We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on + 1-866 272 8822 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Data science is the interdisciplinary field that uses scientific methods, algorithms, and systems to extract knowledge and insights from structured and unstructured data. It encompasses a wide range of techniques and tools from statistics, computer science, and domain-specific knowledge, making it a vital part of modern technology and business strategy.
With the UK Artificial Intelligence (AI) market already at £16.8 billion, Data Science is firmly established as one of the most promising career options. From deciphering complex data sets to deploying advanced Machine Learning (ML) algorithms, these skills are the cornerstone of success in the digital age. This blog explores the top technical as well as non-technical Data Scientist Skills you will need to carve your niche in the competitive and expanding field of Data Science.
Table of Contents
1) Overview of Who is a Data Science Professional
2) Exploring the Technical Skills Required for Data Scientists
a) Python
b) R programming Language
c) SQL
d) Mathematics, Statistical Analysis, and Probability
e) Data Mining
f) Hadoop
g) Data Visualisation
h) Cloud Computing
3) Exploring the Non-technical Skills Required for Data Scientists
4) Conclusion
Overview of Who a Data Science Professional is
A Data Science professional is a versatile and highly skilled individual who specialises in extracting actionable insights from vast and complex datasets. They play a pivotal role in Data Science, the multidisciplinary domain that combines various technical and analytical disciplines to make data-driven decisions.
Data Science professionals possess a unique blend of technical and non-technical skills, including proficiency in programming languages, machine learning (ML) algorithms, Cloud Computing, analytical mindsets and strong communication skills. Theyoften work with Big Data technologies and Deep Learning frameworks to tackle large-scale problems. Furthermore, Data Science professionals are well-versed in ethical considerations surrounding data collection, storage, and analysis, ensuring that their work adheres to legal and ethical guidelines.
Exploring the Technical Skills Required for Data Scientists
Data Science Skills encompass programming proficiency in languages like Python and R, Machine Learning expertise, Data Analysis and Visualisation, Big Data technologies, Deep Learning, business acumen, communication, critical thinking, Project Management, ethical considerations, and a commitment to lifelong learning. These skills empower both professionals and beginners to excel in the data-driven world. Below is a detailed list of the top technical Data Scientist Skills,
a) Python
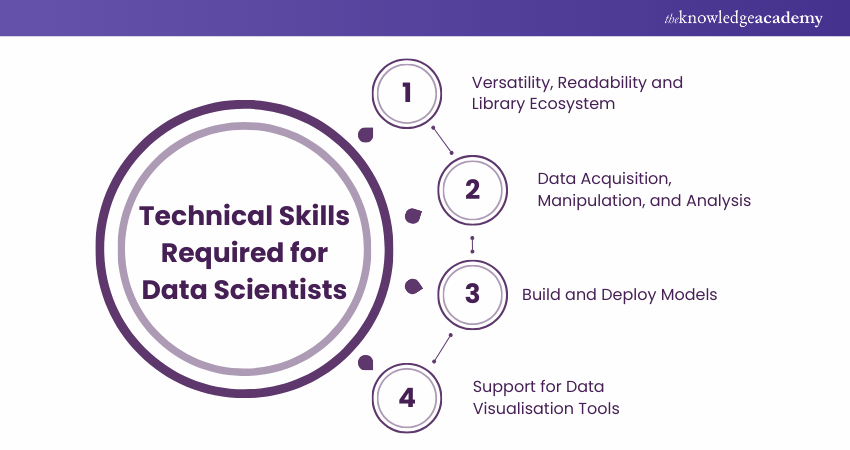
Python programming is an indispensable skill for success in Data Science. Its versatility, readability, and a vast ecosystem of libraries make it the go-to language for Data Scientists. Python facilitates data acquisition, manipulation, and analysis through libraries like NumPy, pandas, and scikit-learn.
With Python, Data Scientists can build and deploy Machine Learning models effectively, automating tasks and processes. Its extensive support for data visualisation tools such as Matplotlib and Seaborn allows professionals to communicate insights clearly.
Furthermore, Python's popularity ensures a thriving community, abundant learning resources, and continuous updates. Proficiency in Python empowers Data Scientists to navigate through real-world data complexities and deliver actionable insights.
Develop and maintain platform-independent applications, by signing up for the Python Programming Training now!
b) R programming language
R programming is a valuable skill for achieving success in Data Science. This open-source language offers a robust Data Analysis, Statistics, and Visualisation environment. Its strengths lie in its statistical modelling capabilities and an extensive collection of packages designed specifically for Data Manipulation and visualisation.
Additionally, Data Scientists proficient in R can perform in-depth statistical analysis, hypothesis testing, and data exploration with ease. R's ggplot2 package enables the creation of highly customisable and publication-quality visualisations, facilitating effective communication of insights.
Furthermore, R's active and passionate community continually develops and updates packages, ensuring its relevance in modern Data Science tasks. While Python is more commonly used for its versatility, R remains the language of choice for statisticians and researchers.
Mastering R programming equips Data Scientists with specialised tools for rigorous Data Analysis, making it an essential skill for those focusing on statistical modelling, advanced data exploration, and academic research within the Data Science domain.
Learn graphic representation, statistical analysis and reporting, by signing up for R Programming now!
c) SQL Programming Language
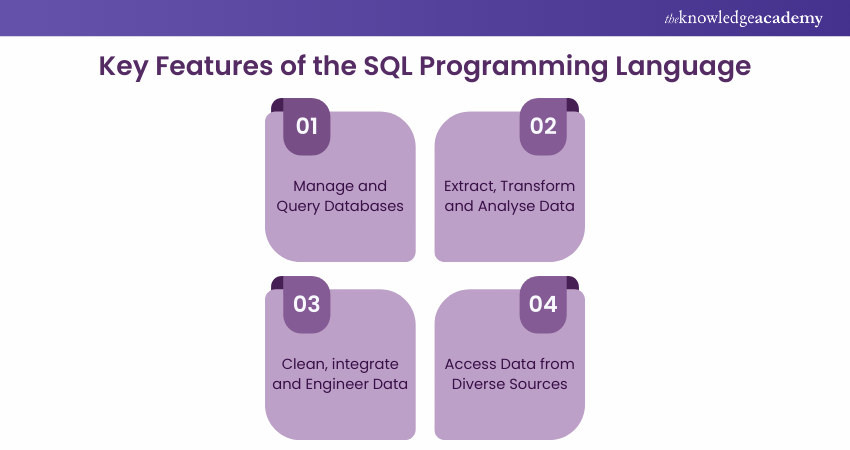
Structured Query Language (SQL) programming is a critical skill for achieving success in Data Science. SQL is the standard language for managing and querying relational databases, which are prevalent in various industries and house vast amounts of structured data.
Data Scientists use SQL to extract, transform, and analyse data efficiently. Proficiency in SQL allows professionals to retrieve specific data subsets, join multiple tables, aggregate information, and perform complex queries. This is particularly crucial for data cleaning, integration, and feature engineering, which are essential steps in the data preprocessing pipeline.
Additionally, SQL skills enable Data Scientists to work with big data platforms such as Hadoop and Spark and NoSQL databases like MongoDB and Cassandra. This versatility makes SQL indispensable for accessing and harnessing data from diverse sources.
Manipulate data with queries on database systems, by signing up for Introduction to SQL now!
d) Mathematics, Statistical Analysis, and Probability
Mathematics, Statistical Analysis, and Probability are the cornerstones of Data Science, providing the foundation for informed decision-making and pattern recognition. Here are the three key domains explained in further detail:
a) Mathematics: Data Science heavily relies on mathematical concepts like linear algebra, calculus, and optimisation. Linear algebra helps in understanding and manipulating data through matrices and vectors. Calculus aids in optimising algorithms, which is crucial for model training and parameter tuning. Proficiency in these areas enables Data Scientists to design efficient algorithms and grasp the underlying mathematics of Machine Learning models.
b) Statistical Analysis: Statistical analysis is the backbone of data-driven insights. Data Scientists use inferential and descriptive statistics to uncover patterns, relationships, and trends in data. Hypothesis testing allows for making decisions based on evidence, while regression analysis models relationships between variables. Statistical methods help validate findings and draw meaningful conclusions from data.
c) Probability: Probability theory underpins uncertainty modelling in Data Science. It enables Data Scientists to quantify uncertainty and make probabilistic predictions. Bayesian probability, for example, is essential for probabilistic machine learning models and Bayesian networks.
Apply the probability theory and statistics in Data Science, by signing up for the Probability and Statistics for Data Science Training now!
e) Data Mining
Data Mining is a vital skill in the Data Science toolkit, focusing on discovering valuable patterns, trends, and knowledge within large and complex datasets. This skill involves using various techniques and algorithms to uncover hidden insights that can inform decision-making and solve real-world problems.
Additionally, professionals skilled in data mining can employ clustering, classification, association rule mining, and anomaly detection methods. These techniques enable them to identify relationships between variables, segment data into meaningful groups, predict future outcomes, and detect unusual patterns or outliers.
Furthermore, Data Mining is particularly valuable for businesses seeking to optimise marketing strategies, improve customer retention, enhance product recommendations, and streamline operations. It also plays a crucial role in fields like healthcare, finance, and cybersecurity.
Effective Data Mining involves a combination of technical expertise, domain knowledge, and critical thinking. Data Scientists skilled in this area are well-equipped to extract actionable insights from vast datasets, making it a vital skill for anyone aiming to harness the data’s power for informed decision-making and innovation.
Learn to transform and discretise data, by signing up for our Data Mining Training now!
f) Data Visualisation
Data Visualisation is a critical skill in Data Science, bridging raw data and actionable insights. It involves presenting complex data in graphical or visual formats, making it easier for technical and non-technical audiences to understand and interpret.
Professionals skilled in Data Visualisation use tools like Matplotlib, Seaborn, Tableau, and D3.js to create charts, graphs, dashboards, and interactive visuals. They understand effective visualisation principles, including choosing appropriate chart types, colour schemes, and labelling, to convey information accurately and intuitively.
Data Visualisation goes beyond aesthetics; it's about storytelling with data. Skilled practitioners can uncover patterns, trends, outliers, and correlations within datasets, enhancing decision-making and communication.
Visualise data on the web, by signing up for the Data Visualisation Training with D3 now!
g) Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing is a transformative skill in Data Science and technology. It involves using remote servers, often provided by third-party cloud service providers like Amazon Web Services or AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform, to store, manage, and process data and applications over the internet.
Moreover, professionals skilled in Cloud Computing can harness its power to access scalable computing resources, store vast datasets, and run complex data analytics workflows. This skill is crucial for Data Scientists as it enables them to work with large-scale datasets, perform resource-intensive tasks, and easily deploy Machine Learning models.
Cloud Computing offers flexibility, cost-efficiency, and global accessibility, making it indispensable for modern Data Science projects. Data Scientists proficient in cloud platforms can collaborate seamlessly, scale their operations as needed, and ensure data security and compliance.
Learn about Cloud models, by signing up for our Cloud Computing Training now!
h) Machine Learning
Machine learning enables data scientists to develop predictive models and sophisticated algorithms using renowned frameworks. Some of the most popular of these frameworks include:
a) TensorFlow
b) PyTorch
c) Scikit-Learn
d) Theano
e) Apache Mahout
f) Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit
Machine learning (ML) skills allow professionals to uncover hidden patterns within vast data sets, predict future outcomes with impressive accuracy, and automate complex decision-making processes. By leveraging machine learning, data scientists can significantly enhance data-driven business strategies, leading to more informed decisions, optimised operations, and a competitive edge in the market
i) Deep Learning
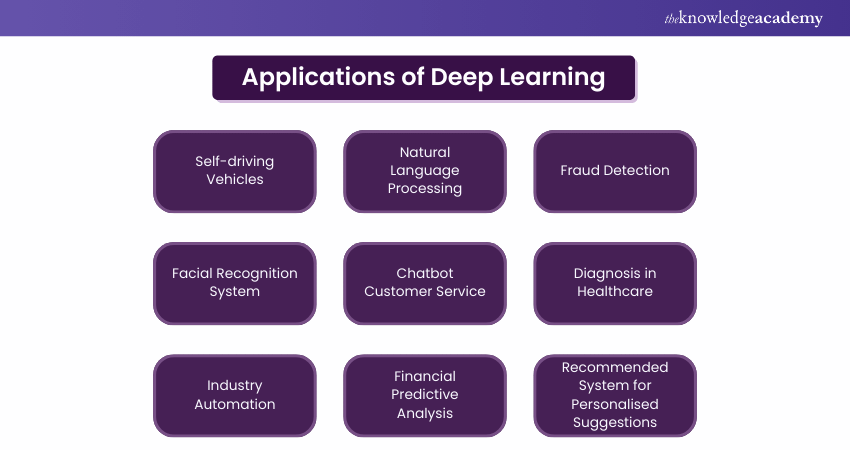
As a subset of machine learning (ML), deep learning focuses on layers of neural networks. It is essential for tackling complex problems involving natural language processing, image and speech recognition and autonomous systems. Consequently, Deep Learning has contributed to awe-inspiring applications such as:
a) Autonomous cars
b) Virtual Autonomous Systems
c) Robots
d) Image Recognition Software
e) Voice Recognition Software
Proficiency in deep learning involves using frameworks like PyTorch and TensorFlow to build, train, and optimise neural networks. Deep learning aims to simulate the human brain and enables data scientists to develop sophisticated models that can learn from vast amounts of data. This drives advancements in AI and provides cutting-edge solutions in various fields.
j) Data Wrangling
Data wrangling referes to the process of cleaning and organising complex data sets to make them easier to access and analyse. While manipulating the data to categorise it by patterns and trends and correcting any input data values can be time-consuming, it's necessary to make data-driven decisions.
This is also related to understanding Database Management. This skill onvolves extracting data from different sources, transforming it into a suitable format for query and analysis, and loading it into a data warehouse system. Useful tools for data wrangling include:
a) Trifacta
b) Altair
c) Alteryx
d) Talend
e) Tamr
Database management tools include:
a) MongoDB
b) MySQL
c) Oracle
k) Data Manipulation and Analysis
Data Manipulation and analysis involves arranging or rearranging data points to make it easier for data analysts to perform necessary insights or business directives. This encompasses a broad range of tools and languages, which may include coding and non-coding techniques:
a) MS Excel
b) Power BI
c) Tableau
d) Pandas
e) NumPy
It is used extensively not only by data analysts but also by business people and accountants to view a project's budget. Data manipulation and analysis help analysts perform exploratory data analysis and prepare data for further modelling and visualisation.
Exploring the Non-technical Skills Required for Data Scientists
Non-technical skills are vital for a successful Data Scientist. Communication, critical thinking, and business acumen enable effective collaboration and align data projects with organisational goals. Ethical considerations ensure responsible data handling.
Lifelong learning ensures staying updated in this dynamic field. These skills complement technical expertise and foster success in Data Science. Here is a list of the non-technical Data Scientist skills described in detail:
1) Communication
Data Scientists with good communication skills facilitate the clear and effective transmission of complex findings to both technical and non-technical stakeholders. Data Scientists must convey insights, methodologies, and implications in a way that is easily understood.
This skill enables better collaboration within multidisciplinary teams and ensures that data-driven recommendations influence decision-making. Additionally, strong writing skills are crucial for documenting methodologies, sharing insights through reports, and disseminating research findings. Effective communication empowers Data Scientists to bridge the gap between Data Analysis and actionable insights, making it an indispensable skill in this field.
Learn to get your message across, by signing up for our Communication Skills Training now!
2) Analytical Mindset
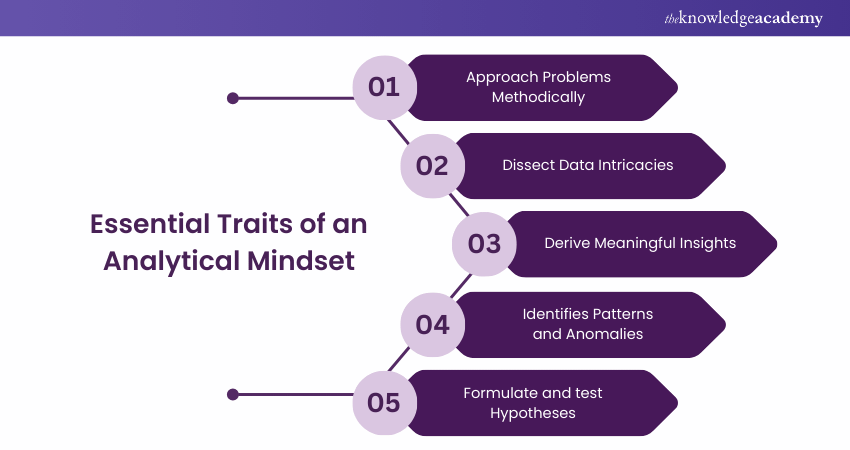
An analytical mindset is the bedrock of a Data Scientist's success. It involves approaching problems methodically, dissecting data intricacies, and deriving meaningful insights. Data Scientists with this mindset excel at identifying patterns, anomalies, and correlations within data. They are critical thinkers who ask the right questions, formulate hypotheses, and rigorously test them.
3) Business Sense
Data scientists not only must know about their own field and how to navigate data, but they must know the field and business in which they work. It’s one thing to know your way around data, but data scientists should deeply understand the business – enough to resolve current issues and consider how data can uphold future growth and success.
This is where Business sense comes in. It’s an essential element of understanding the business and its special needs. Among the most vital Data Scientist Skills, it helps in spotlighting organisational problems and translating data into results that align with organisational goals.
4) Decision Making
Decision-making is pivotal for Data Scientists. They must use data insights to guide critical choices. Effective decision-makers consider the reliability of data sources, assess uncertainties, and weigh pros and cons. Decisions based on data drive informed actions and outcomes, ensuring Data Scientists make a meaningful impact.
Conclusion
Mastering a diverse set of Data Scientist Skills, both technical and non-technical, is the key to excelling in this dynamic field. These skills empower professionals to extract actionable insights, drive innovation, and make informed decisions. Whether you're a novice or a seasoned Data Scientist, continuous skill development is the key to success and we hope this blog helps you expand your prospects in the exciting field of data science.
Study programming and statistical techniques, by signing up for the Data Science Training now!
Frequently Asked Questions

You can become a data scientist even without prior experience. The required skills can be acquired by developing a portfolio of individual projects and learning from online resources.

That depends on the precise work requirements. However, Python is a universally recognised language for Data Science because of its extensive library support and the ease of use.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Data Science Courses, including Python Data Science Course and Data Mining Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Big Data Analysis .
Our Data, Analytics & AI Blogs cover a range of topics related to Data Science, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Data Science skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course




 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


