving, data-driven world!
Master data protection with our Data Privacy Awareness Course – register now and secure your future!
Frequently Asked Questions

The seven main principles of GDPR are:
1) Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency
2) Purpose limitation
3) Data minimisation
4) Accuracy
5) Storage limitation
6) Integrity and confidentiality
7) Accountability
These principles ensure robust data protection and compliance.

GDPR stands for General Data Protection Regulation. It is a legal framework implemented by the European Union (EU) to regulate the collection, use, and protection of personal data, ensuring individuals have greater control over their privacy and data rights.GDPR stands for General Data Protection Regulation. It is a legal framework implemented by the European Union (EU) to regulate the collection, use, and protection of personal data, ensuring individuals have greater control over their privacy and data rights.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various GDPR Training, including Certified EU General Data Protection Regulation (EU GDPR) Foundation and Practitioner, GDPR Awareness Training and Certified EU General Data Protection Regulation (EU GDPR) Foundation. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into GDPR Changes.
Our IT Security & Data Protection Blogs cover a range of topics related to GDPR, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Data Protection skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Certified Data Protection Officer (CDPO)
Certified Data Protection Officer (CDPO)
Fri 10th Jan 2025
Fri 14th Mar 2025
Fri 9th May 2025
Fri 11th Jul 2025
Fri 12th Sep 2025
Fri 14th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


