We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +36 18508731 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
When it comes to creating visually captivating content in today's digital landscape, the challenges are numerous. Graphic Designers face the ongoing challenge of effectively conveying messages and captivating audiences within a highly competitive visual landscape. However, understanding Graphic Design Principles can help you overcome these hurdles and create impactful designs.
According to Glassdoor, the average gross salary of a Graphic Designer in the UK is about £33,000 annually. It could go higher based on your experience as well as your skill set. If you are interested in pursuing this profession, then understanding Graphic Design Principles is crucial.
That's exactly what this blog is all about. In this blog, you will learn about Graphic Design Principles in detail. Let's dive in deeper to learn more!
Table of Contents
1) Overview of Graphic Design Principles
2) Key Graphic Design Principles
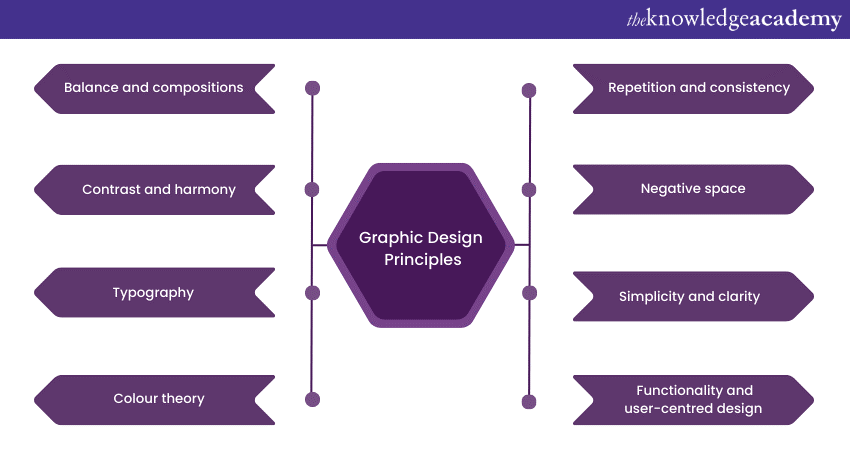
a) Balance and Compositions
b) Contrast and Harmony
c) Typography
d) Colour Theory
e) Proximity and Alignment
f) Hierarchy and Focal Points
g) Repetition and Consistency
h) Negative Space
i) Simplicity and Clarity
j) Functionality and User-centred Design
k) Unity and Variety
l) Emphasis and dominance
3) Conclusion
Overview of Graphic Design Principles
Graphic Design is the art of using visuals to communicate a message, evoke emotions, and direct the viewer’s attention. It is a language that transcends words and speaks to audiences in powerful ways. It blends artistic creativity with strategic thinking to achieve specific goals and outcomes.
Graphic Design influences how we perceive and remember things, whether it’s a logo, a poster, a website, or an advertisement. To create effective and appealing graphics, you need to understand the key Principles of Graphic Design. These rules help design elements work together smoothly and create a balanced and unified composition.
Key Graphic Design Principles
Graphic Design Principles are the guiding framework that designers follow to create visually pleasing and effective designs. These principles are the foundation for successful designs, helping designers make informed decisions about layout, colour, typography, and more. Let’s take a look at them below:
1) Balance and compositions
Balance in Graphic Design refers to the even distribution of elements like shapes, text, and images across a layout. Designers can opt for a balanced (stable) or off-balanced (dynamic) design, which includes three main types:
a) Symmetrical Balance: Achieved by aligning elements evenly along a vertical or horizontal axis, creating mirror-image halves of the layout.
b) Asymmetrical Balance: Utilises scale, contrast, and colour to create a sense of equilibrium, even though the elements are not identical. Common in websites, where different sides of a page are visually balanced with similar elements.
c) Radial Balance: Arranges elements in a circular pattern around a central point, offering a sense of movement and dynamism to the viewer.
Composition refers to how elements are arranged within a design. An effective composition guides the viewer's eye and communicates the intended message clearly.
a) Rule of Thirds: The rule of thirds divides the design canvas into a grid of nine equal parts, placing essential elements along the intersections or lines. This technique enhances visual interest and guides the viewer's gaze.
b) Visual Weight and Balance: Elements in a design have varying visual weights. Larger elements, bold colours, and high-contrast items carry more weight. Achieving balance involves arranging these elements to create equilibrium.
2) Contrast and Harmony
Contrast involves placing differing elements together to create visual interest and highlight key areas. This can include variations in colours, sizes, shapes, and typography styles. Contrast directs attention to focal points and guides the viewer’s eye through the design.
Harmony refers to the cohesive arrangement of elements to produce a unified and aesthetically pleasing visual experience. Achieving harmony requires consistency in design choices, such as a uniform colour palette and typography style. Various Graphic Design software tools are available to assist in achieving harmony and colour consistency.
3) Typography
Typography is the art of arranging letters, numbers, and symbols to make text both legible and visually engaging. It significantly influences the tone, mood, and personality of a design.
a) Choosing the Right Typeface: Different typefaces convey unique personalities and emotions. Selecting a typeface that aligns with the design’s purpose is crucial.
b) Hierarchy and Readability: Creating a clear text hierarchy helps highlight important information. Proper font sizing, line spacing (leading), and paragraph spacing enhance readability.
c) Kerning, Leading, and Tracking: Adjusting letter spacing (kerning), line spacing (leading), and overall character spacing (tracking) refines text legibility and visual harmony.
4) Colour Theory
Colour theory is another important principle that designers have to follow. Understanding colour theory is crucial for creating visually appealing and emotionally impactful designs:
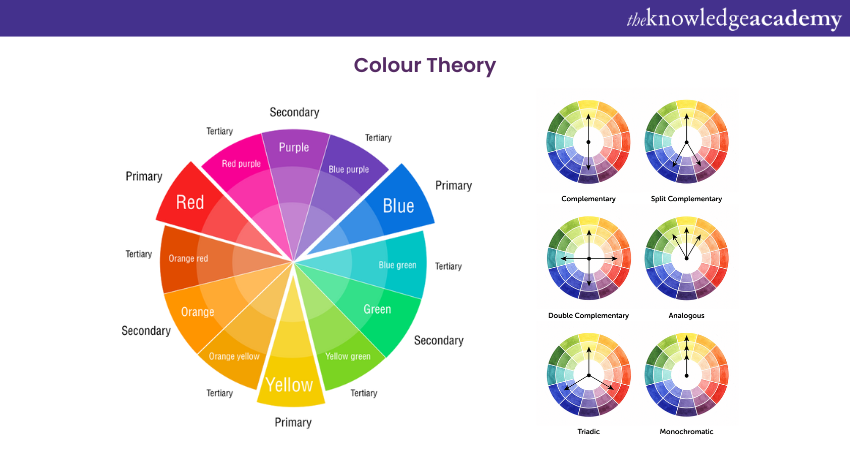
a) Basics of the Colour Wheel: The colour wheel demonstrates colour relationships. Complementary colours (opposite each other) create strong contrast, while analogous colours (next to each other) provide harmony.
b) Emotional Impact of Colours: Colours evoke specific emotions and associations. For instance, red often signifies energy or passion, while blue tends to convey calmness or trust.
c) Creating Colour Palettes: A cohesive colour palette includes primary, secondary, and accent colours. Consistent use of these colours strengthens brand identity and enhances visual coherence.
5) Proximity and alignment
Proximity is about grouping related elements together to establish visual connections and make information easier to understand. By positioning items close to each other, designers can create a logical flow, which helps viewers identify relationships and reduces visual clutter.
Alignment involves arranging design elements along a common axis. Proper alignment creates a sense of order and coherence, making the layout more aesthetically pleasing and easier to navigate. Consistent alignment contributes to a balanced and well-organised design, enhancing overall readability and User Experience.
6) Hierarchy and focal points
Hierarchy in Graphic Design organises content by importance, directing the viewer’s eye through a well-defined sequence. By employing techniques such as size variation, colour contrast, and strategic placement, hierarchy helps ensure that crucial messages capture immediate attention. This logical structure allows viewers to easily navigate and understand the design’s key elements, enhancing overall communication.
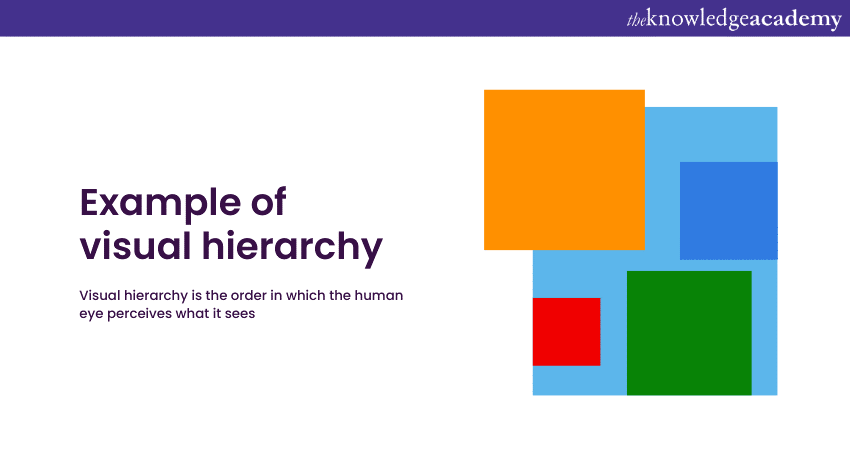
Focal Points are strategically placed areas in a design that draw and direct the viewer’s attention. By highlighting these focal points, designers can effectively emphasise the primary message and enhance the visual impact of the design. This targeted approach ensures that essential information stands out and resonates with the audience.
7) Repetition and Consistency
Repetition involves using consistent design elements throughout a composition. This can include repeating shapes, colours, and typography choices. Repetition creates visual patterns and reinforces the design's identity.
Consistency in design maintains a uniform look and feel across various platforms and materials. It's particularly important for building a strong brand identity and recognition.
8) Negative Space
Negative space, or whitespace, refers to the empty areas around and between design elements. Purposefully incorporating negative space highlights key elements, balancing the design and enhancing clarity.
a) Enhancing visual impact: Skillful use of negative space can create striking visual effects, such as optical illusions, making the design more engaging and memorable.
b) Allowing breathing room: Adequate negative space improves readability and accessibility, preventing overcrowding. This thoughtful approach creates a more inviting and approachable design, allowing the audience to easily navigate and absorb the content. By balancing elements with whitespace, the design achieves both functionality and aesthetic appeal.
Bring your ideas to life with our Managing Virtual Teams– Sign up now!
9) Simplicity and Clarity
Less is often more in design. Simplicity involves distilling a design into its essential elements. Minimalism eliminates distractions and allows the audience to focus on the core message or content.
Clarity ensures that the design effectively communicates its intended message. A clear design layout, combined with concise text and appropriate visuals, prevents confusion and enhances understanding.
10) Functionality and user-centred Design
a) Designing for the User Experience: User-centred design prioritises the needs and preferences of the audience. Design decisions are made with the user's ease of use and engagement in mind.
b) Ensuring Accessibility: Designs should be accessible to all users, including those with disabilities. Incorporating accessible design practices ensures that everyone can interact with the content effectively.
c) Usability vs. Aesthetics: Balancing usability and aesthetics is crucial. While visually appealing designs capture attention, they must also be functional and user-friendly.
11) Unity and Variety
Unity is the principle that brings all design elements together to create a cohesive and well-balanced whole. When elements share common attributes such as colour, shape, or style, they form a sense of unity, making the design feel organised and intentional.
Variety, on the other hand, introduces diversity and visual interest to a design. Incorporating diverse elements like different textures, sizes, and shapes adds excitement and prevents monotony. Balancing unity and variety creates a dynamic composition that captures attention while maintaining coherence.
12) Emphasis and Dominance
Emphasis involves highlighting certain elements to make them stand out and capture the viewer's attention. Creating a focal point using size, colour, contrast, or placement ensures that the most important information is noticed first.
Dominance is the visual weight of certain elements in a design. By designating a dominant element, the designer guides the viewer's focus and provides a clear hierarchy of information.
Conclusion
Graphic Design Principles form the root of successful visual communication. By mastering these 12 principles and adopting them into your design process, you can develop designs that capture attention and convey messages with clarity, impact, and creativity. If you're an experienced Graphic Designer or a beginner, understanding these principles will elevate your work and contribute to the art and science of Graphic Design.
Unlock your creative potential and master the art of Graphic Design with our Virtual Graphic Designer Training. Sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions

Popular tools for applying Graphic Design Principles include Adobe Creative Suite (Photoshop, Illustrator, InDesign), Sketch, Figma, and Canva. These programs offer robust features for creating visually appealing designs with precise control over elements.

Graphic Design Principles, such as hierarchy, contrast, and balance, are crucial in UX/UI design. They enhance usability by guiding users' attention, ensuring clarity, and creating an intuitive interface, leading to a more engaging and effective user experience.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. By tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Virtual Online Job Roles Training, including Virtual Graphic Designer Masterclass, Virtual Event Planner Masterclass, and many more. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Graphic Design Interview Questions.
Our Business Skills blogs cover a range of topics related to Graphic Design, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Graphic Design Skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Virtual Assistant Course
Virtual Assistant Course
Fri 20th Dec 2024
Fri 7th Feb 2025
Fri 4th Apr 2025
Fri 6th Jun 2025
Fri 8th Aug 2025
Fri 3rd Oct 2025
Fri 5th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


