We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on + 1-866 272 8822 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Imagine you’re setting up a new computer and faced with a crucial decision: Linux vs Windows? This decision can shape your entire computing experience. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each Operating System is crucial for making an informed choice. In this blog, we’ll explore the eight key differences between these two popular OS options.
Be it as a Tech Enthusiast, a Business Professional, or simply someone looking to optimise their personal computer, this comparison of Linux vs Windows will provide valuable insights. Let’s dive into the key differences and discover which OS is the best fit for you!
Table of Contents
1) What is Linux?
2) What is Windows?
3) Linux vs Windows: A Short History
4) Difference Between Linux and Windows
5) Conclusion
What is Linux?
Linux is an open-source Operating Software that is free and is majorly preferred for its customisability, security and community support. It is supported on almost every desktop computer, which makes it one of the most widely used Operating Systems.
It can manage hardware resources easily, launch them and handle applications effortlessly. Since every version of Linux is available for any task, it is widely used by developers and has penetrated a vast area of computing.
What is Windows?
Windows was developed by Microsoft. Windows offers a Graphical User Interface (GUI), management of virtual memory and a user-friendly environment for various applications, software, and system management. Windows was developed by Microsoft so that it can be used for both personal and professional works. Windows can run on different hardware such as HP, Dell, Sony and other home-built Personal Computers (PCs).
Linux vs Windows: A Short History
This roadmap outlines the evolution of Windows and Linux, highlighting key milestones and the gradual shift in user preferences.
a) 1985: Microsoft launches Windows 1.0, based on the MS-DOS core, becoming the most popular Program Manager for running applications.
b) 1987: Windows receives its first major update, followed by the release of Windows 3.0 within the same year.
c) 1995: Windows 95 is introduced, widely adopted with its 32-bit user space and 16-bit DOS-based kernel, significantly enhancing the User Experience.
d) 1998: Windows 98 debuts, featuring key elements like the Start Menu, taskbar, and Windows Explorer (later known as File Explorer).
e) 2000: Windows ME is released as the last MS-DOS-based version, marking a shift towards faster evolution in services.
f) 2000s and Beyond: Despite varying success across versions, Windows users begin migrating to alternative platforms such as MacOS and Linux.
g) 1991: Linux, created by Linus Torvalds, launches as a free, bare-bones operating system kernel.
h) 1992: Linux is distributed under the GNU General Public License, evolving from a simple system to over 23.3 million lines of code.
Windows Milestones:
|
Year |
Milestone |
|
1985 |
Microsoft launches Windows 1.0, based on the MS-DOS core, becoming the most popular Program Manager for running applications. |
|
1987 |
Windows receives its first major update, followed by the release of Windows 3.0 within the same year. |
|
1995 |
Windows 95 is introduced, widely adopted with its 32-bit user space and 16-bit DOS-based kernel, significantly enhancing the User Experience. |
|
1998 |
Windows 98 debuts, featuring key elements like the Start Menu, taskbar, and Windows Explorer (later known as File Explorer). |
|
2000 |
Windows ME is released as the last MS-DOS-based version, marking a shift towards faster evolution in services. |
|
2000s |
Despite varying success across versions, Windows users begin migrating to alternative platforms such as MacOS and Linux. |
Linux Milestones:
|
Year |
Milestone |
|
1991 |
Linux, created by Linus Torvalds, launches as a free, bare-bones operating system kernel. |
|
1992 |
Linux is distributed under the GNU General Public License, evolving from a simple system to over 23.3 million lines of code. |
Sign up for our Microsoft Windows Trainings and become proficient in using all its features and functionalities!
Difference Between Linux and Windows
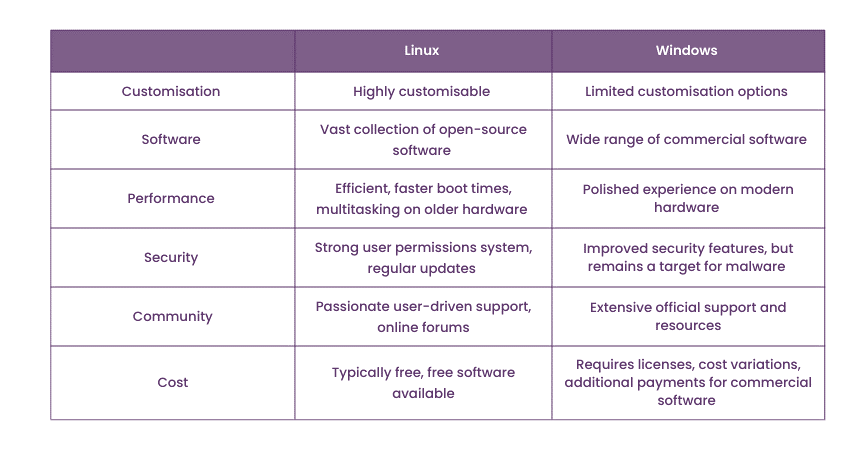
Windows and Linux are two distinct Operating Systems with contrasting features and functionalities. Let’s have a look at how they are different:
1) Linux vs Windows: User Interface
Linux Operating Systems provide users customisable desktop environments such as GNU Network Object Model Environment (GNOME) and K Desktop Environment (KDE). These desktop environments allow users to personalise their interface, adjust themes, and tweak settings according to their preferences. Its users have the flexibility to create a unique desktop experience tailored to their needs.
On the other hand, Windows offers a consistent and user-friendly interface across its different editions. Its interface provides a familiar layout and workflow, making it accessible for users transitioning from previous versions. It prioritises ease of use and aims for a streamlined experience across devices, ensuring a consistent look and feel.
While Linux focuses on customisation and catering to individual tastes, Windows emphasises familiarity and ease of navigation. The choice between them entirely depends on the user's preference for a highly customisable interface or a standardised and user-friendly experience.
2) Linux vs Windows: Software Availability
Linux is renowned for its high security and stability features. With a strong user permissions system and regular updates, it offers enhanced protection against malware and unauthorised access. Additionally, the open-source nature of Linux allows for quick identification and resolution of security vulnerabilities. This feature makes it a reliable and secure choice for users concerned about their data and privacy.
Compared to Linux, Windows has significantly improved security over the years, and it remains a frequent target for malware due to its larger user base. It incorporates security measures such as Windows Defender and constant updates to mitigate risks and ensure system stability. However, you are advised to employ additional security measures and exercise caution while browsing the internet to safeguard your systems effectively.
Manage and troubleshoot Linux systems with our expert-led Administering Linux Systems Course – join us now!
3) Linux vs Windows: Customisation
Linux provides extensive customisation and flexibility options to users. With a plethora of desktop environments to choose from, such as GNOME, KDE, Xfce, and more, Linux users can personalise their interface, modify themes, and customise their system's overall look and feel. Additionally, Linux users can tweak system settings, tailor workflows, and adapt the operating system to suit their specific requirements. This, in turn provides a highly adaptable and flexible computing environment.
In contrast, Windows offers a standardised experience across all its editions, ensuring consistency and familiarity for users. While it provides customisation options like changing wallpapers, themes, and arranging icons, it has limited flexibility compared to Linux. It focuses on delivering a cohesive and user-friendly interface consistent across different devices and editions, making it simpler for users to operate and navigate their systems.
4) Linux vs Windows: Server Performance
The server domain has long favoured Linux for its efficient resource management, stability, and scalability. Its lightweight nature allows it to run smoothly on various hardware configurations, making it a reliable server choice. Linux's robust command-line interface and extensive support for scripting and automation also contribute to its popularity among Server Administrators. Additionally, Linux's open-source nature encourages rapid bug fixes, updates, and optimisations, ensuring high performance.
On the other hand, the user-friendly Windows server offers compatibility with other Microsoft products, making it a convenient choice for organisations already using Windows-based infrastructure. Its servers provide several tools and features that simplify server management and administration. While it may require more system resources than Linux, Windows Server is known for its polished User Experience and extensive compatibility with commercial software.
5) Linux vs Windows: Community and Support
Linux enjoys a passionate and dedicated community of users and developers. Online forums, user-driven support channels, and extensive documentation are readily available resources for its users. The vibrant Linux community fosters collaboration, knowledge-sharing, and troubleshooting. Thus, users can easily find solutions to their queries and receive support when needed.
Windows, backed by Microsoft, offers extensive official support and resources. Microsoft provides documentation, knowledge bases, and official support channels. This feature ensures that users find their systems' assistance. The widespread usage of this OS also means that users can find a wealth of online resources, tutorials, and user forums where they can seek help and engage with the Windows community.
Register for our Linux Shell Programming Course and start creating powerful scripts to solve complex problems!
6) Linux vs Windows: Cost and Licensing
Linux is known for its open-source nature, making it typically free. Users can freely download, use, modify, and distribute Linux distributions without licensing costs. Additionally, a significant portion of the software available for Linux is free and open source, allowing you to access various applications without additional expenses.
In contrast, the Windows Operating System requires a license for most editions. The cost of its licenses varies depending on the version and usage rights, with different editions catering to different user needs. While free editions of Windows are available, such as Windows 10 Home, certain features and functionalities may be restricted or require additional payments. Moreover, commercial software on Windows often comes with separate costs, which users need to consider when calculating the overall expenses associated with using it.
7) Linux vs Windows: Security
Linux provides the best security features. It is very difficult to break through Linux, and this is one of the reasons why it is so popular among developers. It also has a strong user community, which helps identify and fix issues. Linux’s user base has access to the source code. This makes it easier to monitor for issues that can impact the software and makes it less vulnerable to hacking. Moreover, Linux users have limited access, which makes them less vulnerable when a virus attacks the system.
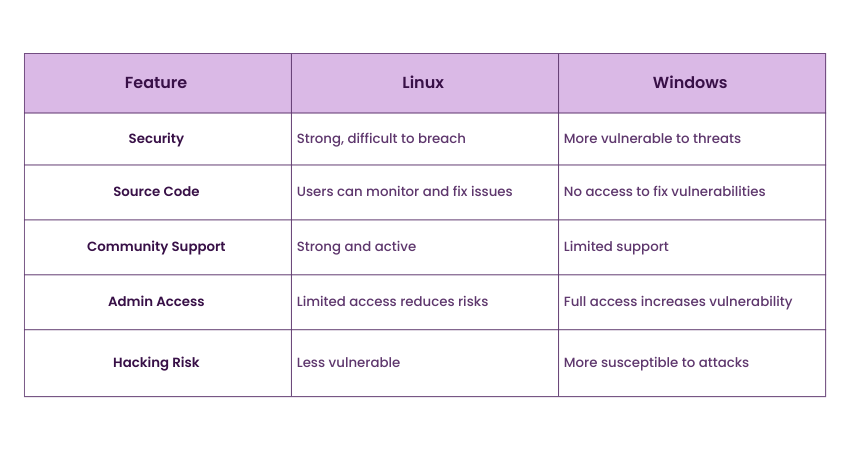
On the contrary, Windows users cannot fix the issue by themselves, as they do not have access to the source code. Since they cannot check the vulnerability of the system, it becomes more susceptible to hackers. In Windows, since users have full admin access over the accounts, the entire system gets quickly corrupted when any virus attacks the system. The Windows OS is also not segmented, which makes it more vulnerable to threats.
8) Linux vs Windows: Performance
There are distinct differences between Linux and Windows which makes them unique in their own way. However, it is often seen than Linux is most of the times faster than Windows. There are several reasons which explains why Linux is faster than Windows. Linux is considered lightweight. In Windows, there are a lot of programs that run at the same time. This eats up the RAM and hence the performance becomes slow when compared to Linux.
Additionally, the file system in Linux is highly organised. All the files are in a cluster, which makes the read-write operation fast. On the contrary, it is observed, that the files are highly disorganised, and they are present all over the place.
Conclusion
Choosing between Linux vs Windows depends on your needs. Linux offers customisation and security, which is ideal for tech enthusiasts, while Windows provides a user-friendly experience and broad software compatibility. Consider customisation, software, security, and community support to make an informed decision.
Become proficient in one of the most versatile Operating Systems – join our LINUX Fundamentals Course today!
Frequently Asked Questions

A Linux server is often preferred over Windows due to its stability, security, and open-source nature. It offers better performance, flexibility, and customisation. Additionally, Linux typically requires fewer resources and provides extensive community support, making it a cost-effective and reliable choice for server environments.

Linux is highly versatile and can operate on multiple processors, from older single-core CPUs to advanced multi-core processors. For optimal performance, a modern processor like an Intel Core i5/i7 or AMD Ryzen is recommended, although Linux is also compatible with ARM and other architectures.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Linux Certifications, including LINUX Fundamentals Course, UNIX Fundamentals, and Linux Shell Programming. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Linux Operating System.
Our IT Infrastructure & Networking Blogs cover a range of topics related to the Linux Operating System, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your software skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course




 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


