We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +852 2592 5349 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Program Life Cycle Management refers to the end-to-end process of managing programs throughout all the lifecycle stages. It involves a structured approach to ensure that programs are successfully delivered on time, within budget and according to the predefined objectives.
Program Management Life Cycle is essential for organisations as it provides a framework to effectively plan, execute, monitor, and control programs. In this blog, you will learn what is Program Life Cycle Management, its key phases and its benefits. Let's dive in deeper to learn more!
Table of Contents
1) What is Program Management Lifecycle?
2) Key Phases of Program Life Cycle Management
a) The initiation phase
b) The planning phase
c) The execution phase
3) Benefits of Program Life Cycle Management
4) Conclusion
What is Program Management Lifecycle?
The Program Management lifecycle consists of distinct phases that guide the program's progression. These phases provide a structured approach to managing programs and ensuring their successful completion. Each phase has its specific objectives, deliverables, and activities that result in the program's overall success.
Understanding the Program Management lifecycle is crucial for Program Managers to plan, execute, and control programs effectively. Program Managers can mitigate risks, address challenges, and achieve desired outcomes by following the lifecycle and its associated processes.

Key phases of Program Life Cycle Management
Program Life Cycle Management consists of several key phases that guide the successful execution of programs. Let's explore these phases:
The initiation phase
The Initiation phase is the starting point of the Program Life Cycle. During this phase, the program is conceptualised, and key activities are undertaken to set the foundation for the program's success. The primary objectives of the Initiation phase are to identify the need for the program, define its objectives, and assess its feasibility.
Program Managers work closely with stakeholders in this phase to understand their requirements and expectations. They conduct thorough assessments to determine the viability and potential benefits of the program.
This involves evaluating financial resources, technical feasibility, market demand, and organisational readiness. Key activities in the initiation phase include:
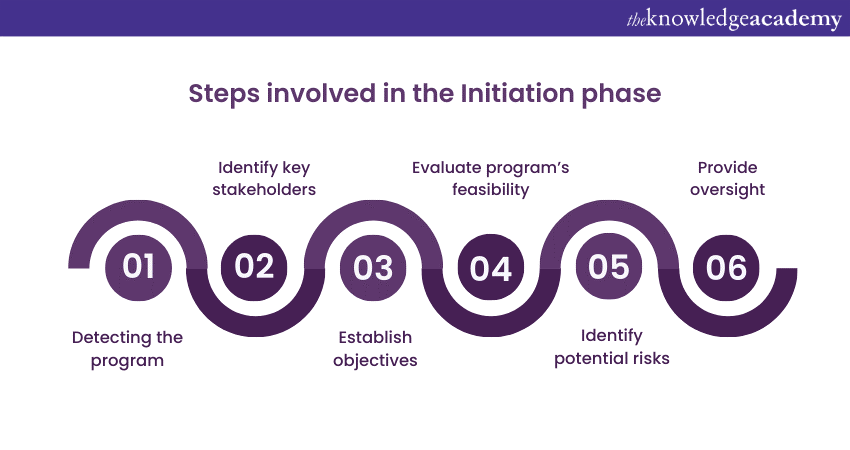
1) Identifying the program: Program Managers identify the need for the program based on organisational goals, market demands, or strategic initiatives. They define the program's scope, boundaries, and intended outcomes.
2) Stakeholder identification: Key stakeholders who will be impacted by or have an interest in the program are identified. These stakeholders may include executives, project sponsors, end-users, customers, and regulatory bodies.
3) Defining program objectives: Clear and measurable objectives are established for the program. These objectives align with the organisation's strategic goals and serve as a guiding force throughout the Program Life Cycle.
4) Conducting feasibility study: A thorough feasibility study is conducted to assess the program's technical, operational, financial, and legal aspects. This study helps determine whether the program is viable and achievable within the given constraints.
5) Risk assessment: Program Managers identify potential risks and uncertainties associated with the program. They analyse the impact and likelihood of these risks and create strategies to mitigate or manage them effectively.
6) Establishing governance structure: A governance structure is established to provide oversight, decision-making authority, and accountability for the program. This includes defining roles and responsibilities, establishing communication channels, and creating mechanisms for monitoring and control.
The Initiation phase sets the stage for the entire program life cycle by clearly understanding the program's purpose, goals, and feasibility. It forms the basis for subsequent phases, enabling Program Managers to plan, execute, and monitor the program effectively.
By successfully completing the initiation phase, Program Managers gain stakeholder buy-in, align the program with organisational objectives, and lay a solid foundation for the successful delivery of the program.
Elevate your Program management expertise to the next level with our specialised Program Management Professional (PgMP)®. Sign up now!
The planning phase
The planning phase is an important step in Program Life Cycle Management that involves developing a comprehensive plan for the program. This phase focuses on defining the program's scope, objectives, deliverables, and strategies to achieve them. Effective planning ensures that the program is well-structured, resources are allocated appropriately, and potential risks and challenges are identified.
During the planning phase, Program Managers collaborate with stakeholders, subject matter experts, and project teams to gather the necessary information and insights. They analyse the requirements, constraints, and dependencies to create a robust plan that guides the successful execution of the program. Key activities in the Planning phase include:
1) Defining program scope: Program Managers clearly define the boundaries and extent of the program. They identify the specific projects, activities, and outcomes that will be included within the program.
2) Defining program objectives: The objectives derived from the overall program goals are outlined in measurable terms. These objectives provide a clear direction and serve as a benchmark for evaluating the program's success.
3) Creating a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS): Program Managers develop a hierarchical breakdown of the program into manageable components, known as the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS). The WBS breaks down the program into smaller tasks, making planning, assigning responsibilities, and estimating resource requirements easier.
4) Identifying dependencies: Program Managers identify the dependencies between various project and program activities. This helps ensure that the program progresses smoothly and that tasks are executed in the correct sequence to avoid delays or bottlenecks.
5) Resource allocation: Program Managers determine the resources required for each project within the project. This includes human resources, equipment, facilities, and budgetary considerations. They allocate resources based on project priorities, availability, and skill requirements.
6) Communication and stakeholder engagement: A communication plan is developed to facilitate effective stakeholder communication. Program Managers identify the key communication channels, establish reporting mechanisms, and define how information will be shared throughout the program.
7) Risk management: Program Managers conduct a detailed risk assessment to identify potential risks and develop strategies to mitigate or respond to them. They prioritise risks based on their impact and likelihood and incorporate risk management plans into the program's overall plan.
The planning phase lays the groundwork for successful program execution. It ensures that all aspects of the program are considered, tasks are well-defined, resources are allocated efficiently, and risks are mitigated. A well-developed plan provides clarity, direction, and a roadmap for the program's execution.
The execution phase
During the execution phase, Program Managers oversee the implementation of planned activities, coordinate resources, and monitor progress. The key components of this phase include:
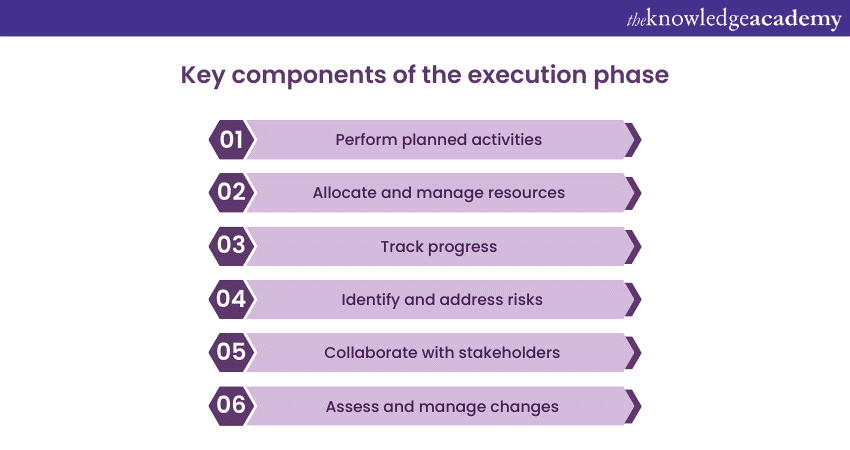
1) Implementing planned activities: Project teams carry out the defined activities within each project, following the established plan.
2) Coordinating resources: Program Managers allocate and manage resources effectively to support project execution.
3) Monitoring progress: Continuous monitoring of project progress against milestones, deliverables, and timelines.
4) Issue and risk management: Proactively identifying and addressing issues and risks that arise during the execution phase.
5) Stakeholder communication: Maintaining effective communication with stakeholders, providing regular updates, and addressing concerns.
6) Change management: Assessing and managing changes that may impact the program, making informed decisions.
The execution phase brings the program plan to life, focusing on efficient implementation, resource optimisation, and stakeholder satisfaction. Program Managers drive project teams, adapt to changes, and ensure the program's success.
The phase of monitoring and control
The phase of monitoring and control in Program Life Cycle Management is crucial for ensuring the program's progress and success. During this phase, Program Managers actively monitor the program's performance, compare it to the defined metrics and objectives, and take necessary actions to keep the program on track. Key activities in the monitoring and control phase include:
1) Performance tracking: Program Managers continuously track the program's progress by monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) and comparing them to the predetermined targets. This allows them to assess the program's overall performance and identify any deviations from the plan.
2) Risk assessment: Program Managers assess and evaluate risks throughout the program's duration. They identify potential risks, analyse their potential impact on the program, and develop strategies to mitigate or manage them effectively. Regular risk assessments help proactively address potential challenges and minimise their negative impact.
3) Quality assurance: Program Managers ensure that the program's deliverables meet the required quality standards. They establish quality control measures, conduct regular reviews and inspections, and implement corrective actions if necessary.
4) Stakeholder engagement: Program Managers maintain effective communication and engagement with stakeholders. They provide regular updates on the program's progress, address any concerns or issues raised by stakeholders, and seek feedback to ensure alignment and satisfaction.
5) Change management: Program Managers manage changes that may arise during the program's execution. They assess the impact of changes, evaluate their feasibility and implications, and implement appropriate change control procedures. This helps maintain program stability while accommodating necessary modifications.
The monitoring and control phase enables Program Managers to have real-time visibility into the program's performance, identify potential risks, and make informed decisions. By actively monitoring and controlling the program, they can proactively address challenges, ensure program alignment with objectives, and take corrective actions when needed.
The closure phase
The closure phase marks the final phase and the end of the program. Project managers ensure that all project deliverables are completed, conduct final evaluations, and obtain feedback from stakeholders. They document lessons learned and identify opportunities for improvement in future programs. Proper closure ensures a smooth transition and benefits the organisation from the program's outcomes.
The closure phase allows Program Managers to assess the program's overall success and gather valuable insights. By analysing the outcomes and lessons learned, Program Managers can improve their Program Management practices and enhance future program delivery.
Navigate and mitigate risks with confidence and precision with our PMI-RMP® Certification Training. Sign up now!
Benefits of Program Life Cycle Management
Program Life Cycle Management offers several benefits to organisations. Some of the key benefits include:
1) Improved program visibility: Program Life Cycle Management provides a structured framework that enhances visibility into the program's progress, risks, and challenges. This enables stakeholders to have a clear understanding of the program's status and make informed decisions.
2) Increased stakeholder satisfaction: Program Management Life Cycle emphasises effective communication and stakeholder engagement. By involving stakeholders throughout the program's lifecycle, Program Managers can meet their expectations and enhance stakeholder satisfaction.
3) Better resource utilisation: The Program Management Life Cycle helps optimise resource allocation by providing a structured approach to identify and allocate resources effectively. This ensures that resources are utilised efficiently, leading to cost savings and improved program outcomes.
4) Alignment with strategic goals: The Program Management Life Cycle ensures that programs are aligned with the organisation's strategic goals. It provides a systematic approach to link programs to the broader organisational objectives, enabling the organisation to achieve its desired outcomes.
5) Enhanced risk management: By following the Program Management lifecycle, Program Managers can identify and mitigate risks throughout the program's duration. This proactive approach minimises the impact of risks on the program's objectives and ensures its successful delivery.
Conclusion
We hope you read this blog and understood Program Life Cycle Management thoroughly. It is a systematic approach that enables organisations to effectively plan, execute, monitor, and control programs from initiation to closure. By following these phases, organisations can achieve successful program outcomes and align with strategic goals.
Supercharge your project management skills with our comprehensive PMP® Training. Sign up today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Project Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 PMP® Certification Training Course
PMP® Certification Training Course







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


